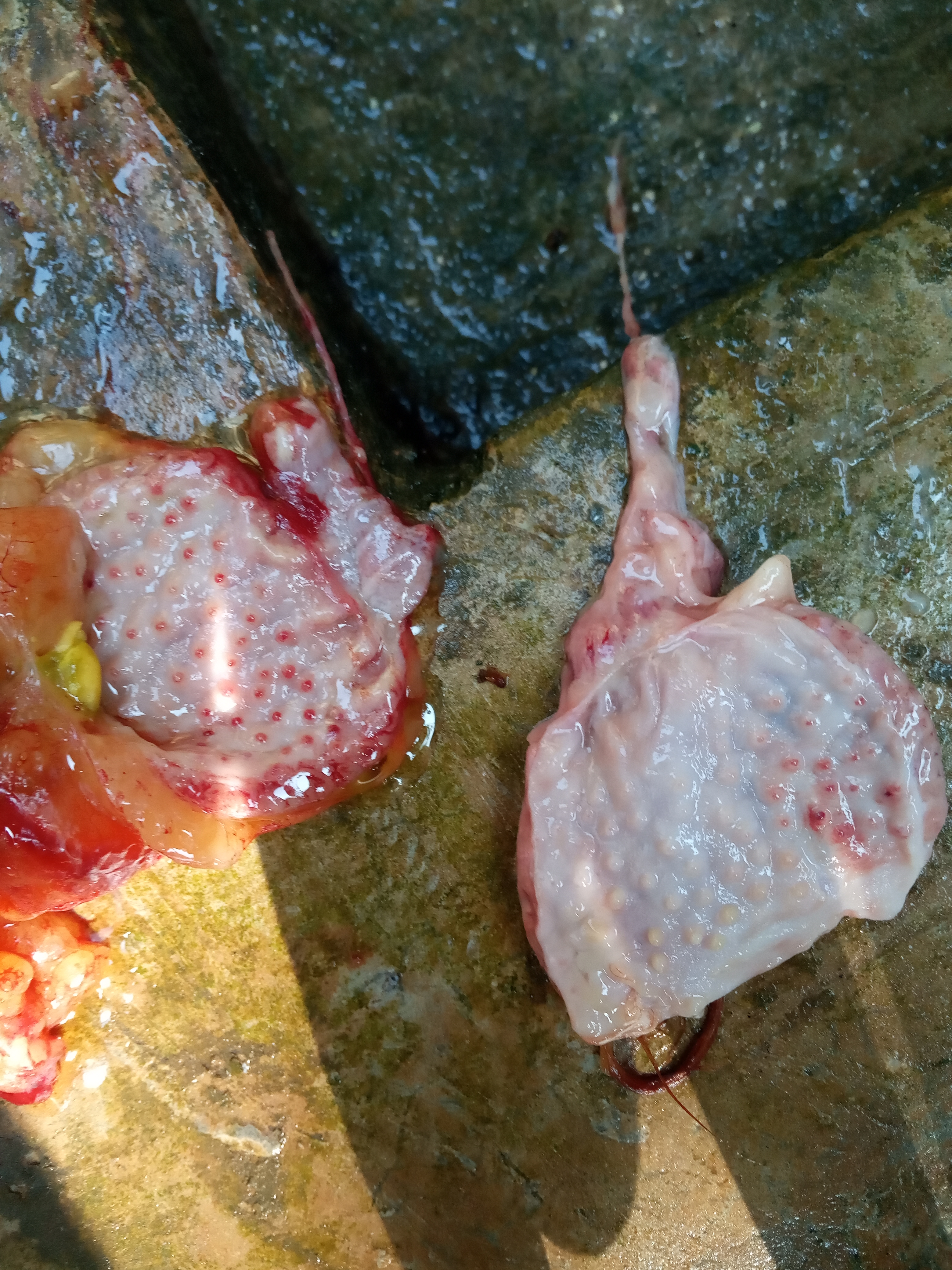
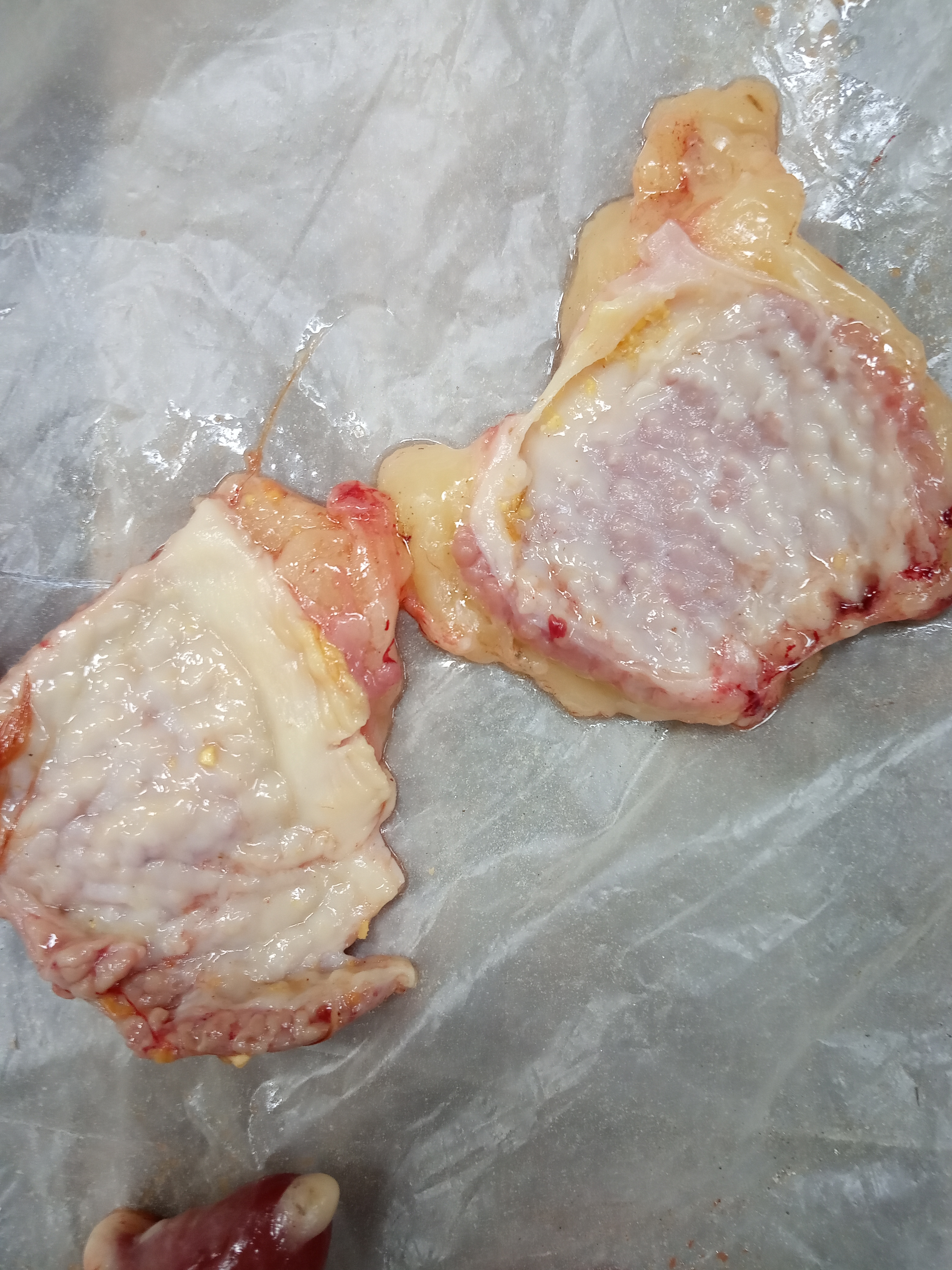
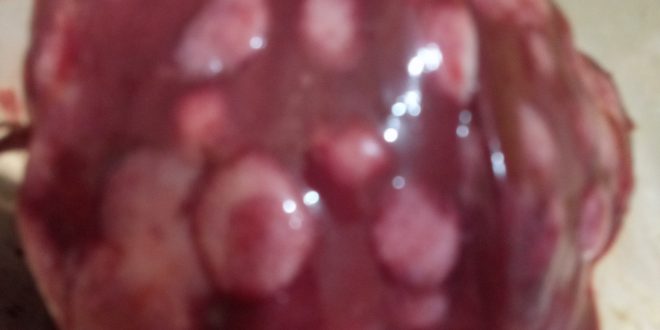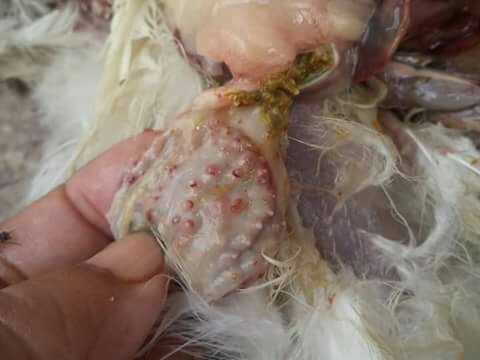
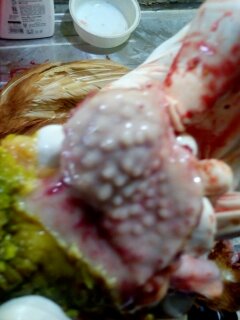
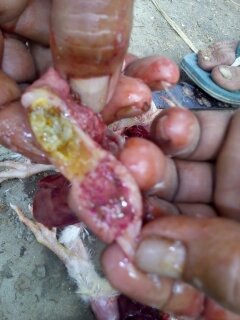
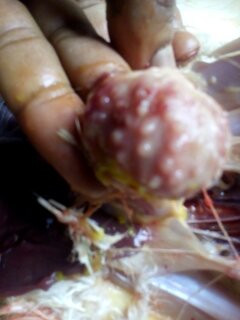
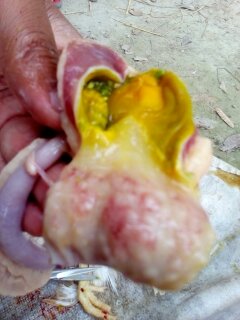
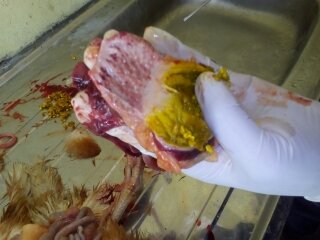


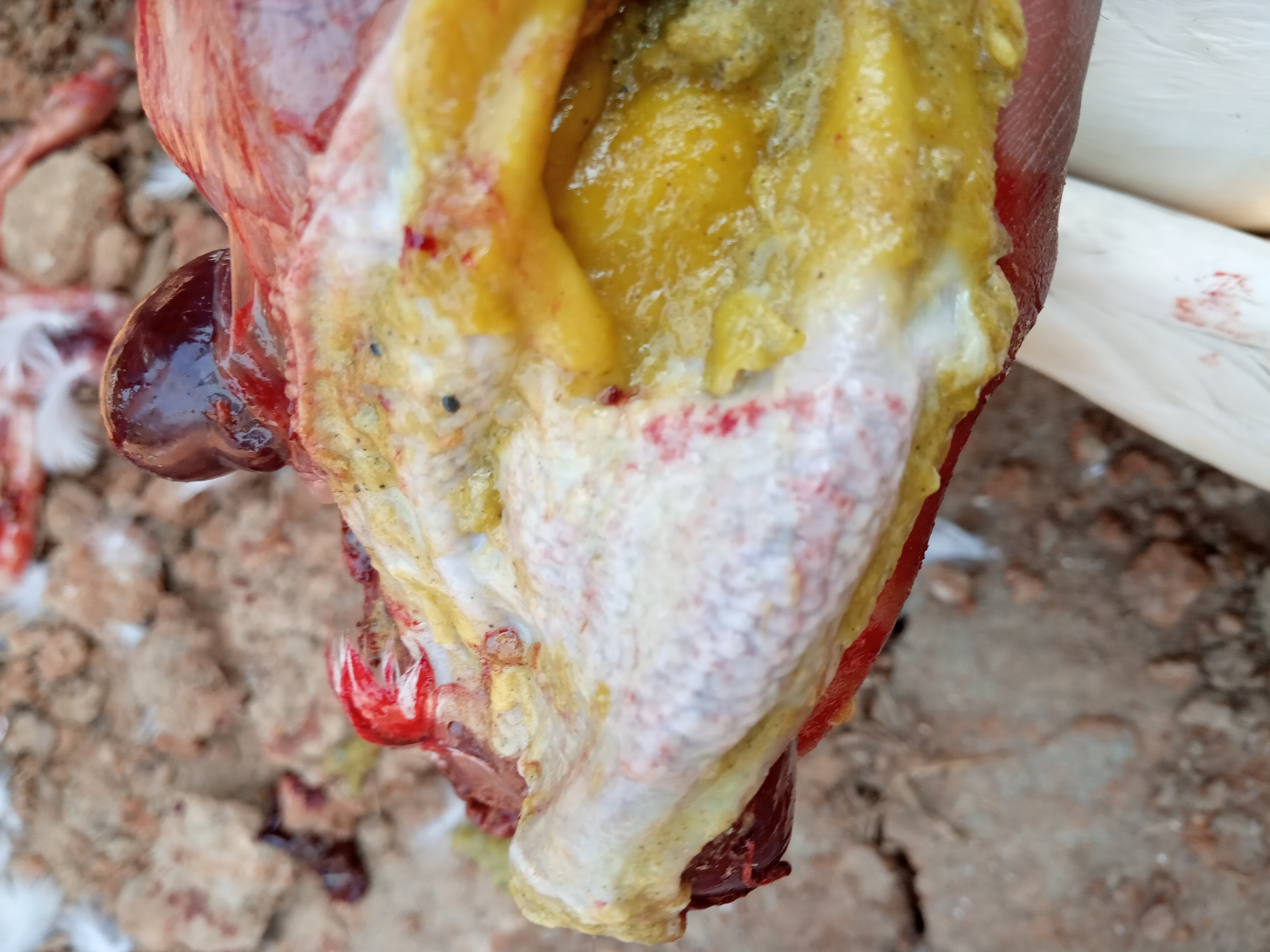
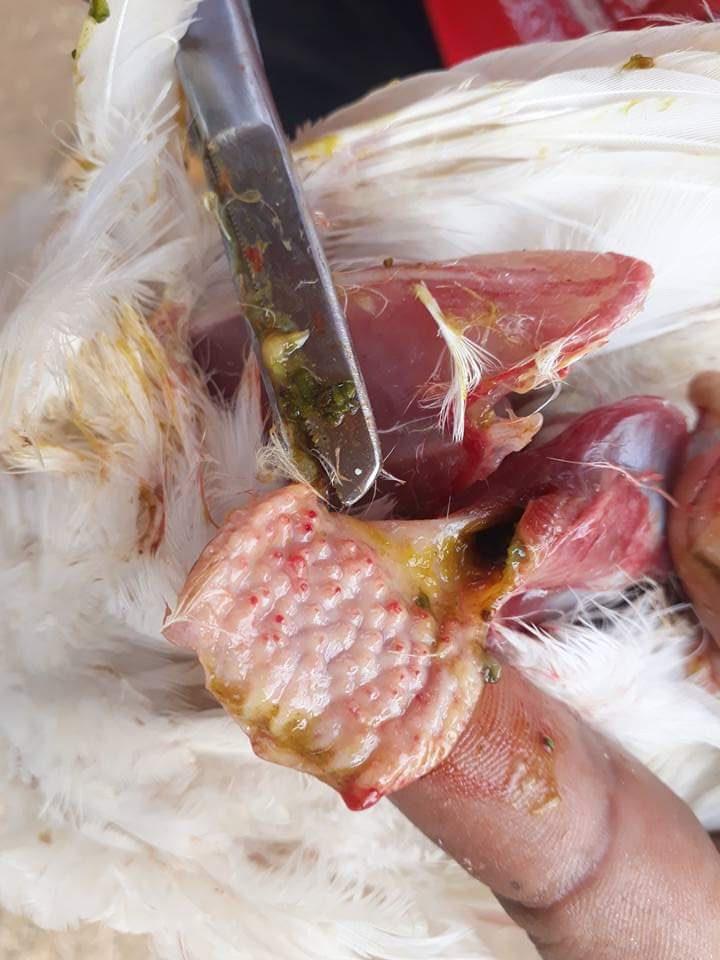
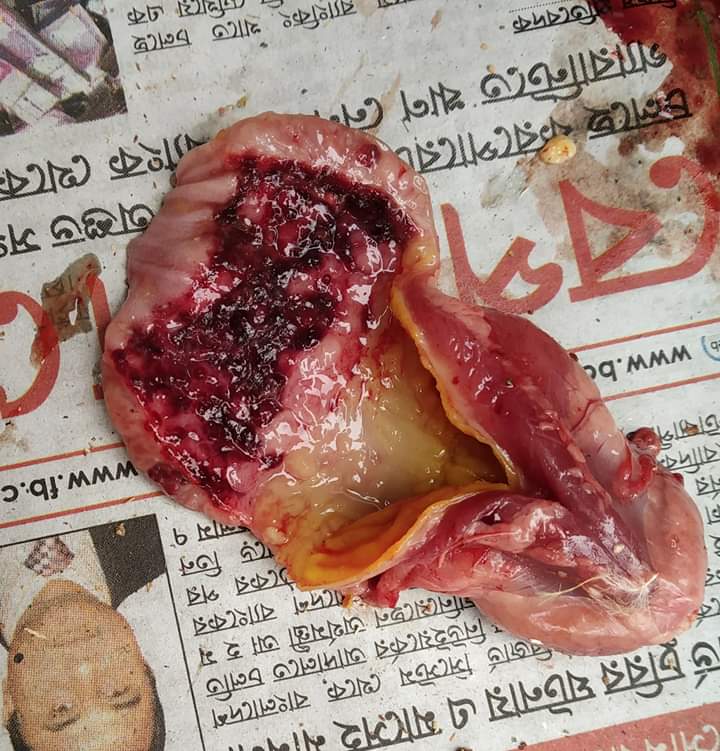
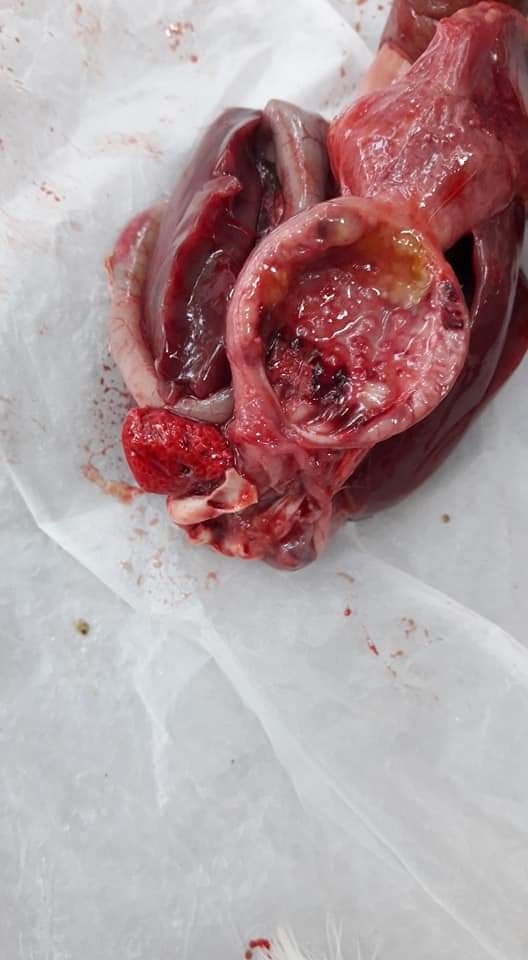
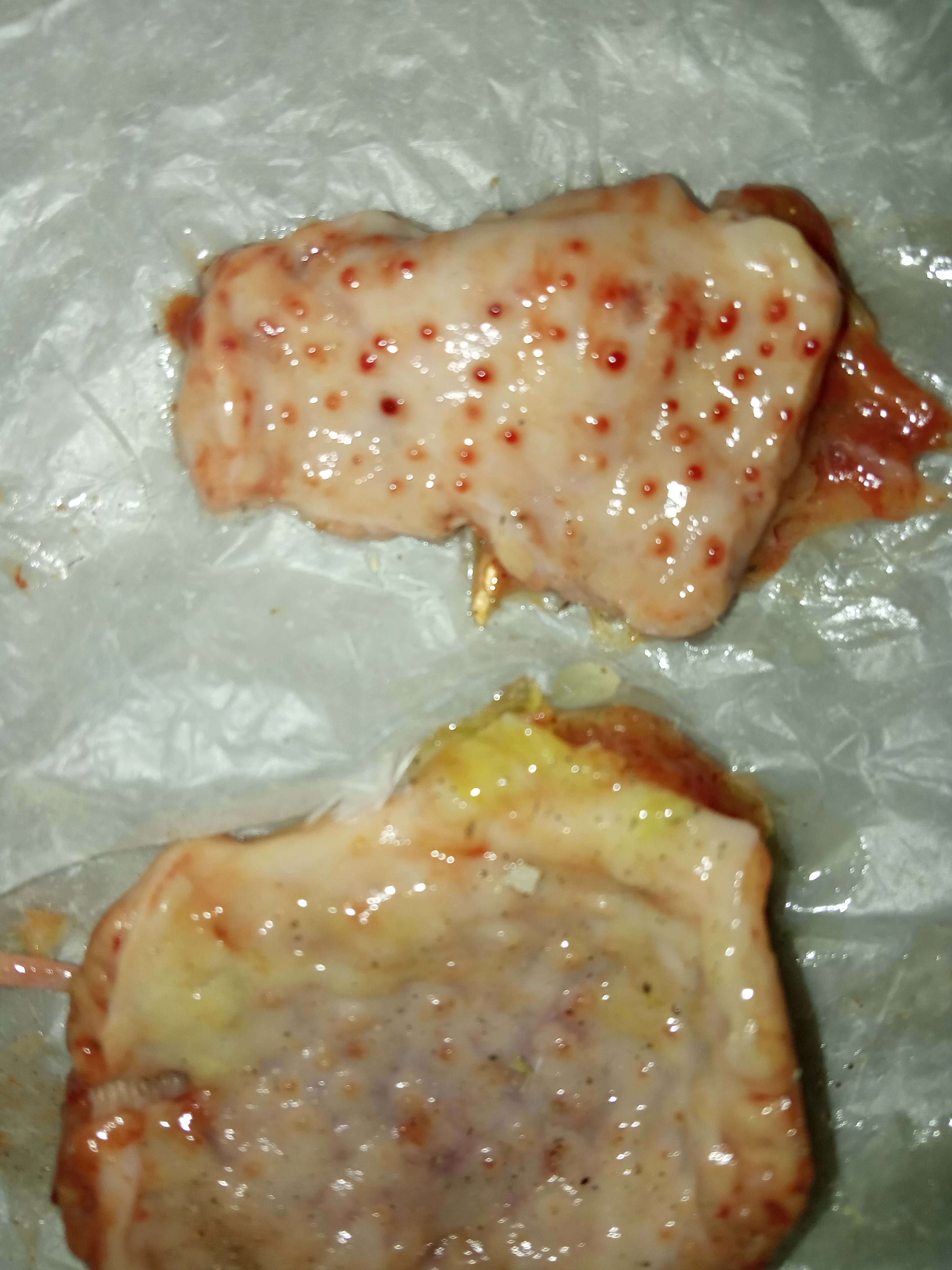
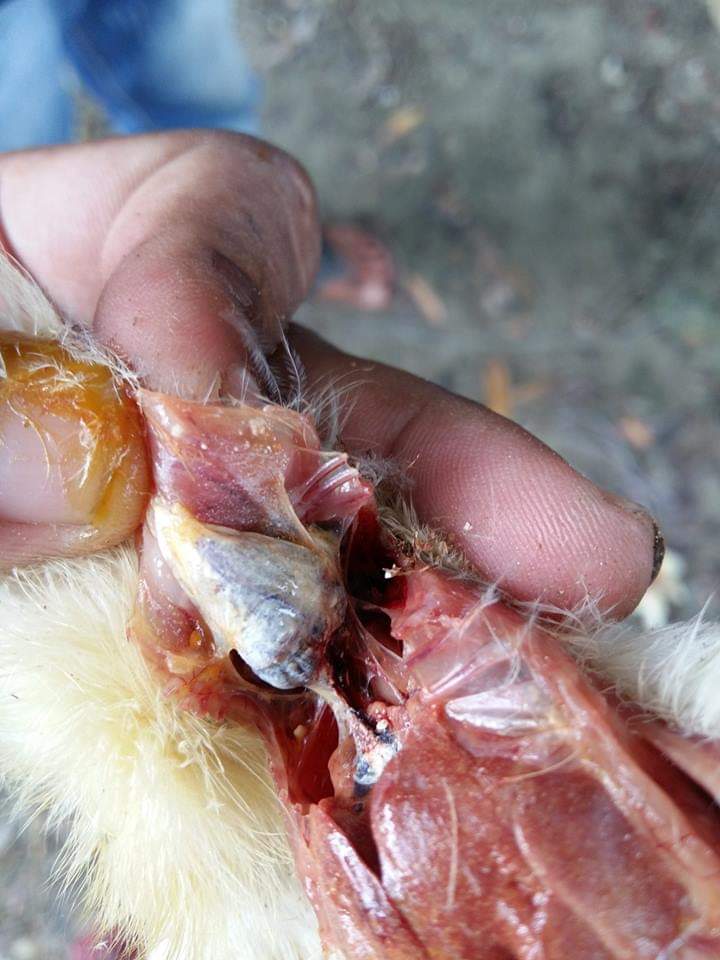
১.proventriculous:প্রভেন্টিকোলাস দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়.(Muscle stomach/Glandular stomach)
1、Glandular nipple top bleeding – Newcastle disease.
2、Glandular nipple bottom bleeding – flu
3、Glandular mucosal hemorrhage,musculoskeletal corneal hemorrhage – influenza, Newcastle disease
4、Glandular edema thickening,nipple ulcer swelling
(Severe nipple disappears), muscle and cornea corneal hyperplasia,ulcers, erosion – muscle gastritis, glandular gastritis.
5、A hemorrhagic zone is formed between the stomach and the glandular stomach – the bursa of Fabricius.
6、Hemorrhage between the glandular stomach and the stomach and stomach,corneal and subkeratal hemorrhage – poisoning.
7、The glandular stomach is swollen and thickened and the nipple presents a tumor nodule – Marek’s disease,
Lymphocytic leukemia,reticuloendotheliosis.
Anatomically cooperate with the appearance of the chicken, including feces, respiratory symptoms, feed intake, water intake, combined with systemic organ lesions, for accurate diagnosis, some lesions are easy to diagnose from a single organ and some diseases become compatible with multiple organs at the same time Judging the diagnosis, therefore,can not rush to draw conclusions!
1.Hemorrhages at the tips of glands: ND.
2.Patchy hemorrhage in mucosa
#:Orchratoxicosis( pale yellow liver & Hemorrhage on intestine)
# Patulin toxicity(Hemorrhage in Gizzard & intestine)
#Sulpha drug toxicity or Hemorrhagic syndrome(Hemorrhage in Spleen,muscle & intestine).
3.linear hemorrhage between glands: spirochaetosis.
4.Thickening of proventiculus wall,nodular & grey.
#Mareks, immature bird
#Avian leucosis: sexually mature bird
6.small whitish foci visible from serosal surface of proventriculus:
avian influenza with high mortality
7.impaction of foreign body:
impaction of proventriculus
8.yellow pus like material: Pantothenic acid deficiency
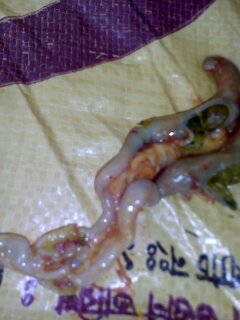
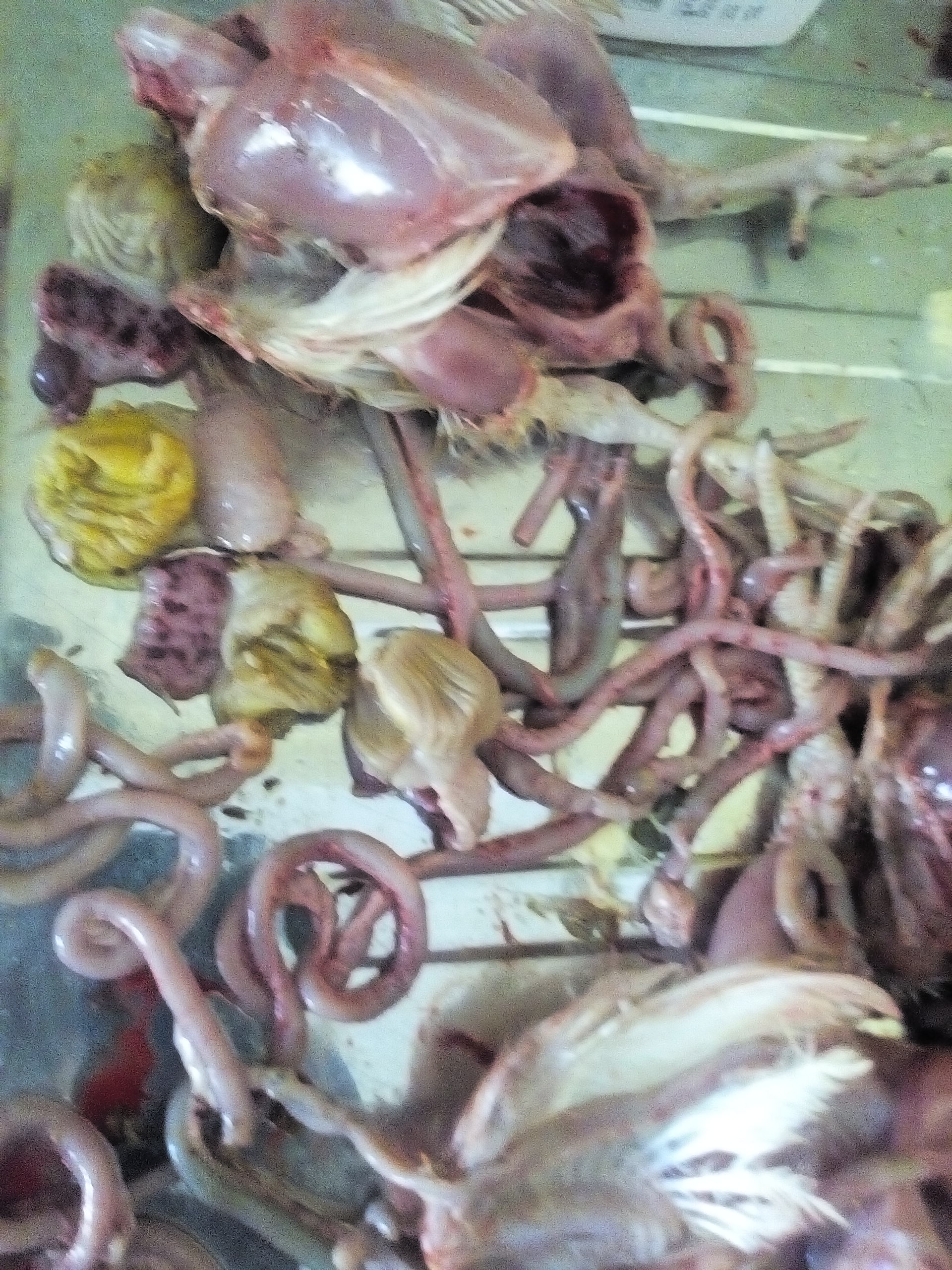
9. Hemorrhagic spots in proventriculus glands with worms embedded: Dyspharynx, nasuta worm..
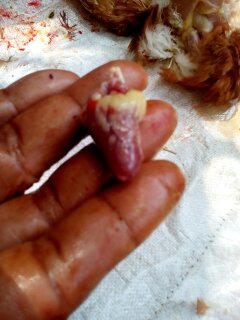
২.গিজার্ড দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়






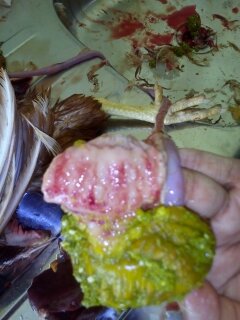


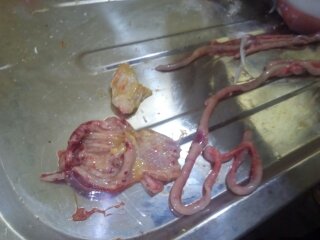
1.Hemorrhage in mucosa / adjoining proventriculus
# IBD
# patulin toxicity
# mouldy corn toxicity
2.small white,pinpoint sized,white foci in gizzard muscle:
A I (rare)
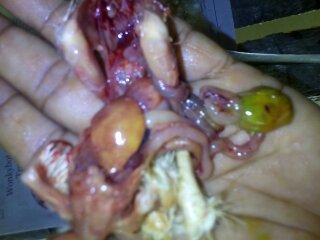
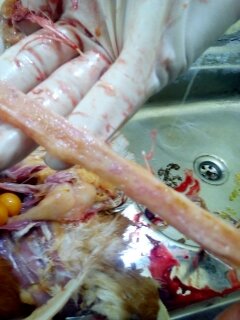
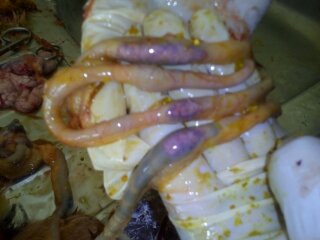
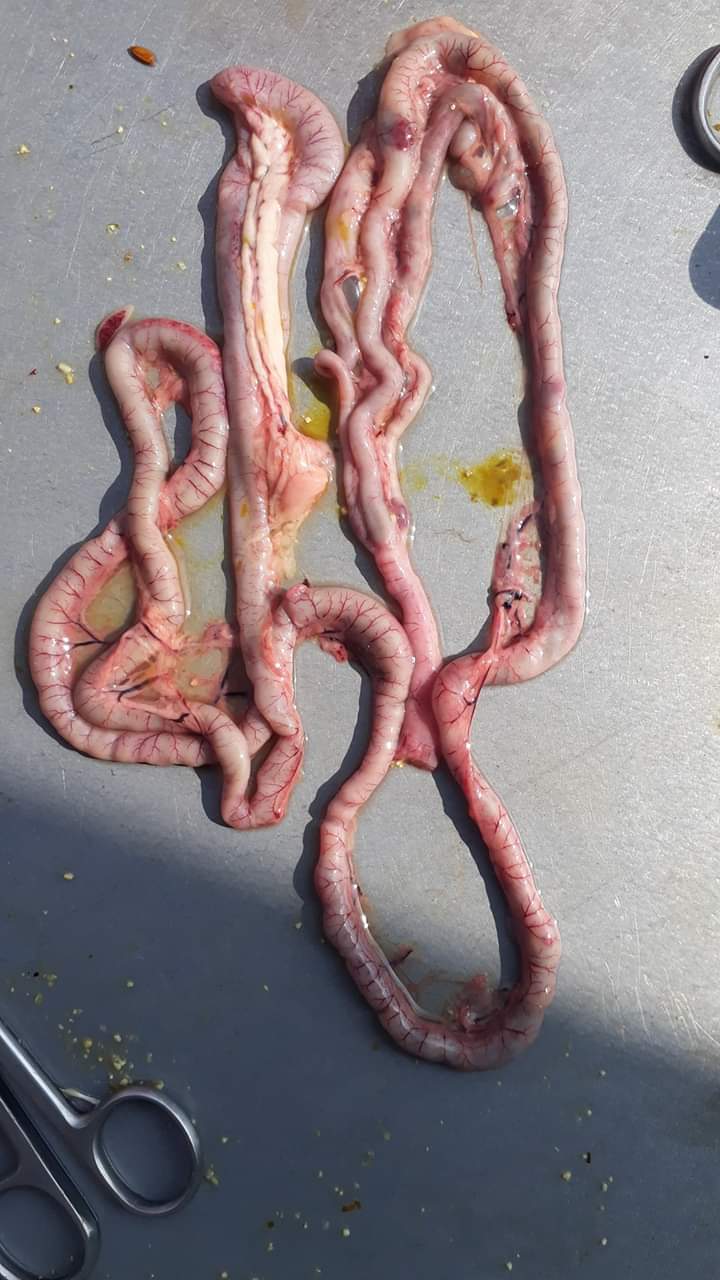
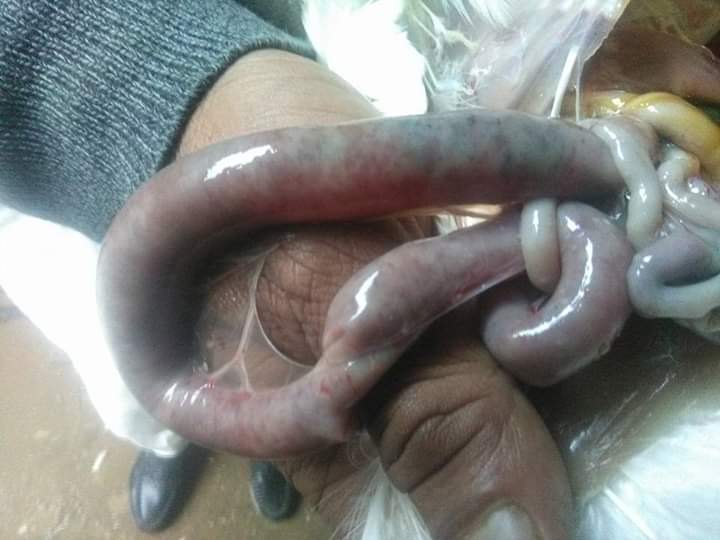
৩.ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র (Intestine)দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
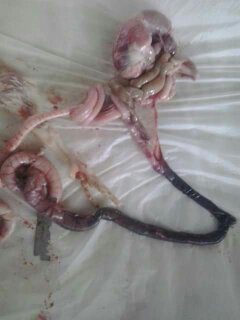
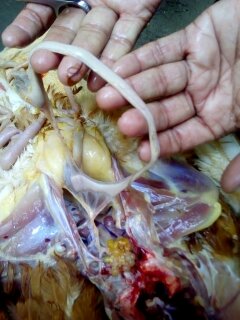
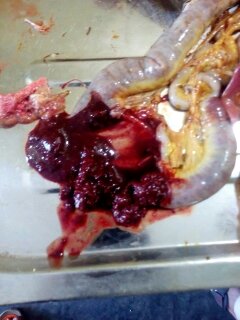
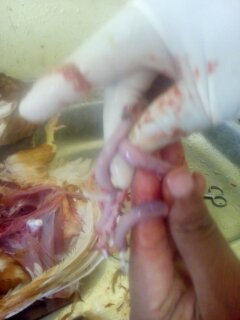
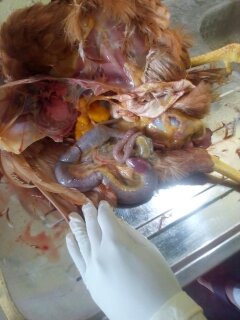
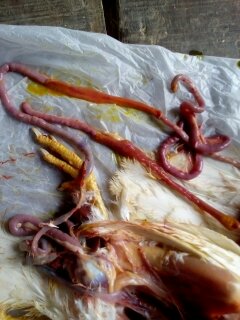




 1
1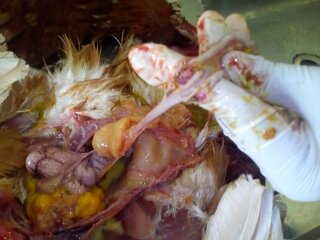



 .
.


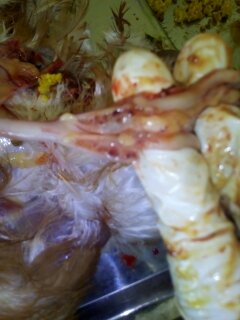
 Raised,hemorrhagic ulcers along with length of small intestine:
Raised,hemorrhagic ulcers along with length of small intestine:
ND,sudden death
2.pinpoint hemorrhagic spots or greyish,pinpoint spots,better visible without cutting intestine open:
Intestinal Coccidiosis,(2-3 wks,anemia,emaciation)
3.Mucosa of duodenum & adjoining parts of small intestine( negative for coccidia) looking velvety,red & puslike or bloodtinged contents
#.Bacterial enteritis( E coli,salmonella,pseudomonas,campylobactor,chlamydia)
any age of bird but more in grower,pericarditis indicate E coli or salmonella
4.Necrotic mucosa of small intestine with cracked surface:
Necrotic Enteritis( liver small)
5.Raised,granuloma,visible from serous surface as raised grain of millet in bunches:
# Coligranuloma ( e coli)
# Tapeworm
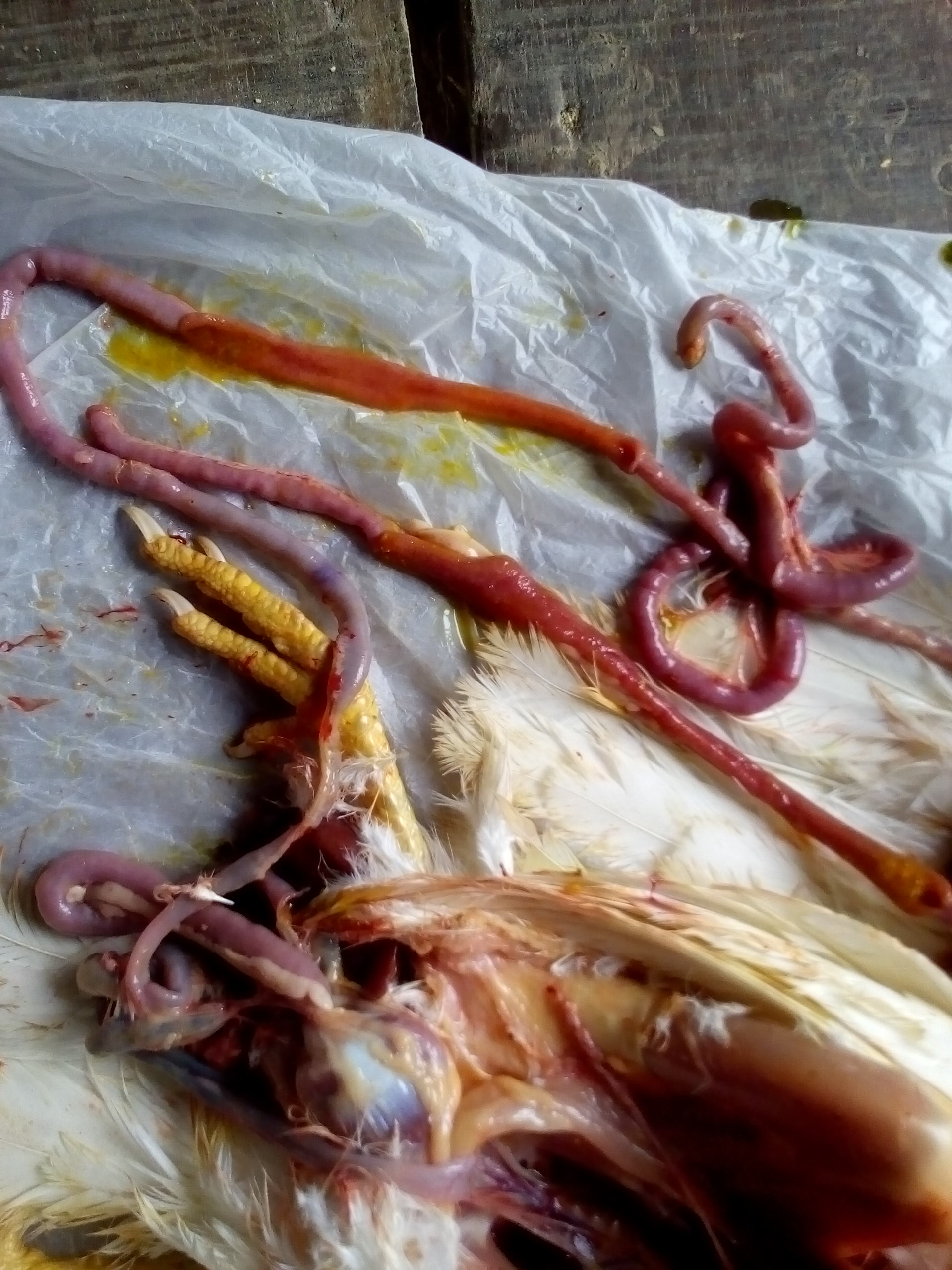
7. Round worm in small intestine:
Ascaridia galli
8.Congested intestine with greenish contents or bloodtinged contents:
#.Acute diffuse coccisiosis.
9.Tumer ( cauliflower like growth in intestinal wall):
# Avian Leucosis
# Mareks
10.Pasty vent: Reovirus enteritis.
11. Yolksac inflammed : Omphalitis
12.Hemorrhagic cecca
:caecal Coccudiosis
13.prolapse of rectum or swelling or eversion of cloca:
Fusariotoxicosis,cystic oviduct,enlarged bursa.
৪.স্নায়ুতন্ত্র ( Nervous system)দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
1.Soft hemorrhagic or necrotic spot in cerebellum or other part of brain:




# Enceohalomalasia
#vit E deficiency ( head pulldown,backward or lateral,
muscular weakness
2. Edema of brain +- hemorrhage
same diseases
3.Congestion of hemorrhage
ND
without hemorrhage
A I
4. Thickened,edematous nervers in birds more than 3 months of age:
Classcal Mareks
5. Hemorrhage( petecial) in brain & edema of head’
septicemia due to pseudomonas & E coli wirh fever.
6. Swelling & edema ( yellow) of sciatic or brachial nerve in chicks
advanced Riboflavin Deficiency
leg bent outward,paralysis leg,curle toe paralysis.
৫।বার্সা দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
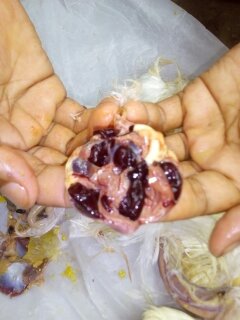
1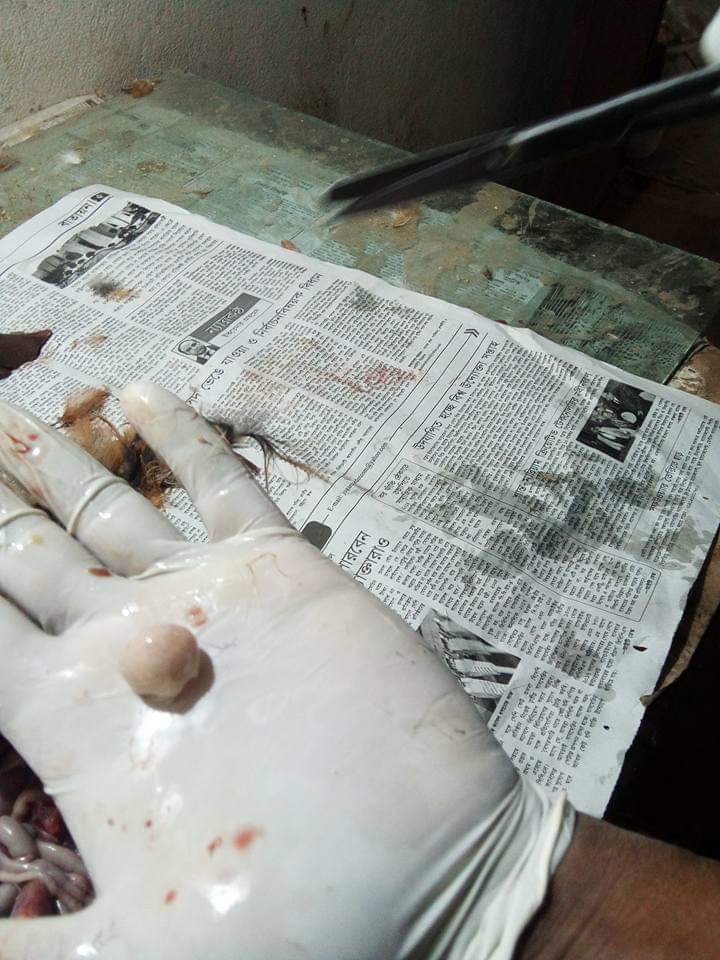 .Enlarged,edematous & congested
.Enlarged,edematous & congested
I B D: (nephrosis,hemorrhages in muscle)
2.Cheesy necrotic mass in bursa:
#I B D in late stage.
# Hypovitaminosis A
3.Small atropic bursa of fabricus:
# late I BD
#Aflatoxicosis(fatty change,congestion,retarted growth,susceptible to other diseases
#Rota virus enteritis: diarrhoea,dehydration,presence of gas & abdominal fluid in intestinal contents
# Rubratoxicosis:enlarged liver
#Inclusion body hepatitis
4.Enlarged bursa:
#Fusariotoxicosis(enlarged comb,prolapse of cloca,cystic oviduct,most common in turkey.
# avian leucosisণ
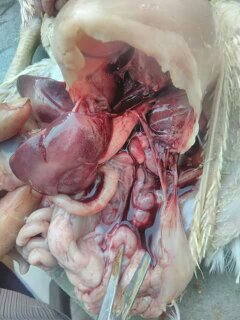
৬.স্পিলন ( Spleen) দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
Spleen
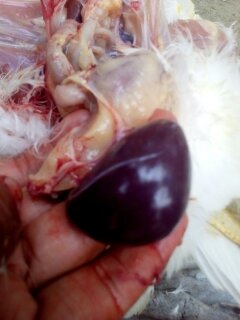

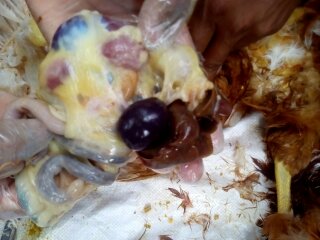

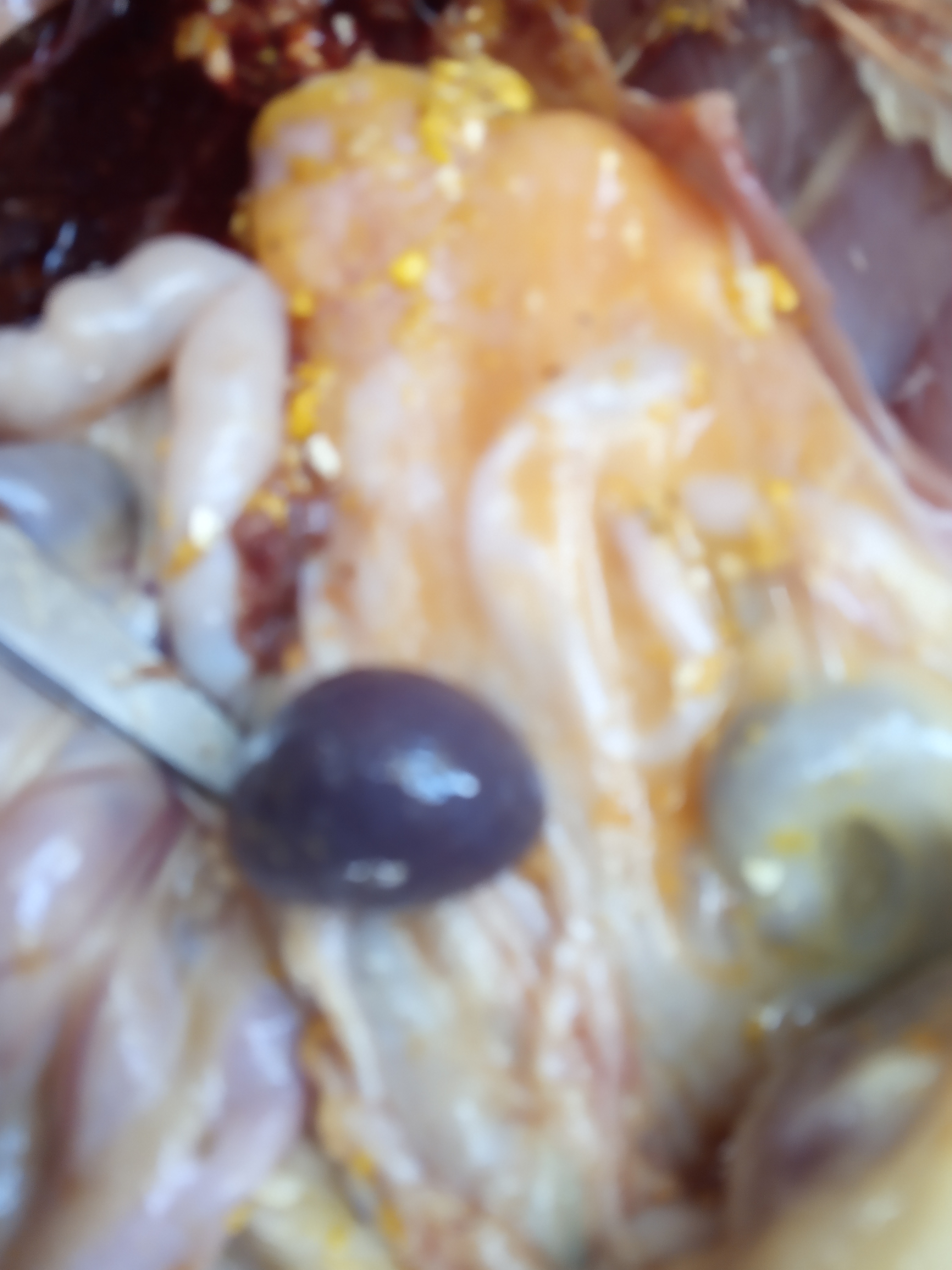

1、The splenomegaly becomes rounded (the surface has gray-white hyperplastic nodules or scattered fine white spots) – Marek’s disease, lymphocytic leukemia, reticuloendotheliosis.
2、Splenomegaly, hemorrhage – caused by acute viral diseases such as Newcastle disease and avian influenza.
3、Splenomegaly, dark purple, spleen marrow softened like mud – avian cholera, E. coli.
৭.মুখ দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
1.Diptheric( necrotic) area in mouth
#pox ( SKIN & COMB)
2. Drooling of mucus from mouth
# FC ( Fowl cholera) Acute.cyanosis of wattle,comb, Fever,whitish or greenish diarrhoea.
# NE( Necrotic Enteriti) Necrosed,yellowish mucus of small intestine. low mortality, chronic diarrgoea.
#Fungal Toxin
3.Inflammation of oral cavity, pharynx,& oesophagus
# Fusarium toxicosis( intestine,liiver.proventriculus)
3.Inflamation of oral cavity,pharynx & esophagus
#Fusarium toxicosis( intestine,liver,proventiculus)
4.Necrotic spots on tongue,palate or crop( yellowish discolor & drying of tip of tongue
#Stchybotrystoxicosis, retard growth & appetite,saliva from mouth.)
৮.Saliva দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
saliva flows out from beak ( chronic diseases)
# N E
# Fungal toxin
# Staphylococcus
Drooling of saliva( Acute diseases)
# F C
#Causes of Huddling near heat source
E coli,pollurun,thrush & salmonellosis.
#Causes of watery abdomen
# Aflatoxicosis
Ochratoxicosis
chick edena
# phosphorus deficiency or more carbon dioxide in brooding.
৯.কিডনি দেখে মুরগির রোগ নিরনয়
 ১.
১.  কিডনি ফুলে যায় এবং সাদা চকের মত পদার্থ
কিডনি ফুলে যায় এবং সাদা চকের মত পদার্থ
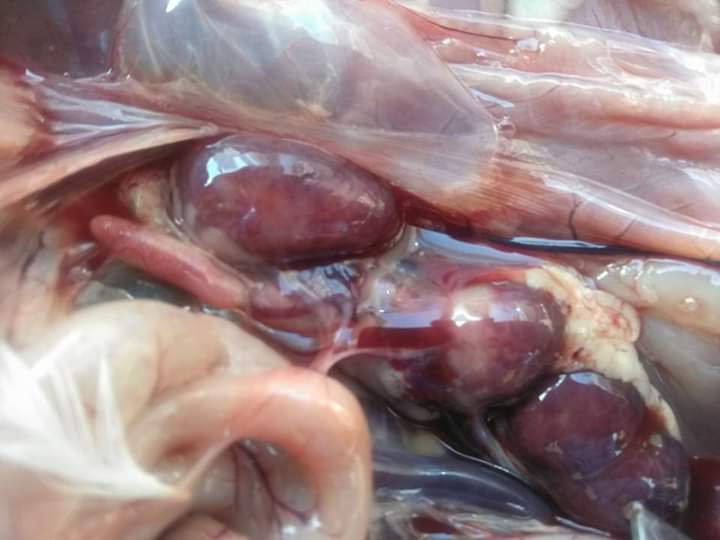
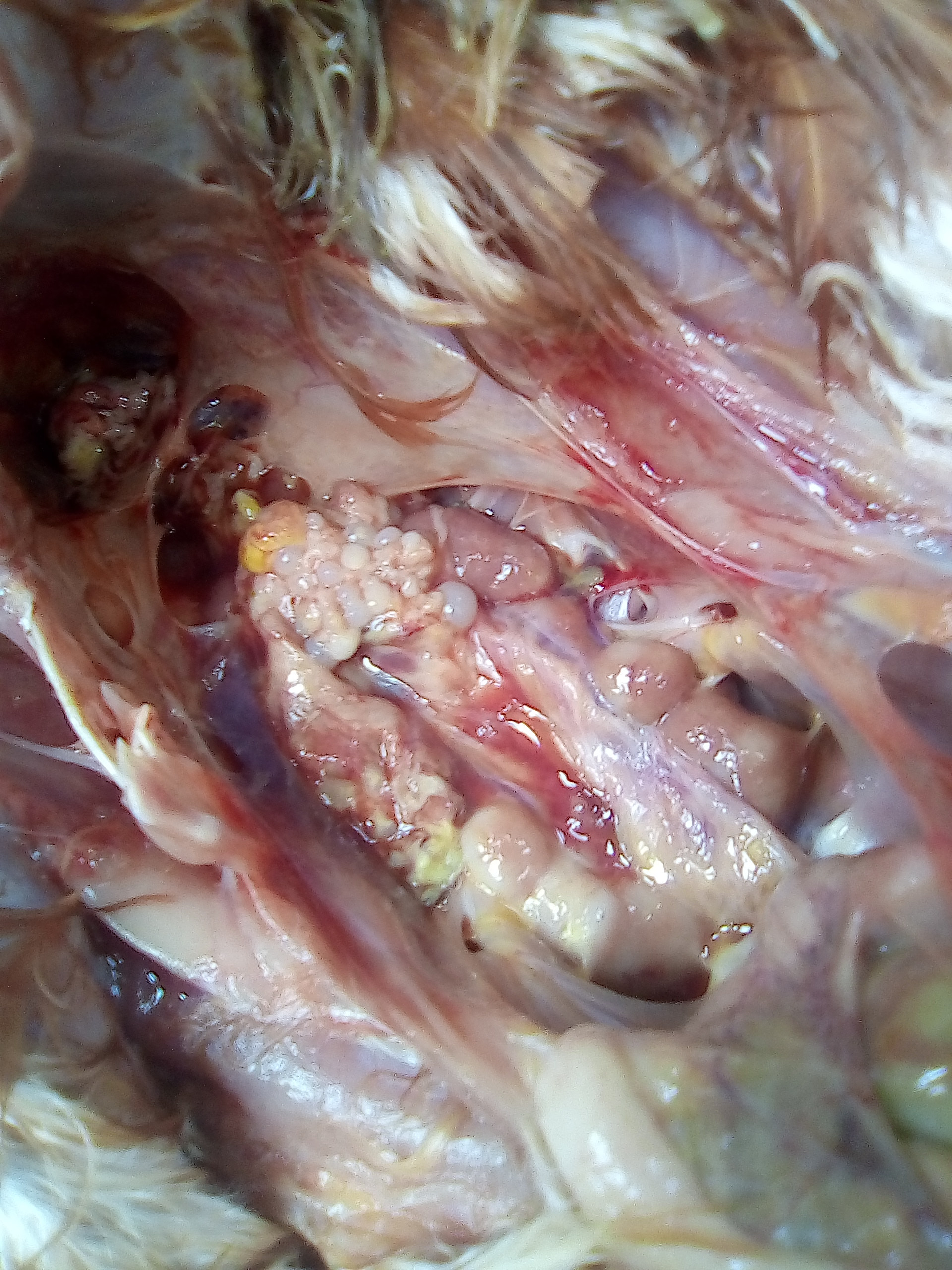
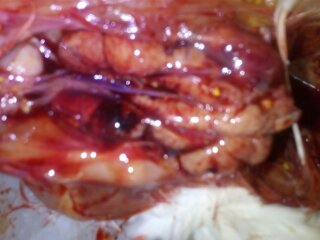

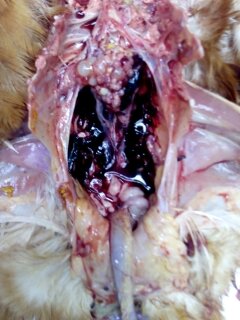
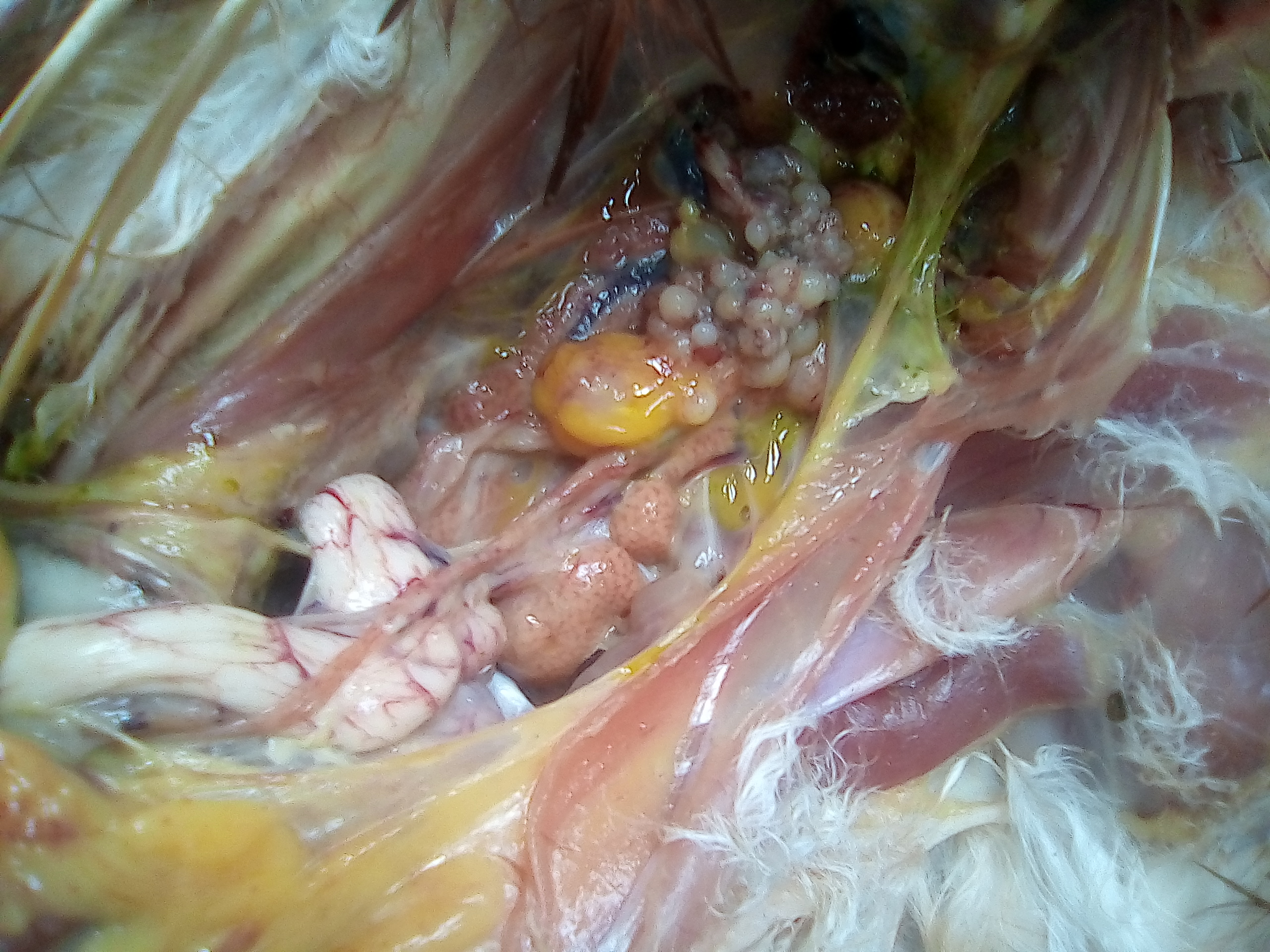
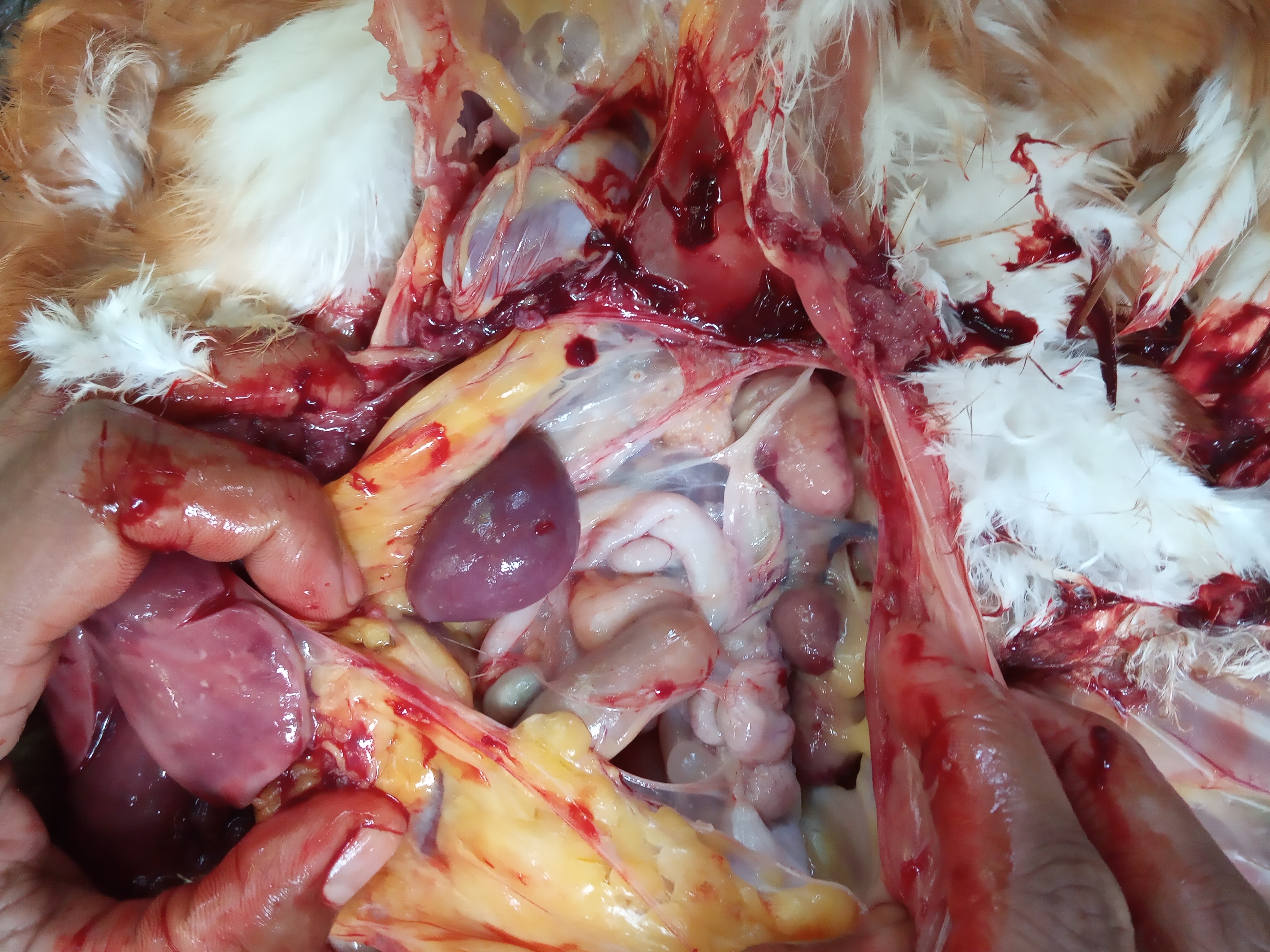 গাউট ,তবে আই বি এইচের জন্য ও হতে পারে।
গাউট ,তবে আই বি এইচের জন্য ও হতে পারে।
২. ধুসর( গ্রেইস) কালার টিউমার
মেরেক্সস
৩. বিবন্ন বা হলুদ কালার
ফেটি লিভার এন্ড কিডনি সিন্ডম
বয়স ২-৪ সপ্তাহ এবং মৃত্যহার ২৫% এর কম
৪. প্রদাহ বা ইনফেকশন এবং পুজের(pus) মত পদার্থ
ই -কলাই বা সালমোনেলা,
গামবুরু বা ব্রংকাইটিস,
পায়েলুনেফ্রাইটিস.
৫.ইউরেটস কিডনি বা সেরাস মেমব্রেনে জমা হয়
বেবি চিক নেফ্রোপেথি,ভাইরাল নেফ্রাইটিস(৪ সপ্তাহ)
ব্রংকাইটিস(১-৩ সপ্তাহ)
৬.ক্যালকুলি বা সাদা পাথর
লেয়ারে : অজানা বা বেশি কেলসিয়াম,
গাউট,
ভিটামিন এ এর ঘাটতি.
৭. একক বড় টিউমার
নেফ্রোব্লাস্টুমা.
১০.লিভার দেখে মুরগির রোগ নির্ণয়ঃ
Liver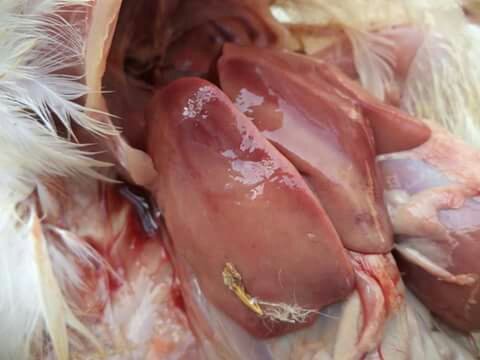
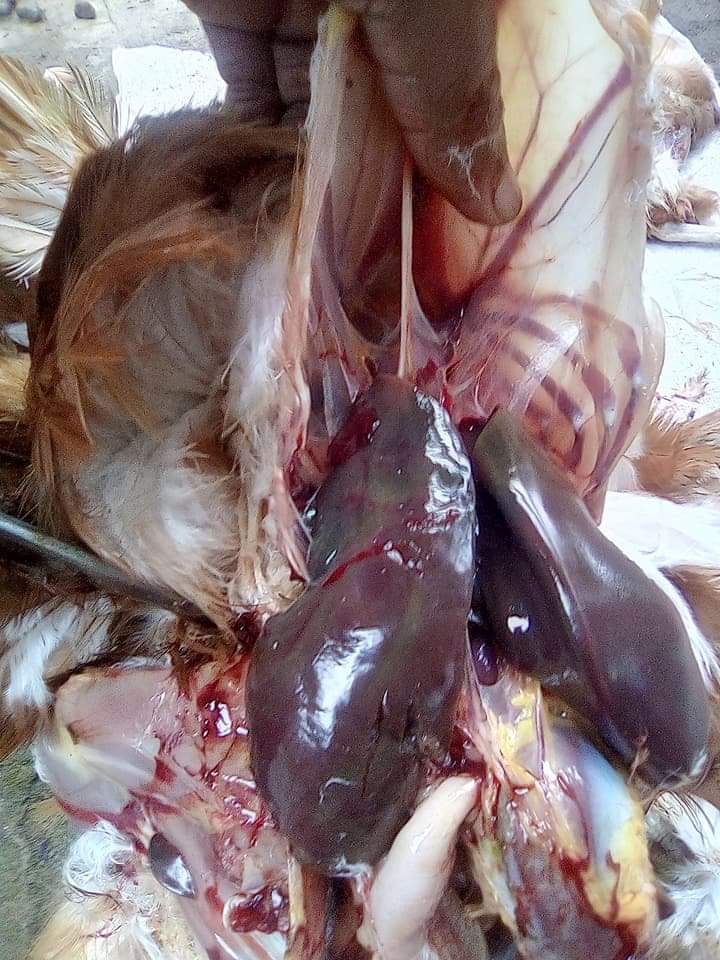
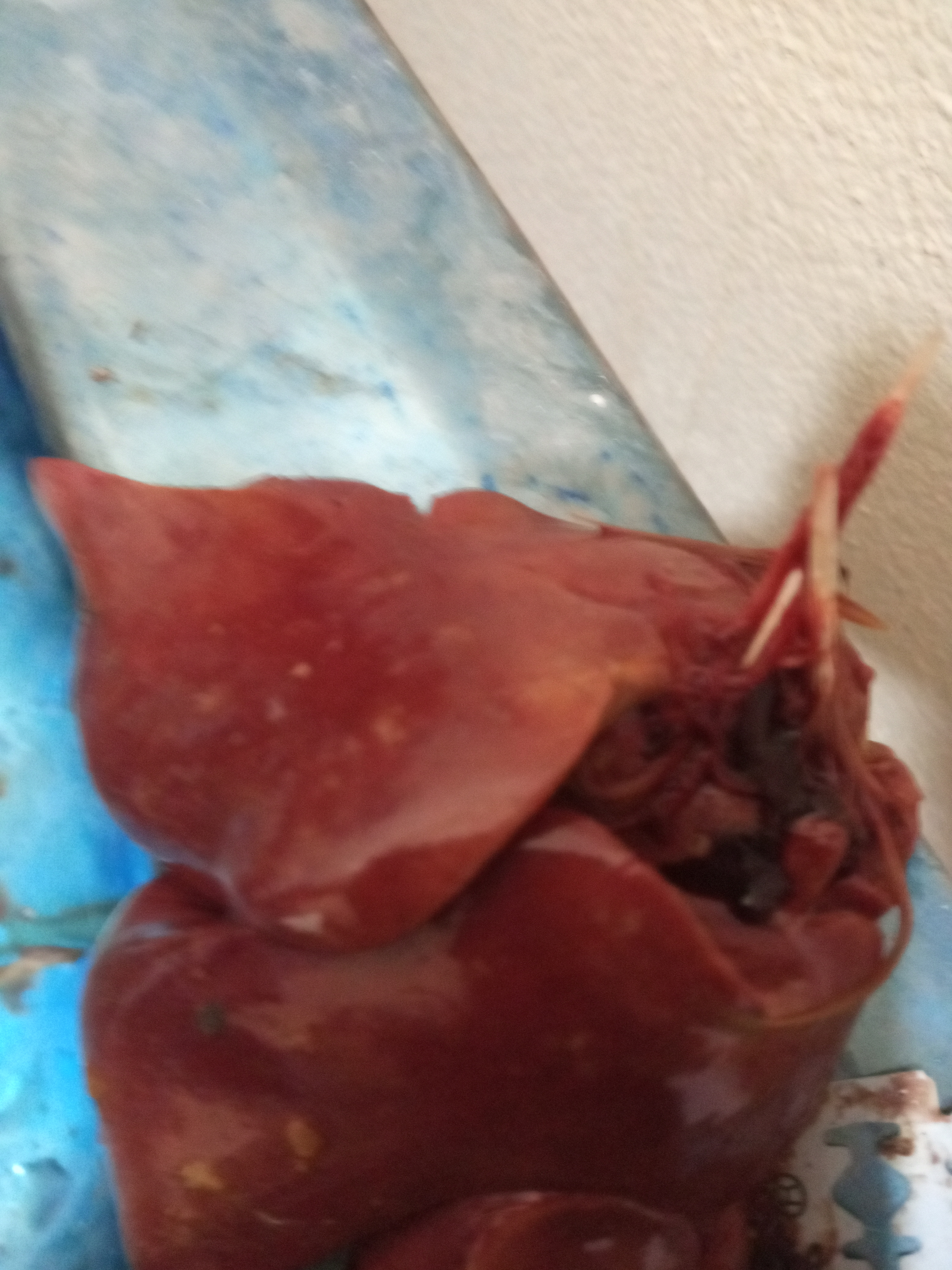
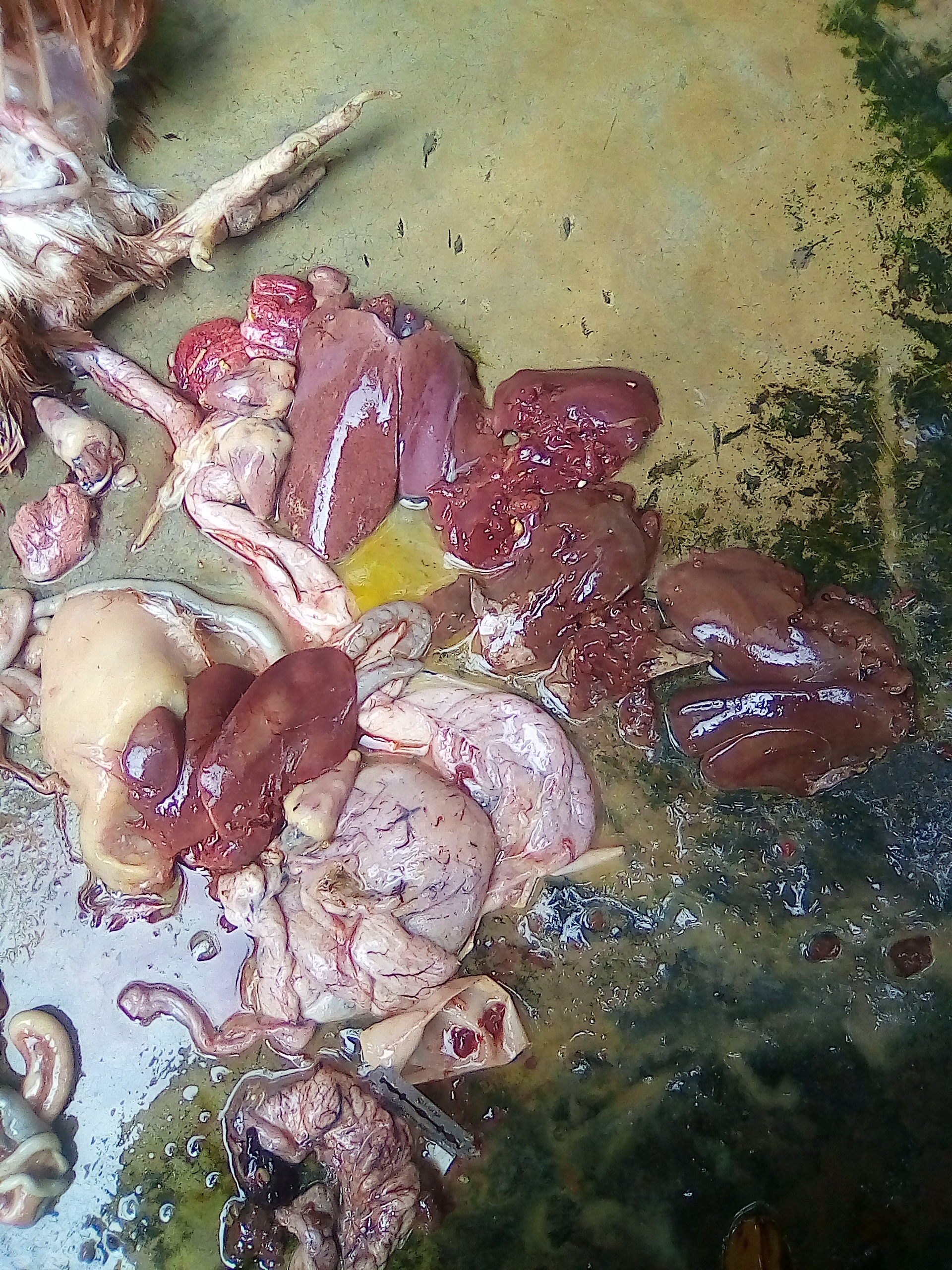
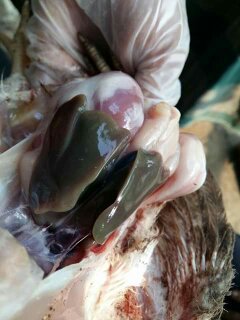
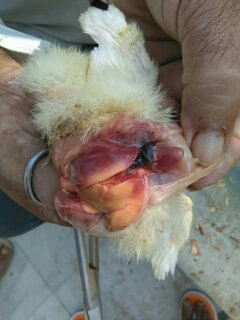
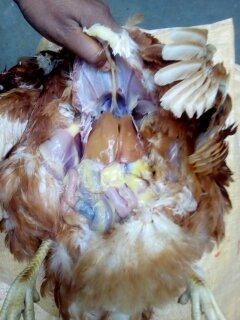

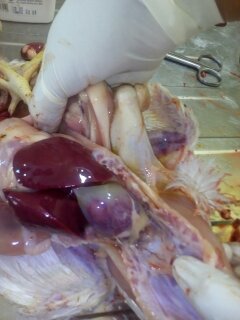
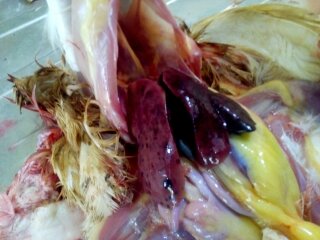


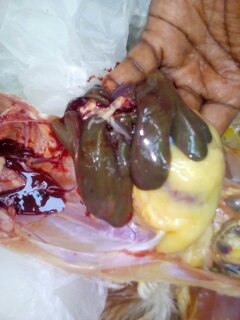


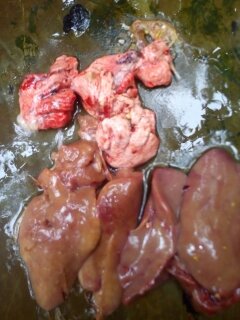
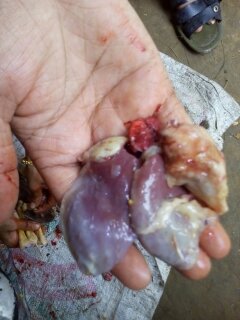
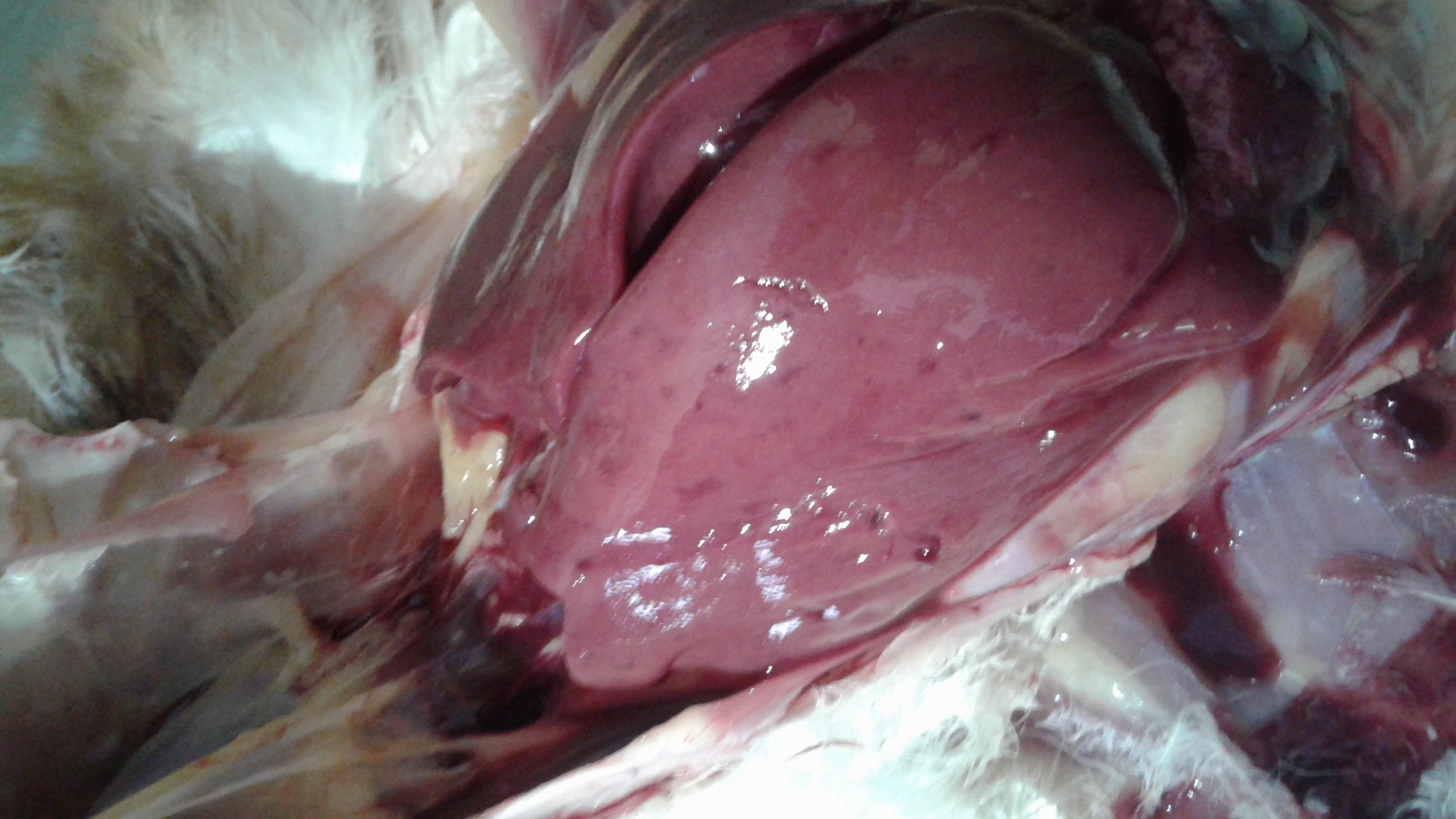


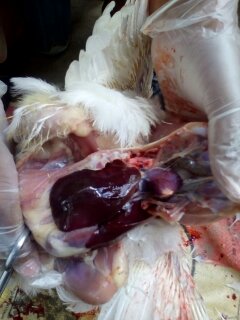



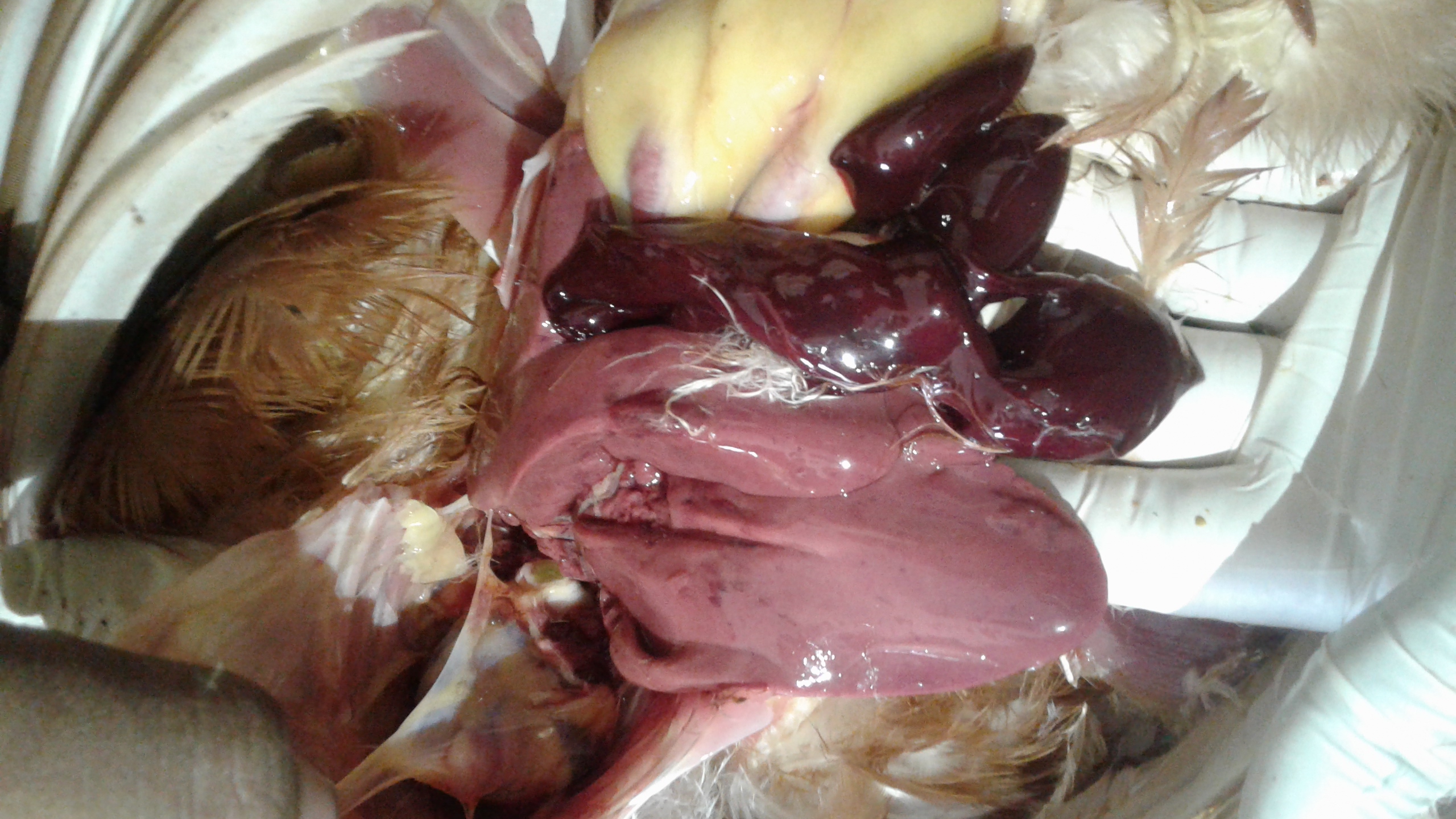

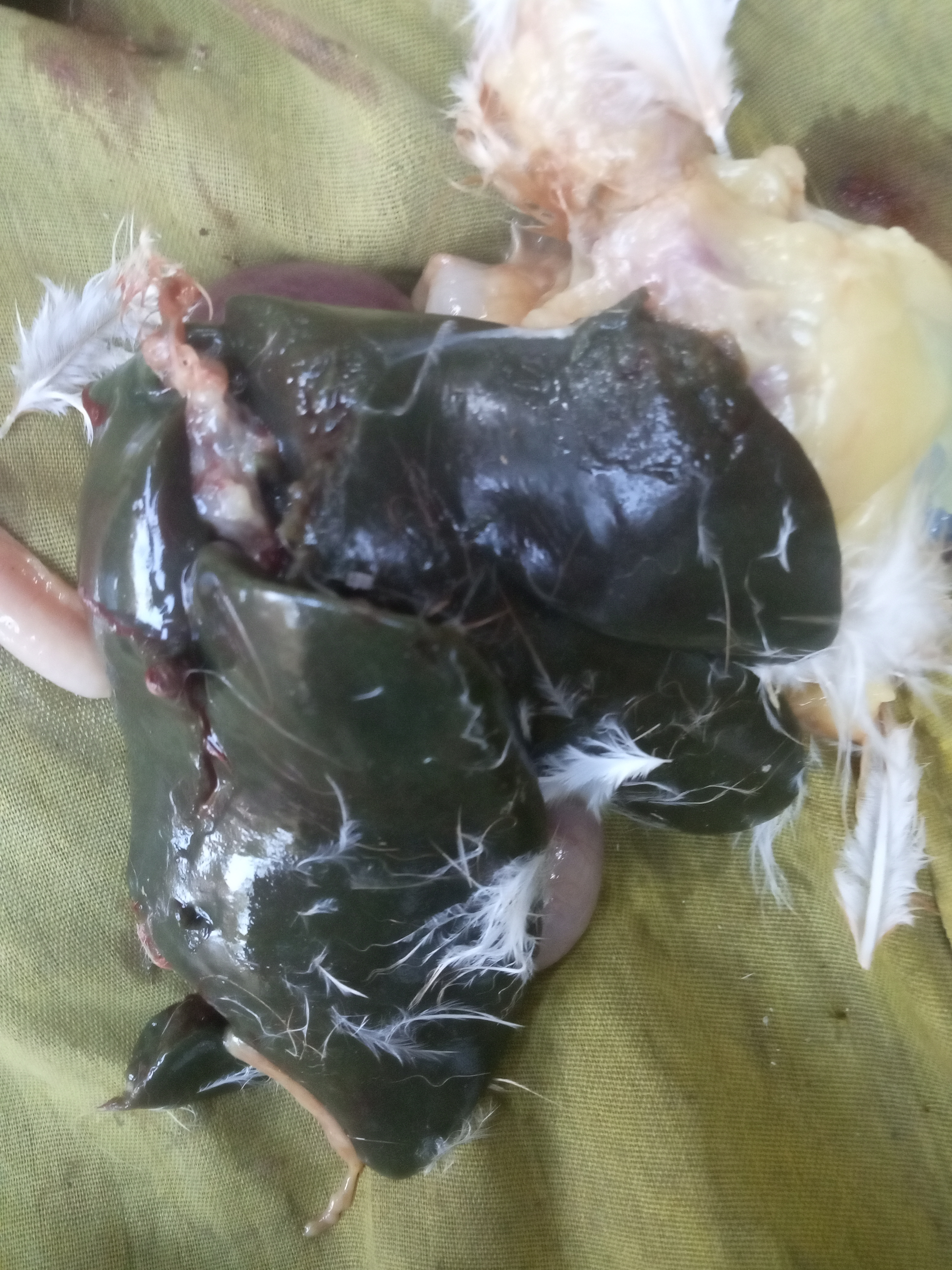

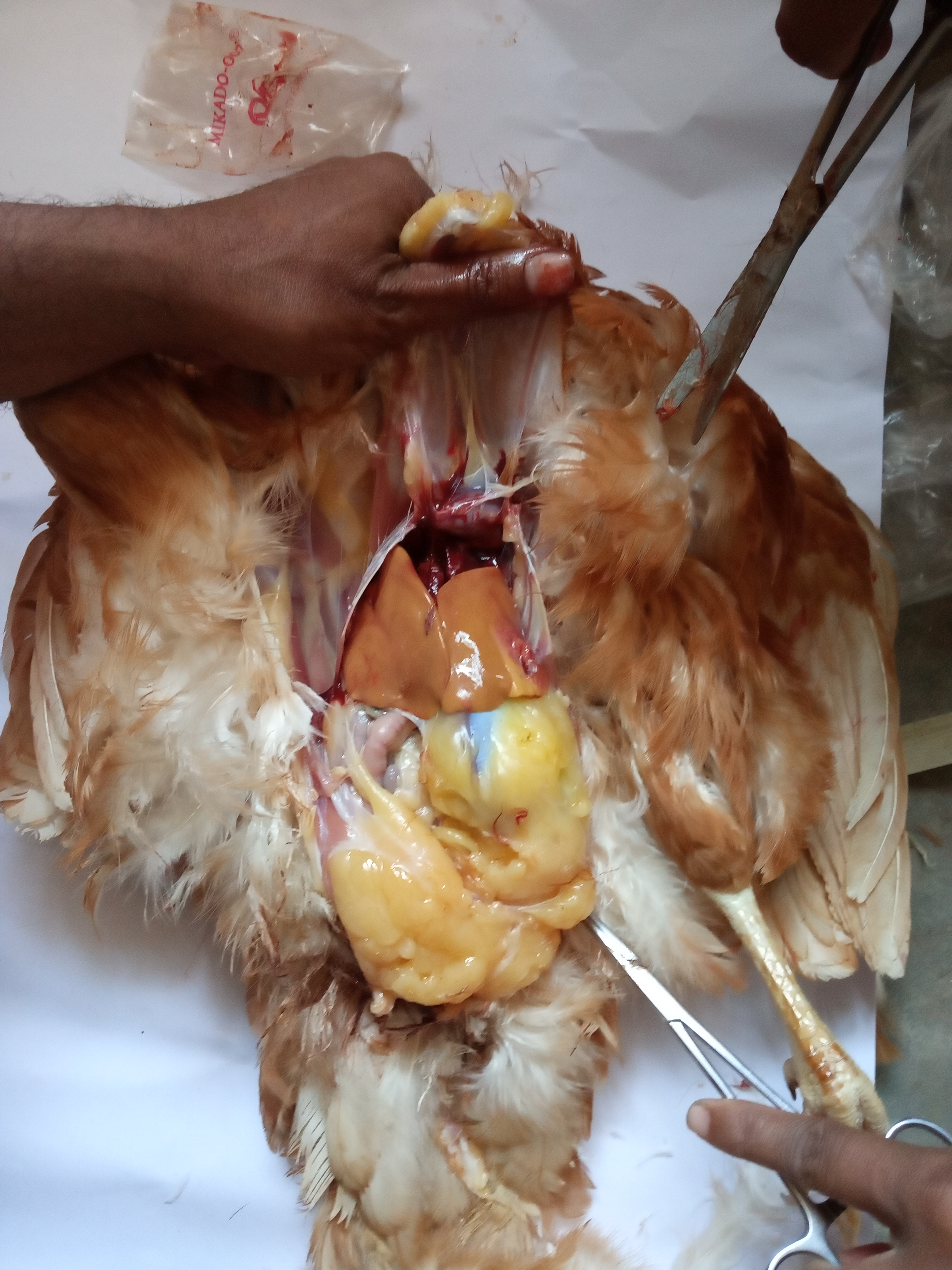
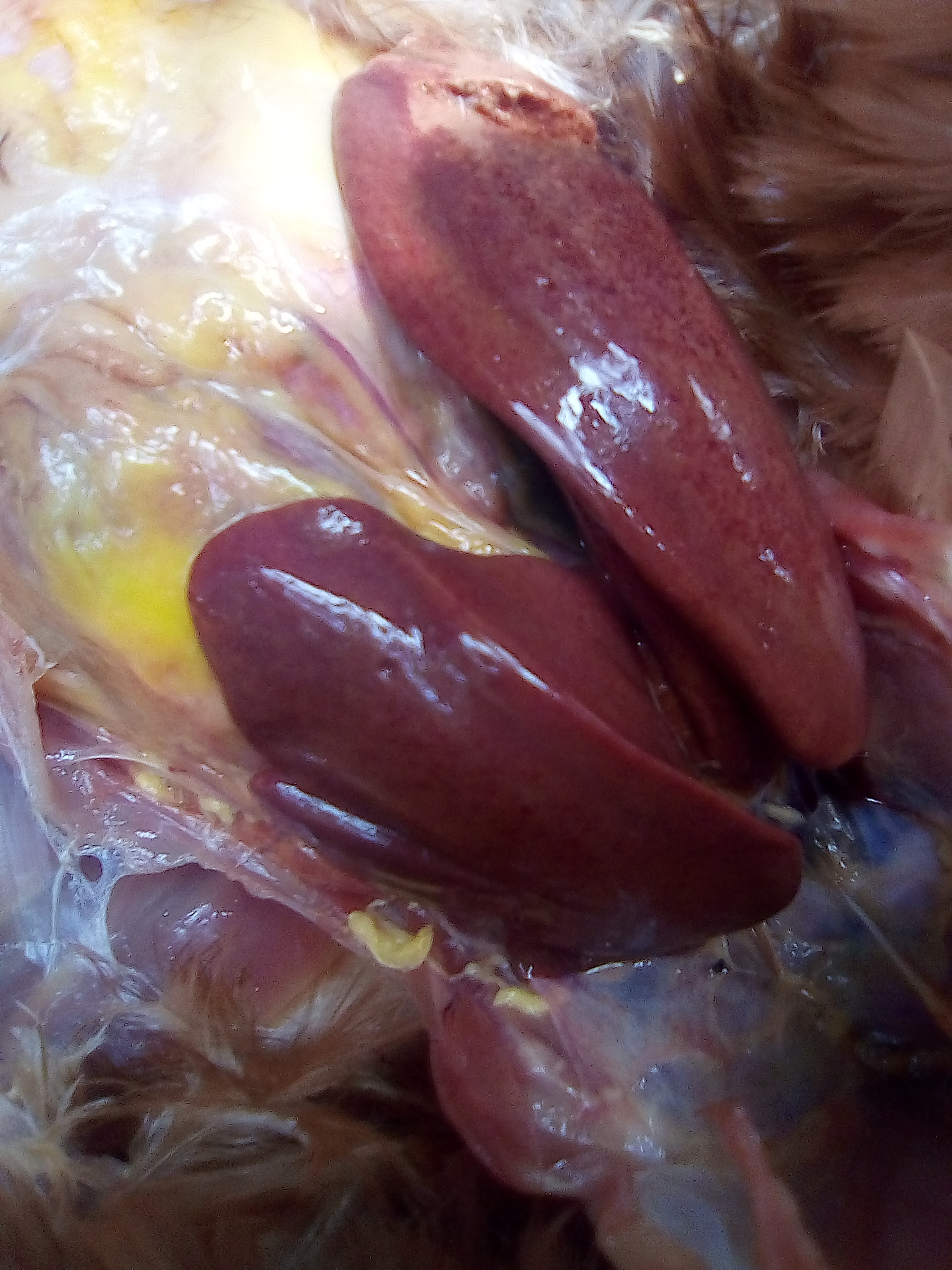
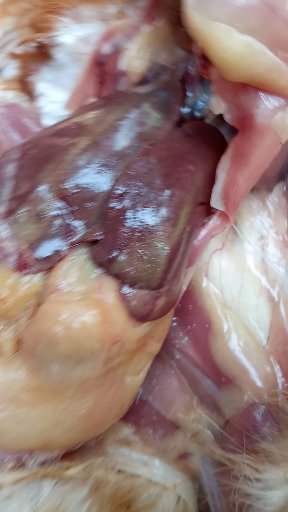

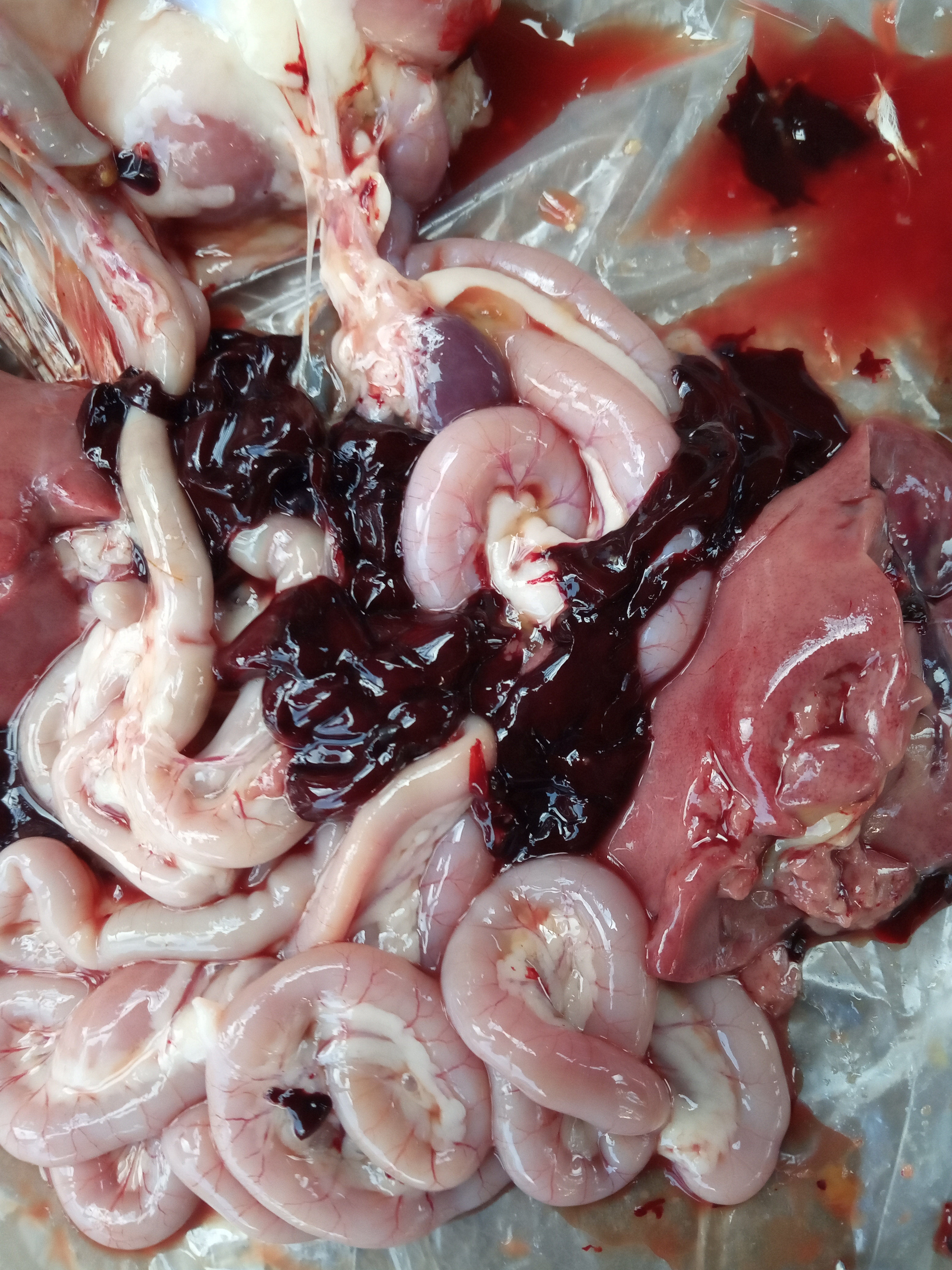
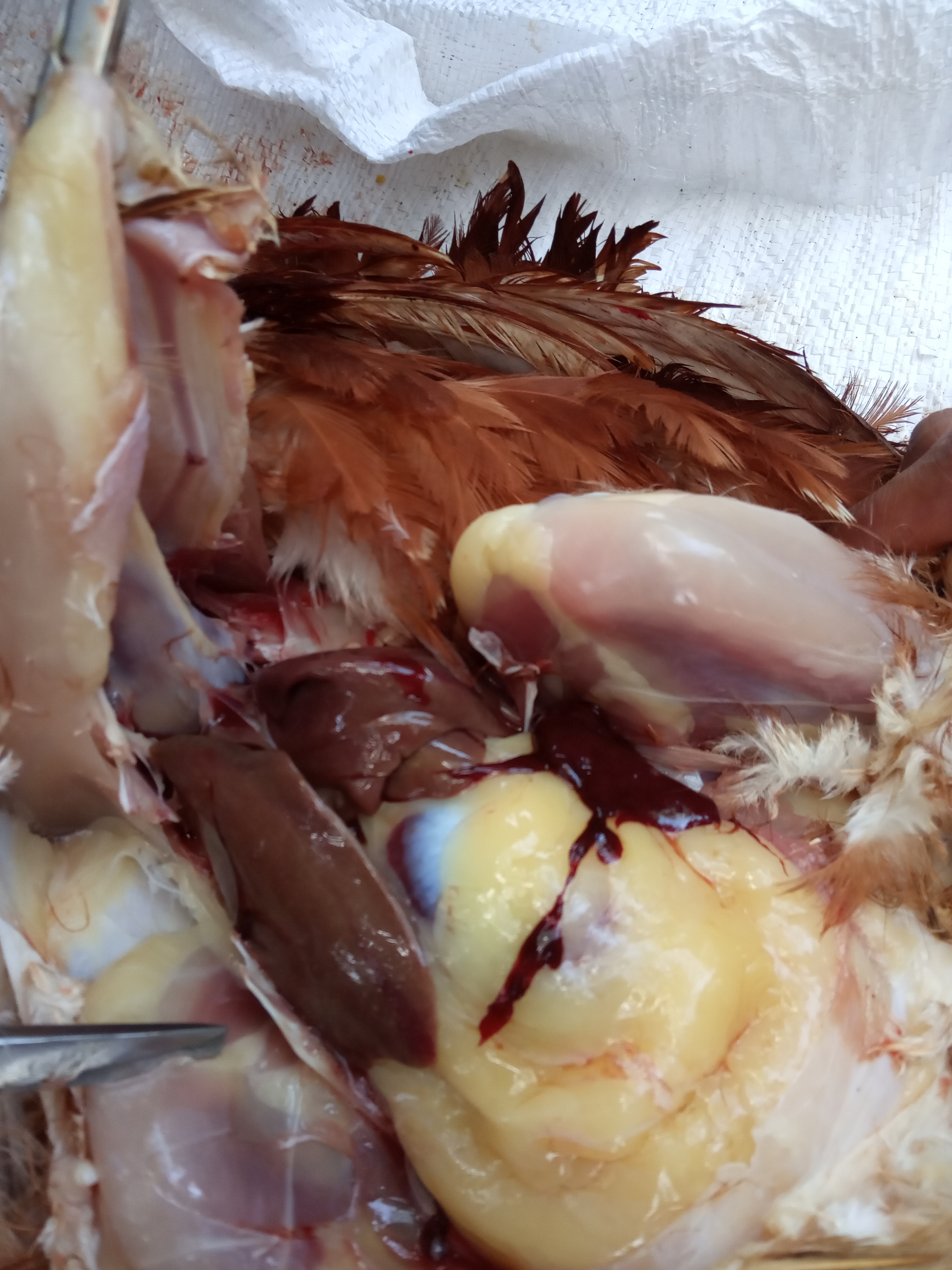
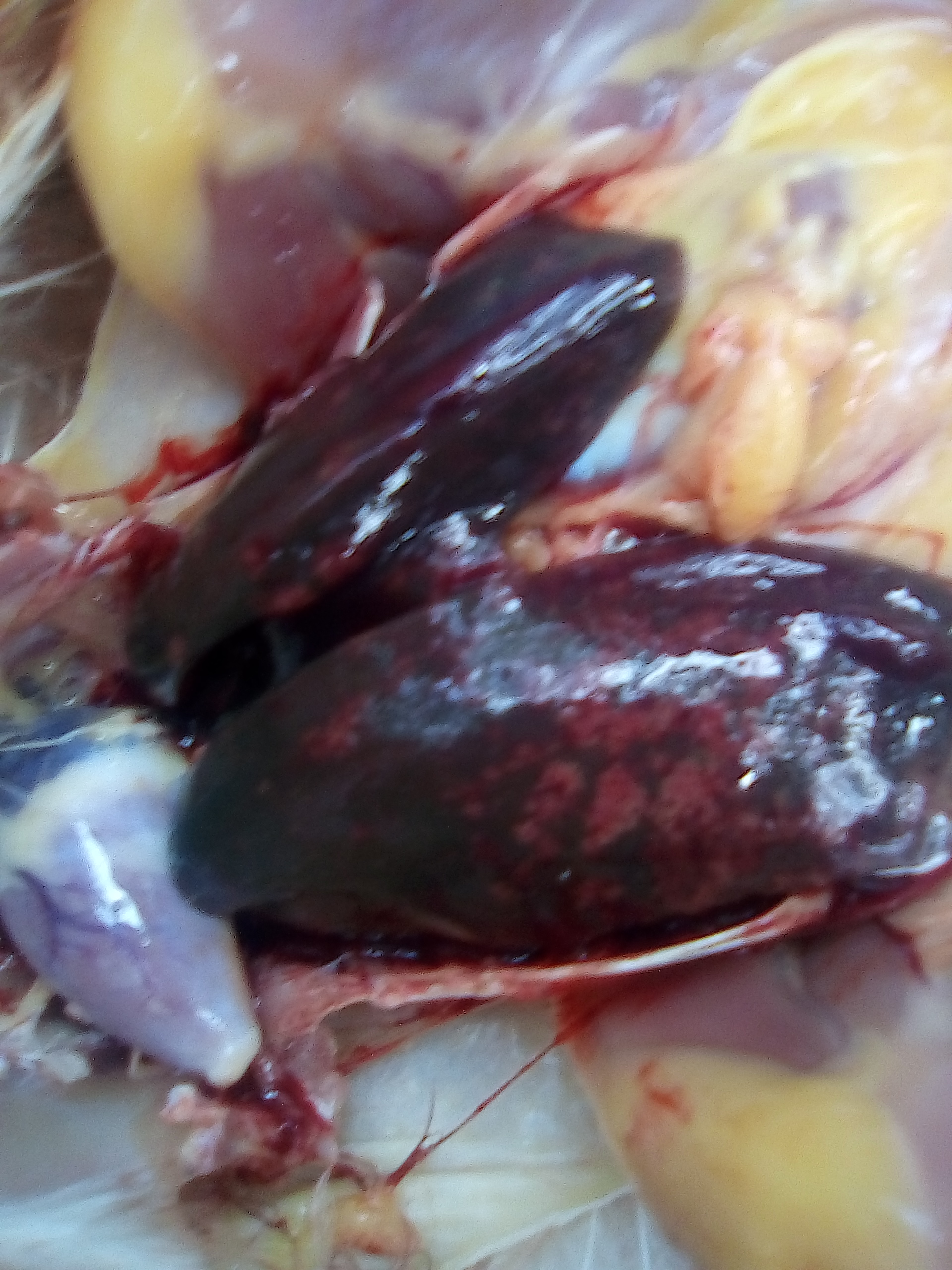
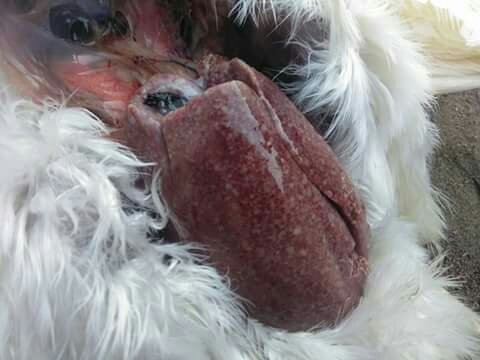
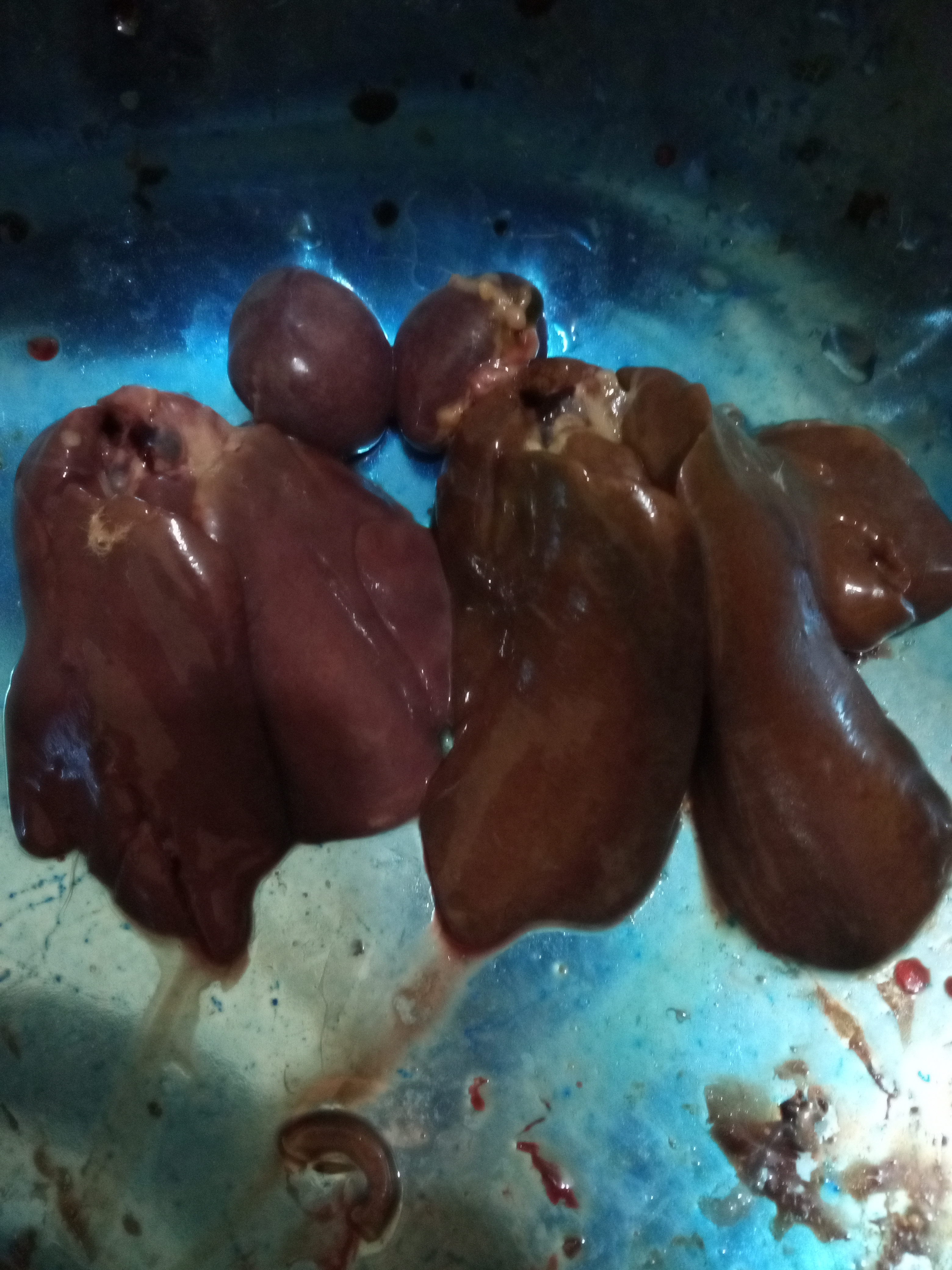
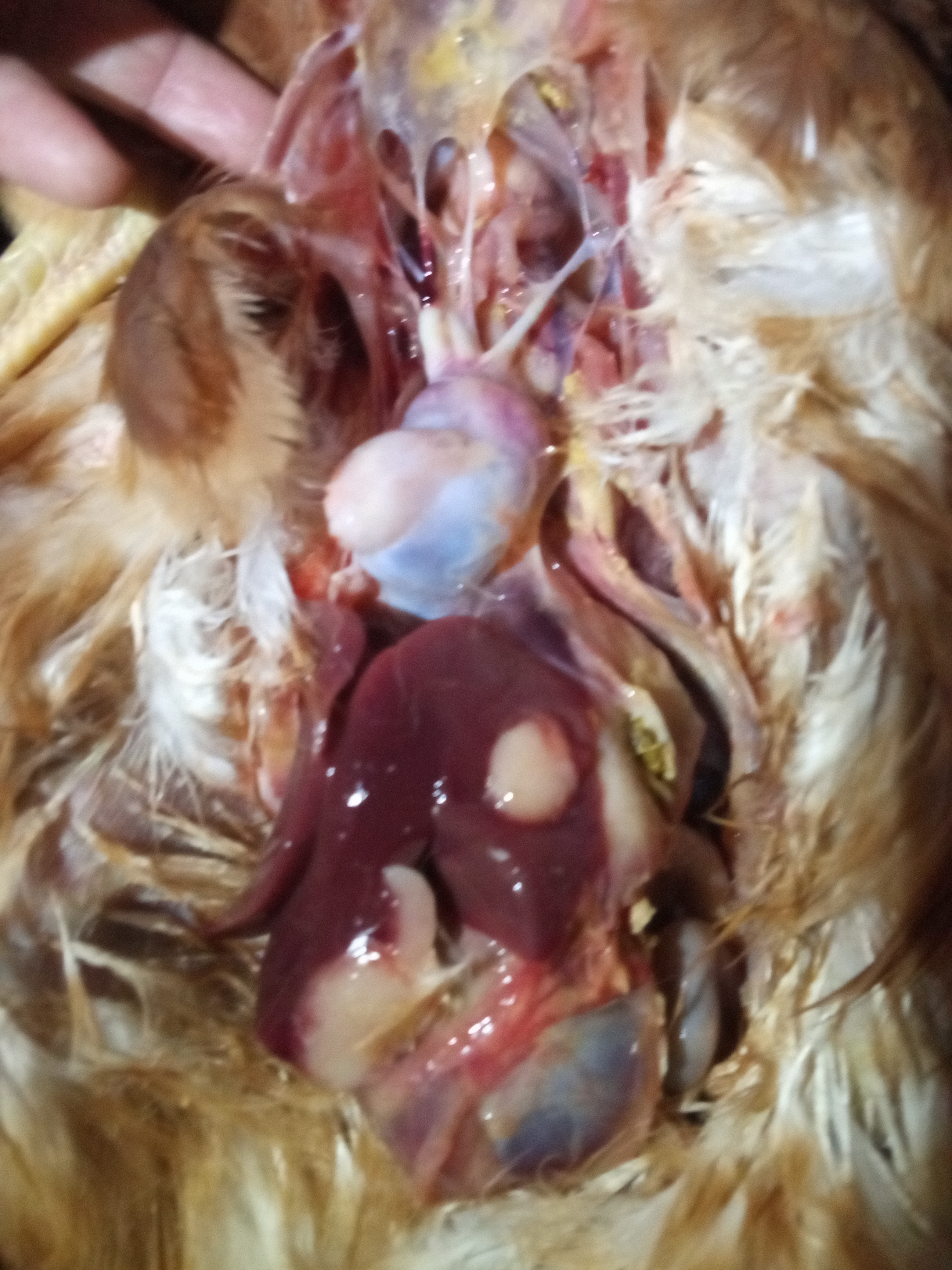



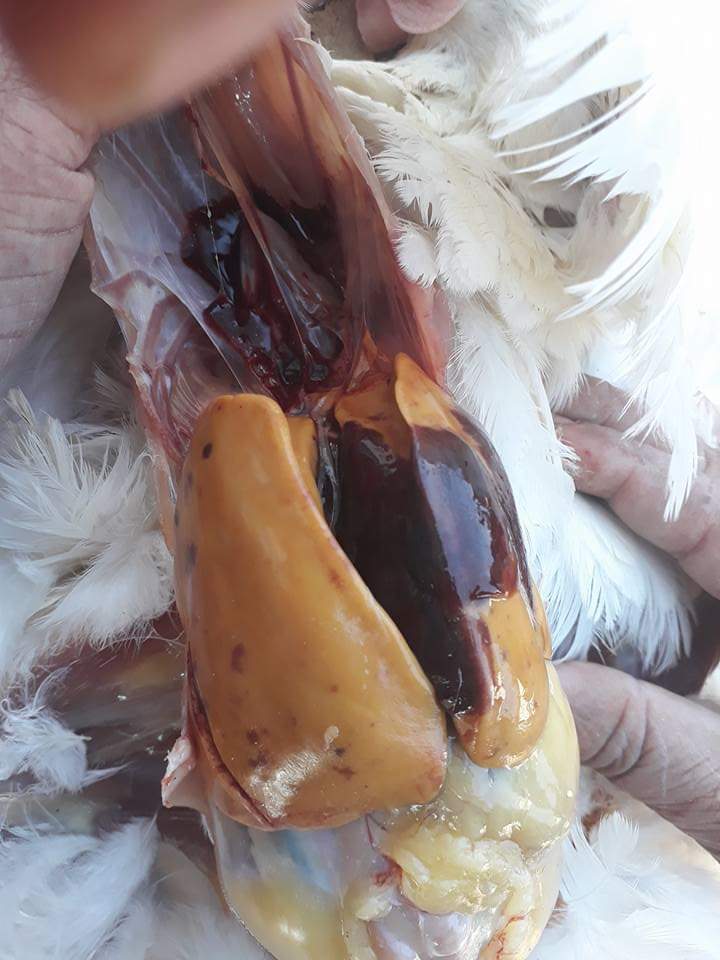
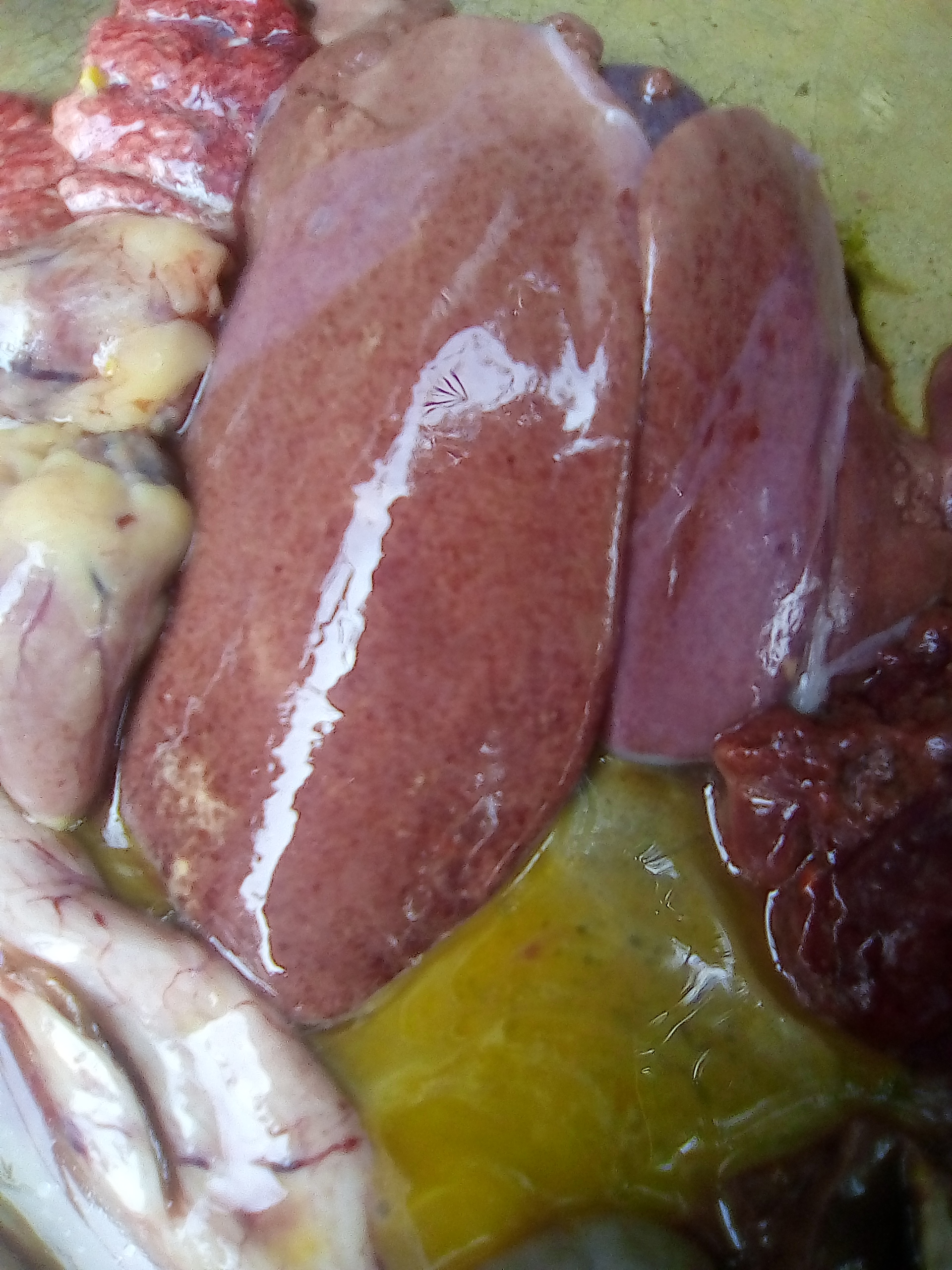
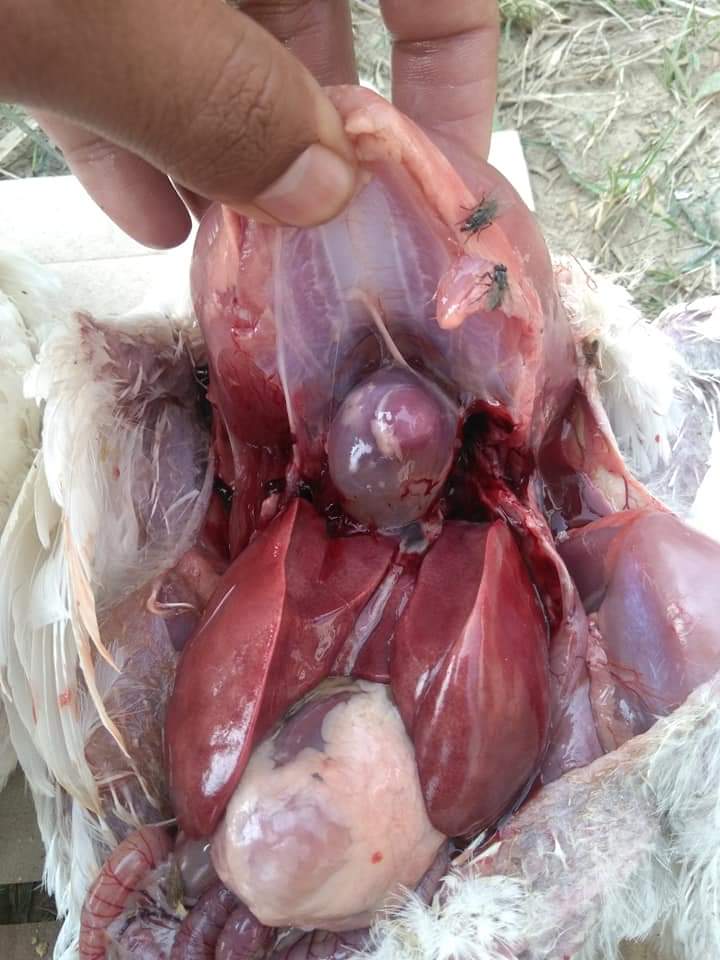
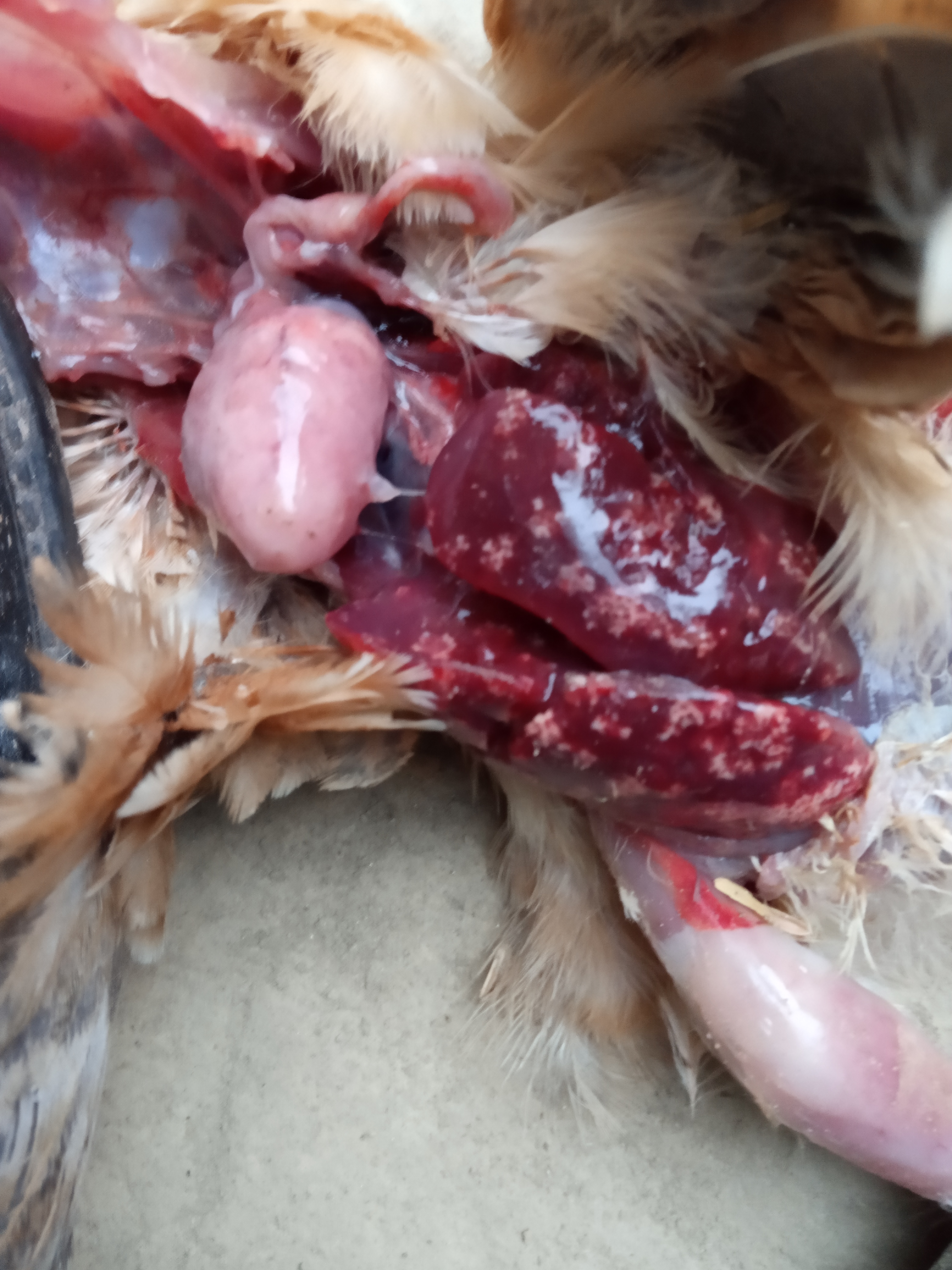



1、Liver black bleeding – poisoning
2、Liver yellowing, bleeding (with blood clots) – sudden death syndrome
3、There are grayish yellow and grayish white nodules or tumors on the surface of the liver – Marek’s disease, lymphocytic leukemia, tuberculosis.
4、Perihepatitis (hepatic enlargement, thickening of the capsule and adhesion of yellow exudate) – Escherichia coli, Salmonella.
5、The hepatomegaly is bronzed and has a tip-sized bleeding site – Salmonella.
6、On the surface of the hepatomegaly, there is a necrotic nodule of rice size – Kaposi’s leukocyte protozoal disease.
7、The liver enlargement is yellowish – bursa and fatty liver.
8、There are uneven disk-like necrosis on the liver – cecal hepatitis and Vibrio hepatitis.
১. লিভার বড়,বোঞ্জ কালার এবং নেক্রোটিক ফোকাই
সালমোনেলা বা তুতে পয়জনিং.
২. সাদা নেক্রোটিক ফোকাই
এ আই,প্যারাটাইফয়েড,কলেরা,ই কলাই,স্পাইরুকেটোসিস.
৩. গ্রেইস কালার এবং বড় লিভার সাথে টিউমার
এভিয়ান লিউকোসিস বা মেরেক্সস
৪. লিভারের উপর সাদা পাতলা ফাইব্রিনাস
পরদা
ই কলাই,সি আর ডি সাথে ই কলাই
৫. হলদে লিভারের উপর লাল স্পট
পলোরাম ডিজিজ( সালমোনেলা)
৬.মটলেড,বড় লিভার এবং রেটিকোলার প্যাটারন অফ হেমোরেজ
এডেনোভাইরাস( ইনফেকশাস এনেমিয়া)
৭ হলদে এবং নরম লিভার
ফ্যাটি লিভার সিন্ডম
৮. গ্রানুলার,গ্রেইস মরুক্কু লেদার এপারেন্স
লিউকোসিস
৯. রাপ্সার অফ লিভার উইথ ব্লাড ক্লট ইন এবডোমেন
ফ্যাটি লিভার সিন্ডম
১০.জন্ডিস লিভার
সালফার ড্রাগ টক্সিসিটি. এডেনোভাইরাস( আই বি এইচ ,লিভারের কিনারা ছুরির মত ধারালো হবে),স্পাইরুকেটোসিস
১১. বড়, বিবন্ন লিভার এবং রেটিকুলেটেড লবোলার প্যাটারন
আল্ফাটক্সিকোসিস
১২ হেমোুরেজিক লিভার
অক্রাটক্সিকুসিস,স্টেপ্টুকক্কুসিস
১৩.বড় লিভার এবং চেরি রেড কালার
ইরাইথ্রোব্লাস্টুসিস,লিউকোসিস.
১১.মুরগির শ্বাসতন্ত্রের লক্ষণ দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়

১.তীব্র রোগে,মুখ হা করে(গ্যাস্পিং) নিশাস নেয়
রানিক্ষেত,আই এল টি
মুখ বন্ধ করে শাস নেয়(গ্যাস্পিং)
ক্রনিক শাসতন্তীয় রোগ
২.বাচ্চায় গ্যাস্পিং (শাস কষ্ট) এবং রেটলিং সাউন্ড
আই বি(ব্রংকাইটিস)
৩.বাচ্চায় গ্যাস্পিং সাউন্ড
এস্পারজিলোসিস
৪.Dyspnea(কষ্টকর শাস)
করাইজা,শাস নালিতে কৃমি
১২.**টাকিয়া এবং ব্রংকাই দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
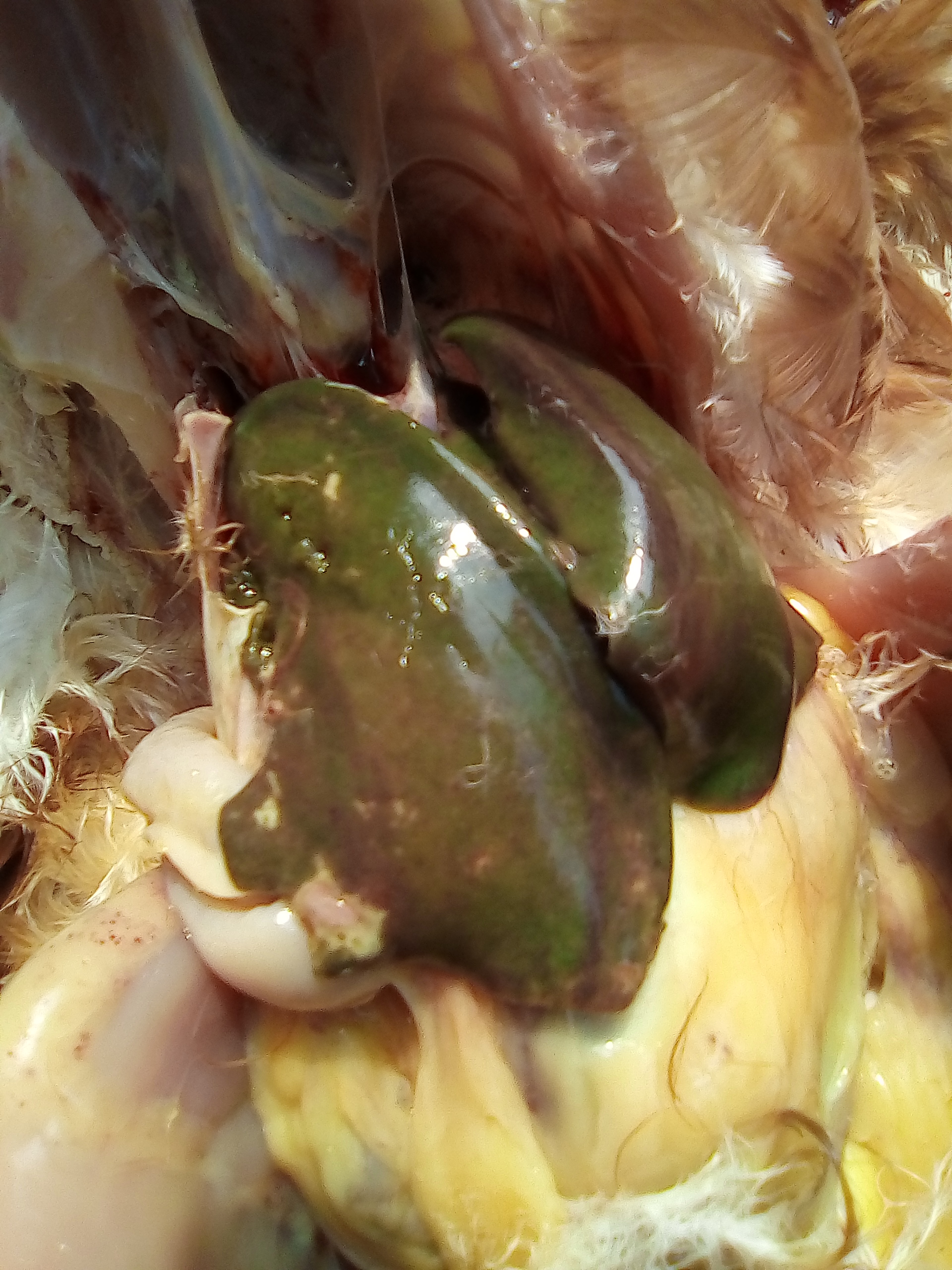
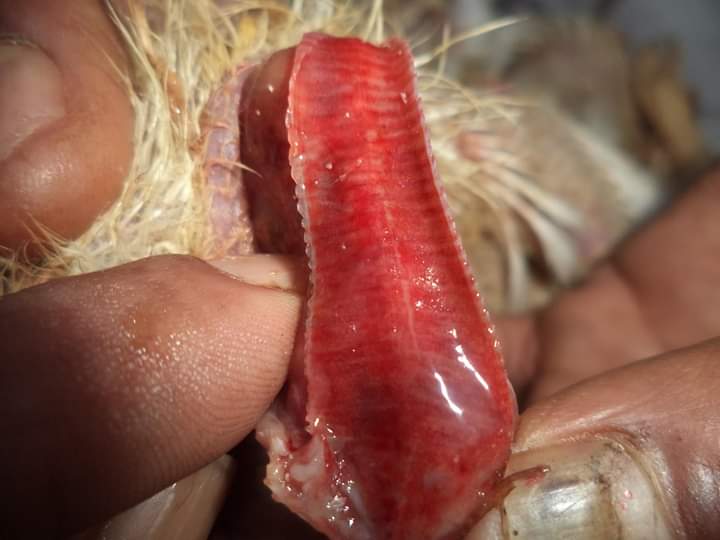 টাকিয়াতে মিউকা
টাকিয়াতে মিউকা





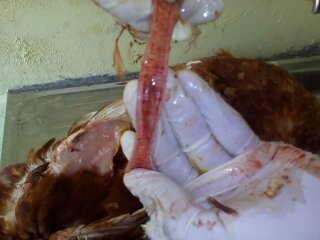




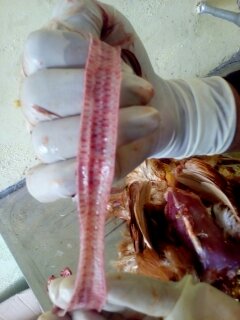






আই বি,রানিক্ষেত,আই এল টি
টাকিয়াতে রক্ত
আই এল টি,এন ডি
টাকিয়াতে পাতলা পরদা
ভিটামিন এর ঘাটতি
টাকিয়াতে লাল সুতার মত
সিংগামাস টাকিয়া কৃমি
১৩.ঝুটি, ফেইস এবং ওয়াটল দেখে মুরগির রোগ নির্ণয়



১ ঝুটি বড়
ভিটামিন এ এর ঘাটতি
ঝুটি নীল এবং ফোলা
কলেরা এবং এ আই ও স্পাইরোকেটূসিস.
২.সাদা পাউডার ডিপুজিট এবং ওয়াটল ফোলা(ঠান্ডা)
ক্রনিক কলেরা
৩.ঝুটি গরম এবং ফোলা ও নডিউলযুক্ত
#করাইজা,পক্স(skin,eyelid,face & base of beak)
৪.ফেইস ফোলা, কম্ব এবং, ওয়াটল নীল:
#কলেরা
৫.ফেস এবং ইনফ্রাঅরভিটাল সাইনাস ফোলা সাথে +- কনজাংটিবাইটিস
#.করাইজা,( চোখ)
# এ আই( লিভার)
৬.Non inflammatory swelling of wattles +-edema of face
#Toxic Feed
7. parrot beak
biotin or panthoneic deficiency
8.Large comb
#Fusarium Toxicosis( enlarge ovary & bursa,prolapse of cloca,cystic oviduct.
8. Bluish combs & wattle
#Spirochaetosis ( fever,dullness,enlarge liverr & spleen)
# Blue comb diseases( no fever,drop production,diarrhoea)
9.greyish scab like deposit at corner of mouth or eyelid.
#Riboflavin deficiency ( chicks)
১৪.জয়েন্ট এবং পা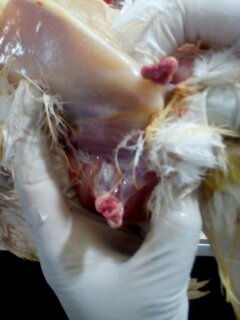
মোটা এবং প্রদাহ
স্ট্যাফাইলুক্কাসিস,ইনফেক্সাস সাইনুভাইটিস,
১৫.মুরগির পালক দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
১.পাখনার নিচে ভেজা পালক :
করাইজা
২.পালক উঠে যাওয়া:
মোল্টিং
৩.পালকের রং পরিবরতন
আইরন,লাইসিন এবং ফলিক এসিড এর ঘাটতি
৪.পালক খাওয়ার অভ্যাস
মেথিওনিনের ঘাটতি
৫.২-১০ সপ্তাহে অল্প পালক
গিজাডে ক্ষত. ,
পায়ের হলুদ রং পরিবরতন
আমাশয়,ভিটামিন এ এর ঘাটতি,
১৬.মুরগির চোখ দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়:

 লক্ষন এবং রোগ
লক্ষন এবং রোগ
১.চোখে পানির মত পদার্থ : করাইজা,সি আর ডি
২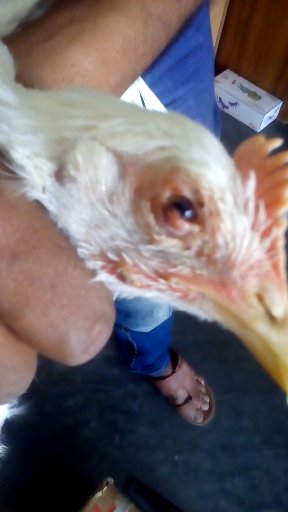






 .
.
চোখের পাতার নিচে পনিরের
মত পদার্থ : পক্স,ফাংগাল ইনফেকশন,ভিটামিন এর ঘাটতি
৩.অসসছ বা ঘোলাটে লেন্স:
এ আই
৪.চোখ বড় এবং ফোলা:
সি আর ডি
১৭.ডায়রিয়া দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়:
# তীব্র: আমাশয়,গাম্বোরু,রানিক্ষেত,তাছাড়া শীতকালে নন স্পেসেফিক এন্টারাইটিস হয়.
# হলদে কালার:
টাইফয়েড
# হলদেটে সবুজ
রানিক্ষেত,টাইফয়েড,ক্লেমাইডোসিস,স্পাইরুকেটোসিস
#পেস্ট লাইক হোয়াইট( pesty vent)
ই কলাই,আই বি এইচ,পলোরাম.
# সাথে রক্ত
আমাশয়
#সালফার কালার মাইল্ড(mild)
গাম্বোরু,আফ্লাটক্সিকোসিস,হিস্টোমনিয়াসিস
১৮.মাথা দেখে
#ফোলা( face & around eyes)মুখ এবং চোখের আশপাশ.
করাইজা,রানিক্ষেত,এই আই( এভিয়ান ইইনফ্লুয়েঞ্জা)


১৯. মারা যাওয়া দেখে
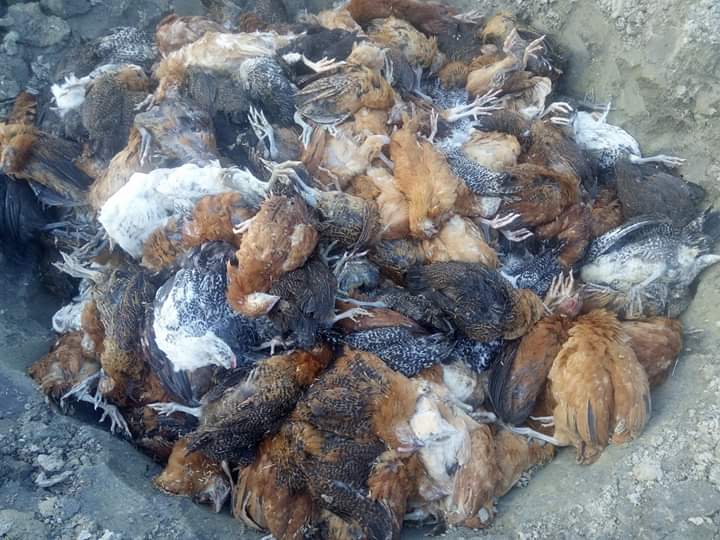






# হঠাৎ মারা যায়
হিট স্টোক,পানির অভাব,ফেটি লিভার সিন্ডোম
# লক্ষন অনুযায়ী মারা যায়
এন ডি,কলেরা,এই আই,গাম্বোরু,তীব্র আমাশয়,সালমোনেলা,ই কলাই,পয়স্নিং
২০.চামড়া এবং মাংস দেখে
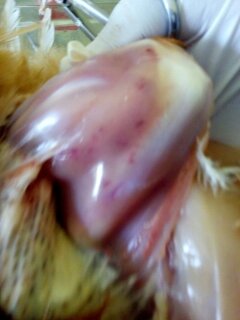
1.Hemorrhagic& gangrenous inflamation of skin & muscle +- greenish color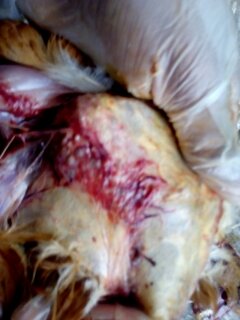

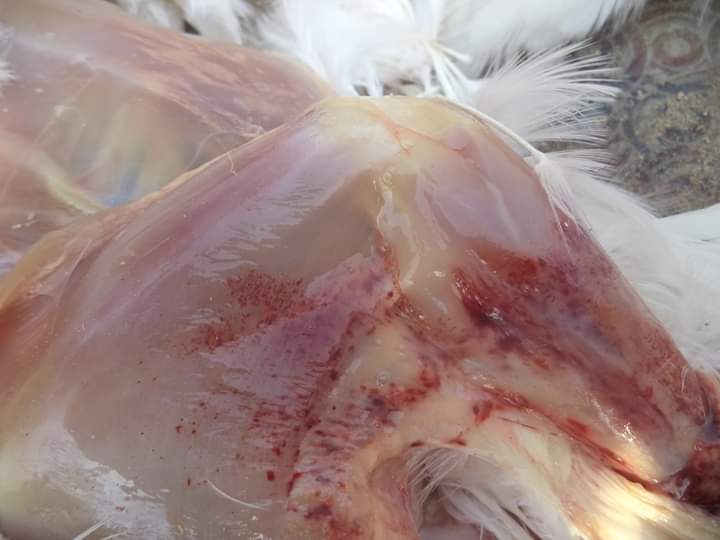

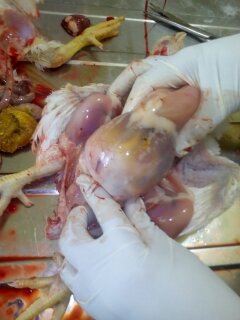


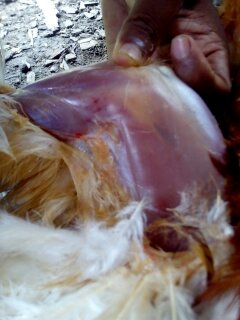
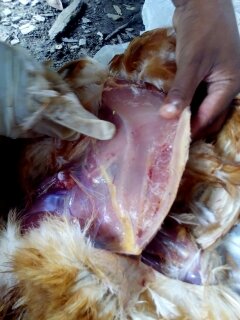

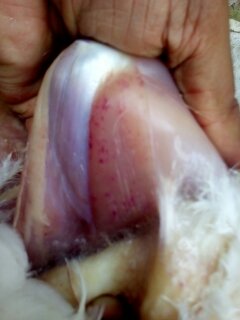

#Gangrenous dermatitis( clostridium perfingenes)wing,head,breast & legs.
# Staphylococcus dermatitis with clostridium
#Bluish color dermatitis of wings
blue wing diseases by E coli,staphylococous,clostridium( 2-3 wks)
# A I
2.Swollen feather follicle
Cutaneous Mareks( neck & thigh)
3.Hemorrhagic spots of variable size in muscle off thigh,breasts
# Mouldy corn toxicosis,(4-8wks)
#I B D
#Sulphonamide toxicity
4.S/C edema + asitis
Nacl poisoning
5.caseous exudate under skin of head & neck
# mycoplasma synoviae
6.Serosanguinous( blood tinged fluid) under skin
#vit E or selenium deficiency
7.poor feather growth
Folic acid deficiency ( chick)
8.Lice on feathers
pediculous( pdoduction loss)
9.white bands of degenerating breast muscle
Vit E deficiency +-methionine,choline deficiency
10.Clubbed feathers
Ribidlavin deficiency
11.Formation off dry brown scabs in skinkin wiithout loss of feathers
mite infestation
12.small hemorrhagic spots in skin on inner wings,thighs +-anaemia
Ticks infestation
13.loss of feathers due to breaks att their base
Depluming mite infestation
14.Injury to skin around vent,flesh eating
Cannabolism.
15.hemorrage in muscle
IBH with other sign
২১ হাড় ও পা দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়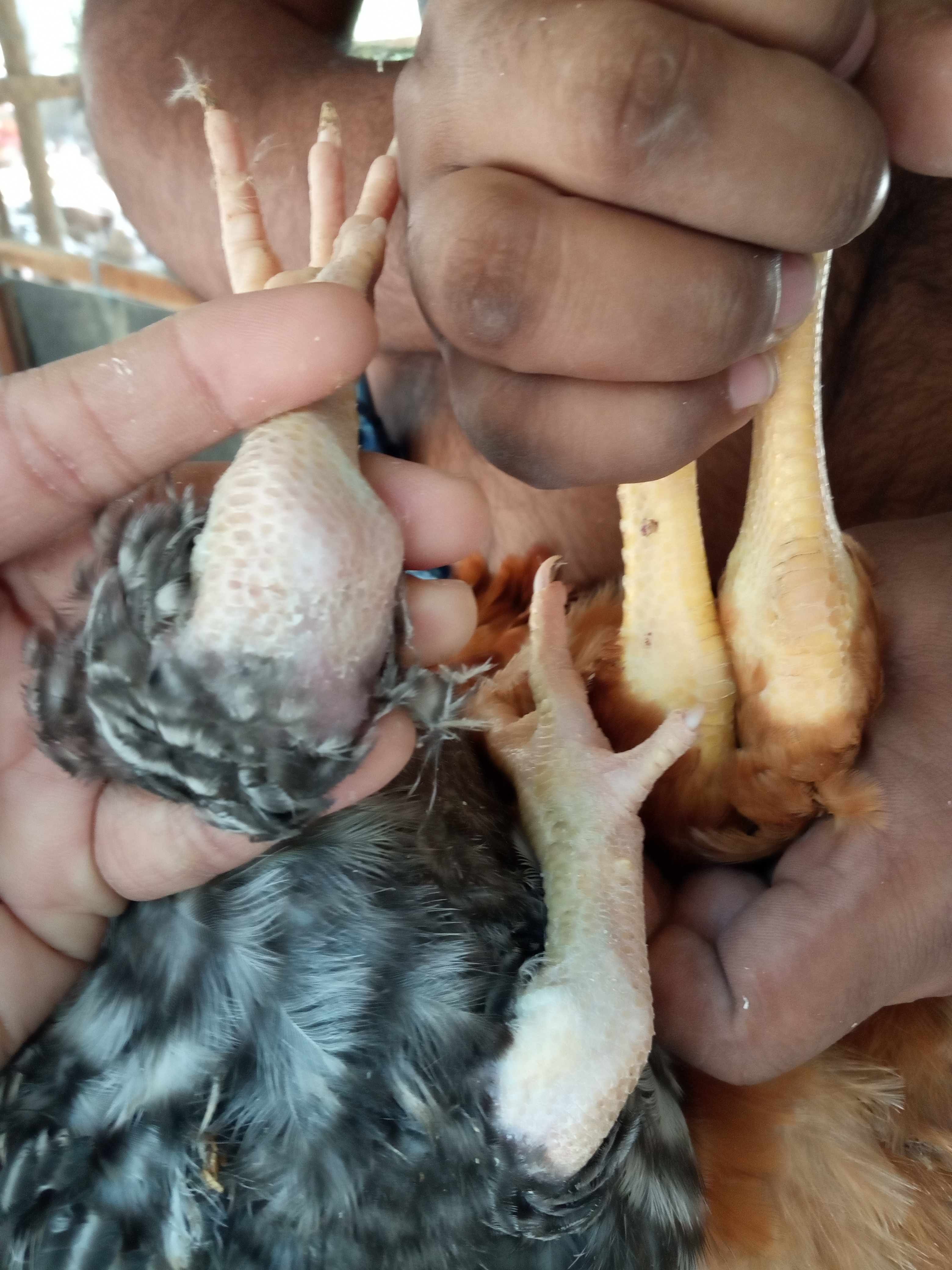
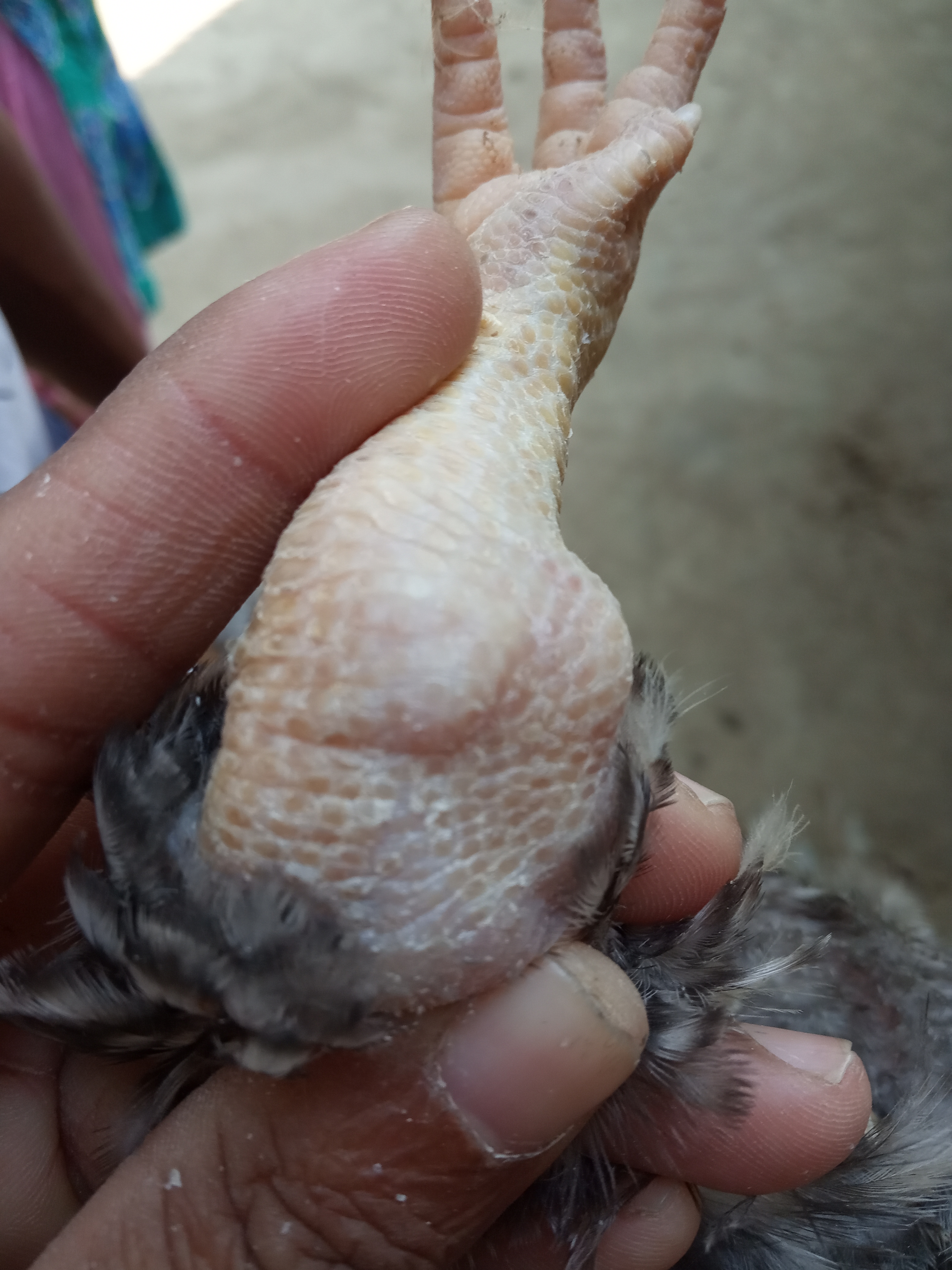
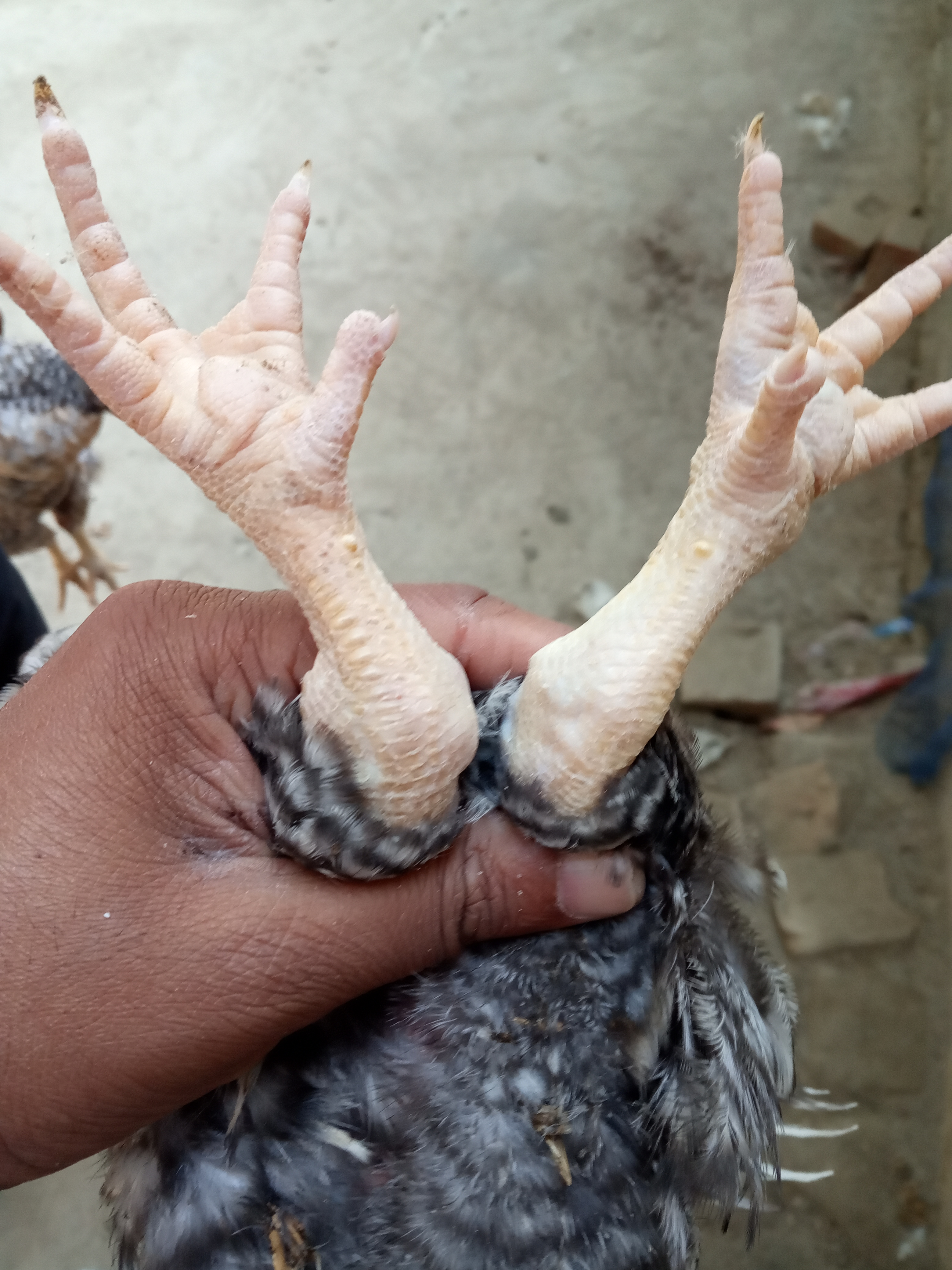


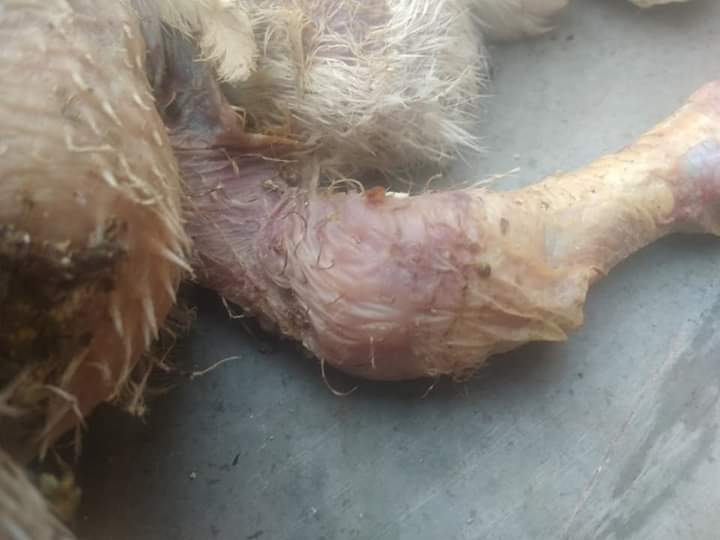



1.Soft rubbery boners enlarged headed costochondal junction
#.Rickets,not movement
2.soft, easily breakable bones inn adult
#Cage layer fatigue,cal,p,D3 deficiency.
3.Shimy,pale bonemarromow
Erythroblastosis(immature RBC),Anemia,cheery red liver)
4.Thickened leg( shank)
Osteopetrosis,narrowbone( hot leg)ALC
5.nodules granuloma with necrotic foci in marrow off longbone.
22. Glandular lesions
1. petecial gen rrragez in panancrease
Aflatoxicosis,liver big
2.Atrophy of pancreases inn growers
Aflatoxicosis,
selenium deficiency ( retard growth,exudative diathesis)
3.Adrenal gland larger than normal
Thiavin deficiency
edema off S/C tiissue.
3.pancreases looks granular due to whitish spot
Blue comb
২৩.Oesophagus & crop দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
1.Dilated crop filled with rancid liquid contents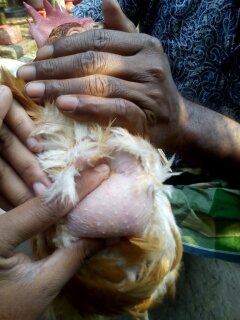
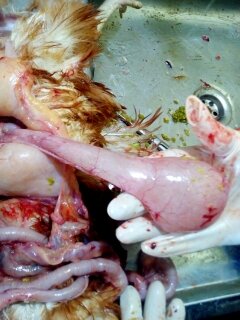
Pendulous crop
2.Distended crop filled with foreign,undigestibe material
# Impaction of crop ( feather)
3.Turkish towel like thickening of crop mucosa + ulcer
# Candidiasis( proventriculus,)
4.Raised,vesicular orr pustules of oesophagal gland
#Vit A deficiency (cheesy exudate under eyelid,stunted growth,nephrosis,bursa necrosis)
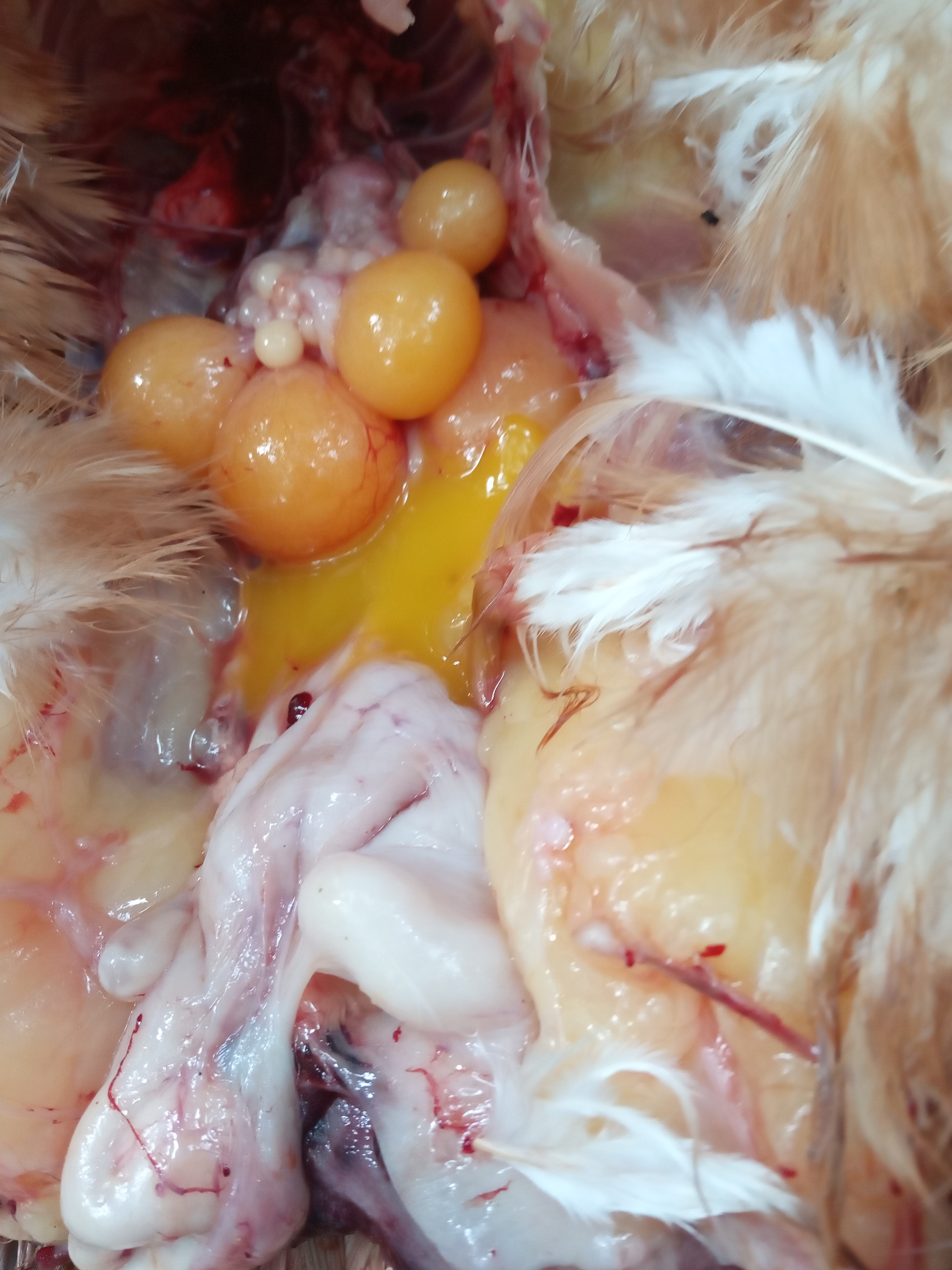
২৪.ওভারি দেখে রোগ নিরনয়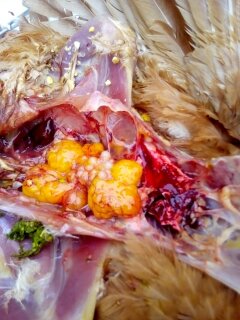

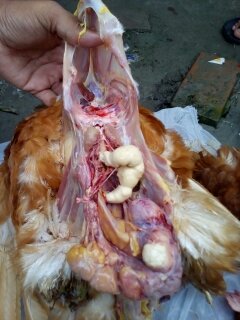
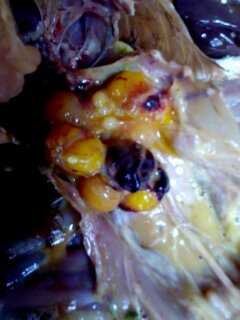
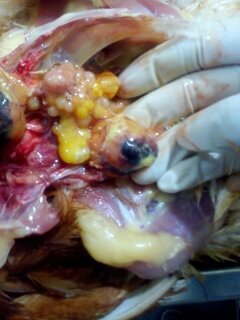

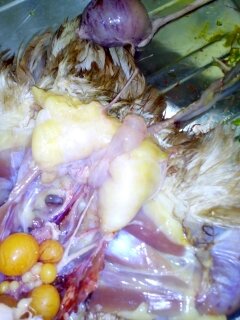
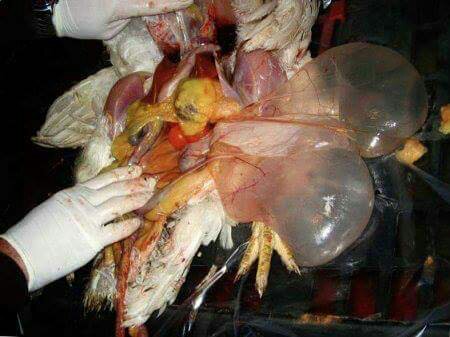

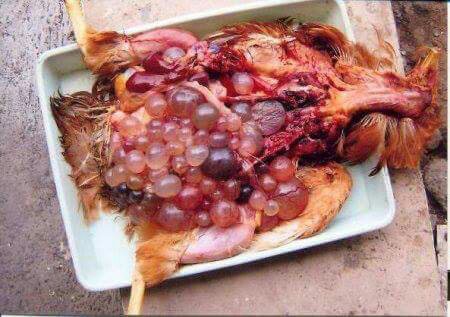
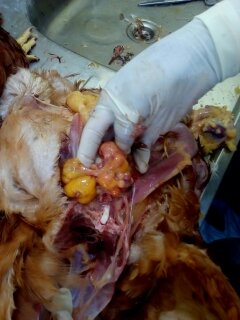

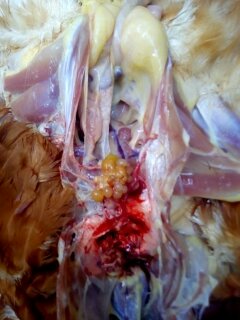
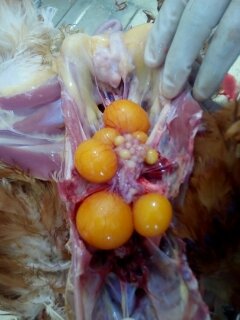
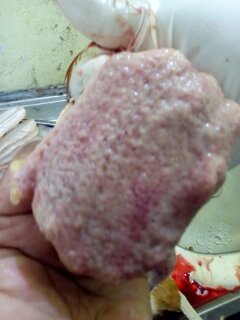
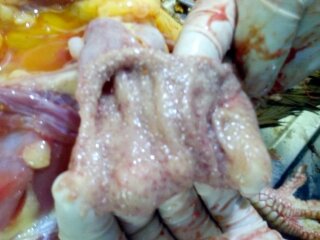
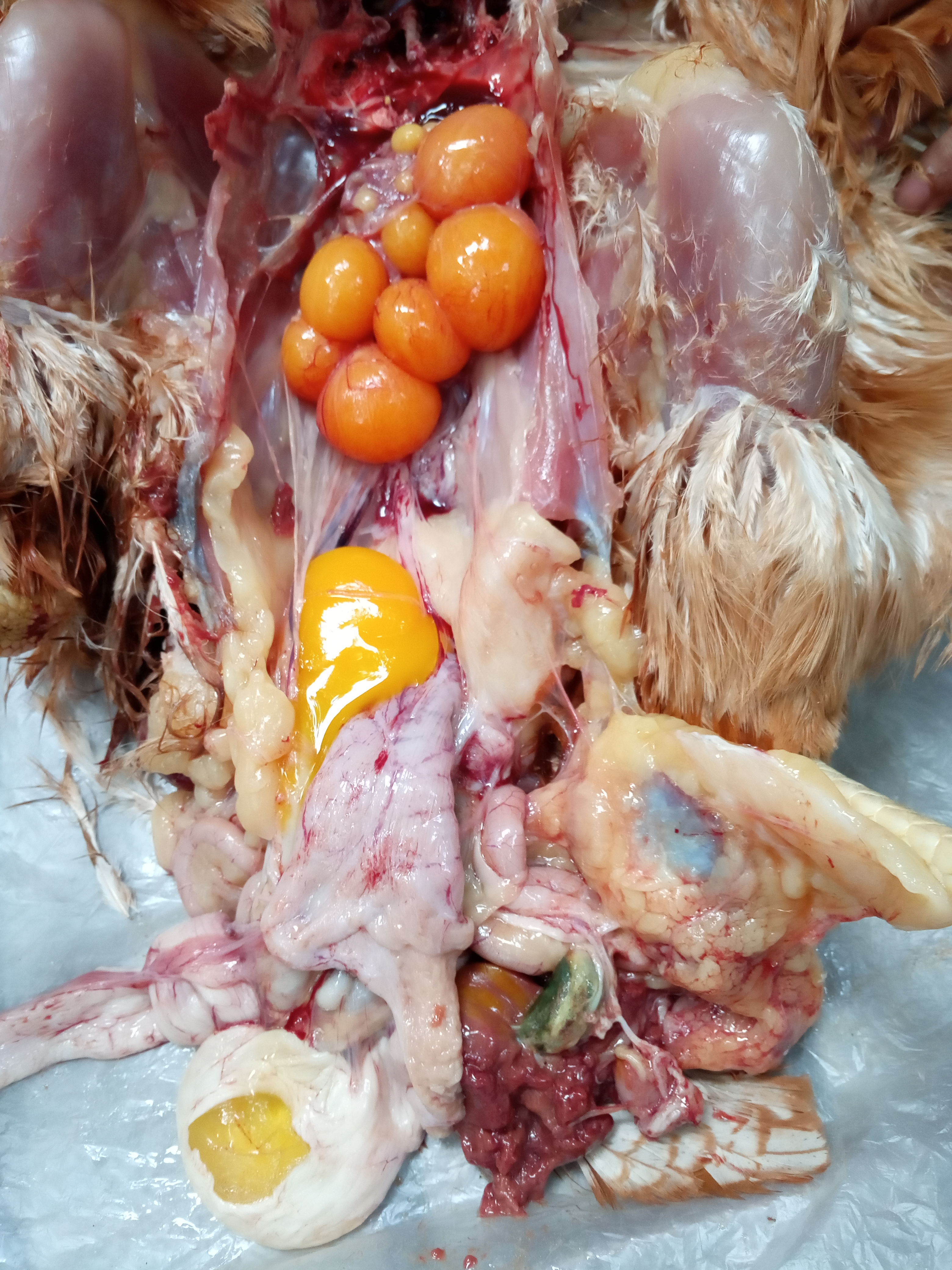
1.Deformed,discolor,flattened ova inn layers
#Typhoid
#pollurun
2.Ruptured ova with congestion in ova
#F C acute
# ND
# Heatstroke
3.Tumer of ovary
#Avian leucosis
# Mareks
4.Ovary. reeplased by grape like bunch of cyst
# cyst adenoma of ovary
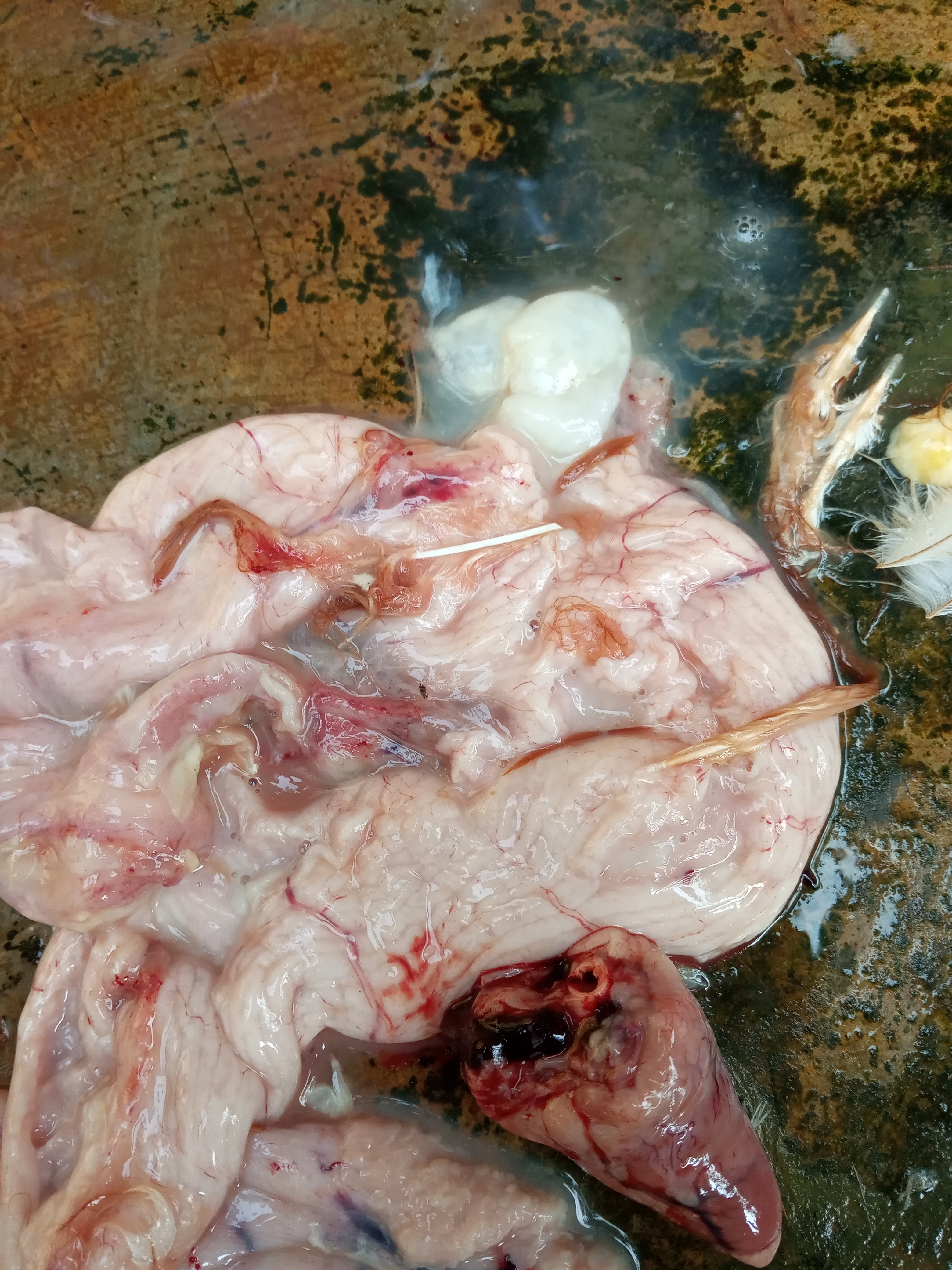
২৫.জরায়ু দেখে রোগ নিরনয়
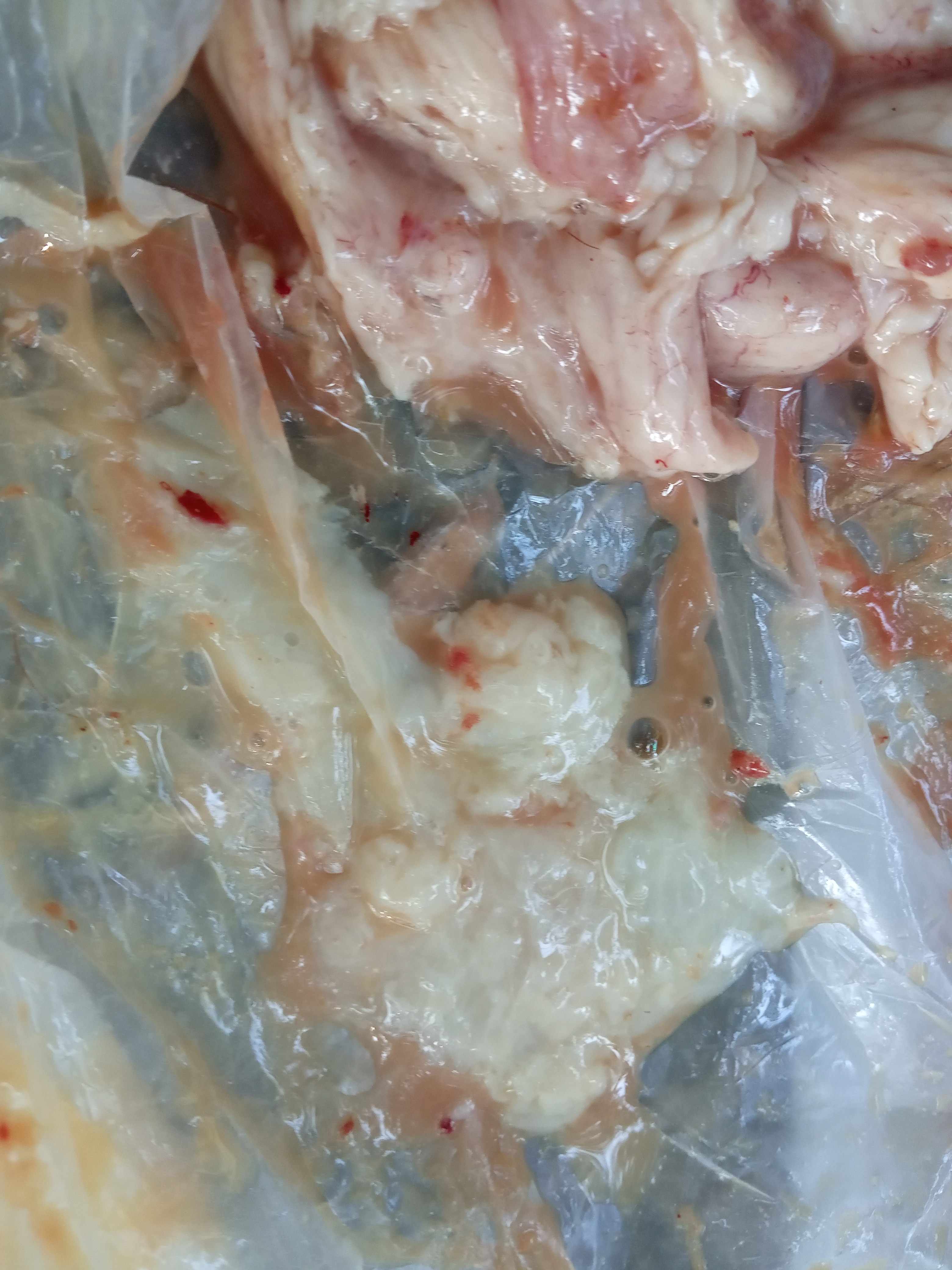
1. present of cheesy exudate in oviduct
present of cheesy exudate in oviduct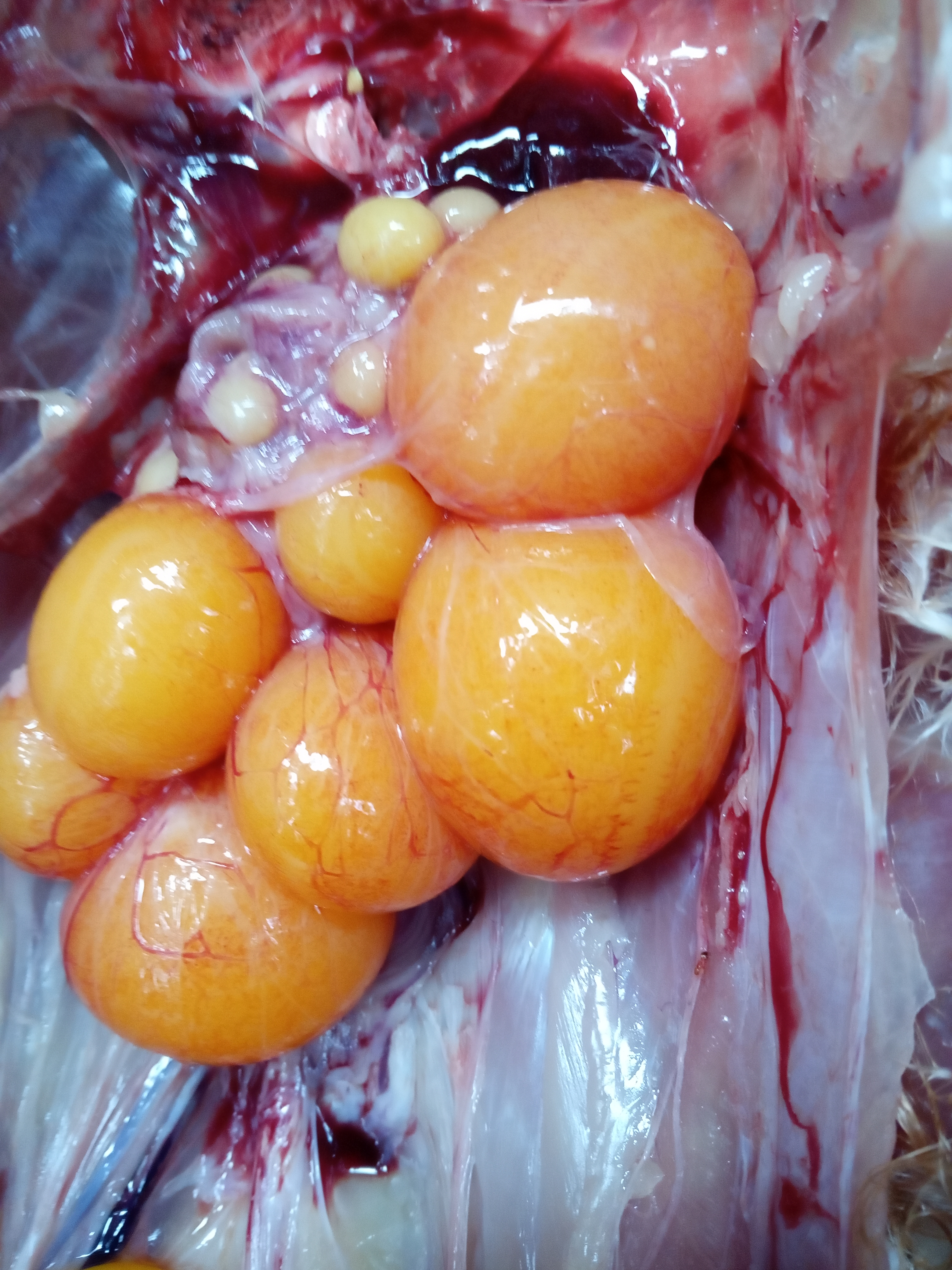
#salpingitis ( E coli)
# Mycoplasma galisepticum
2.Atropic miiddle part off, associated with low egg production or deformed egg
# I B
3.Uniformly atropic
# EDS
4.Cystic oviduct,right
Fusarium toxicosis
5.Egg struckup in oviduct
# Egg bound syndrome
6.Reduced egg size
# Fusarium toxicosis
২৬.ফুসফুস দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়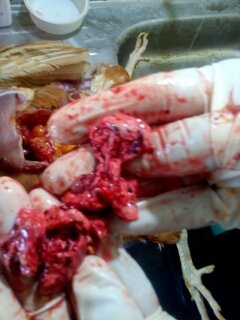
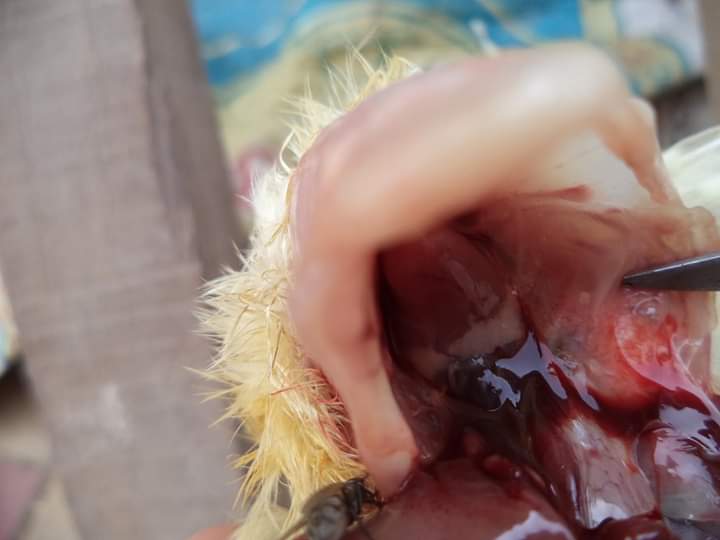

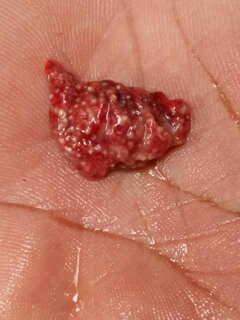


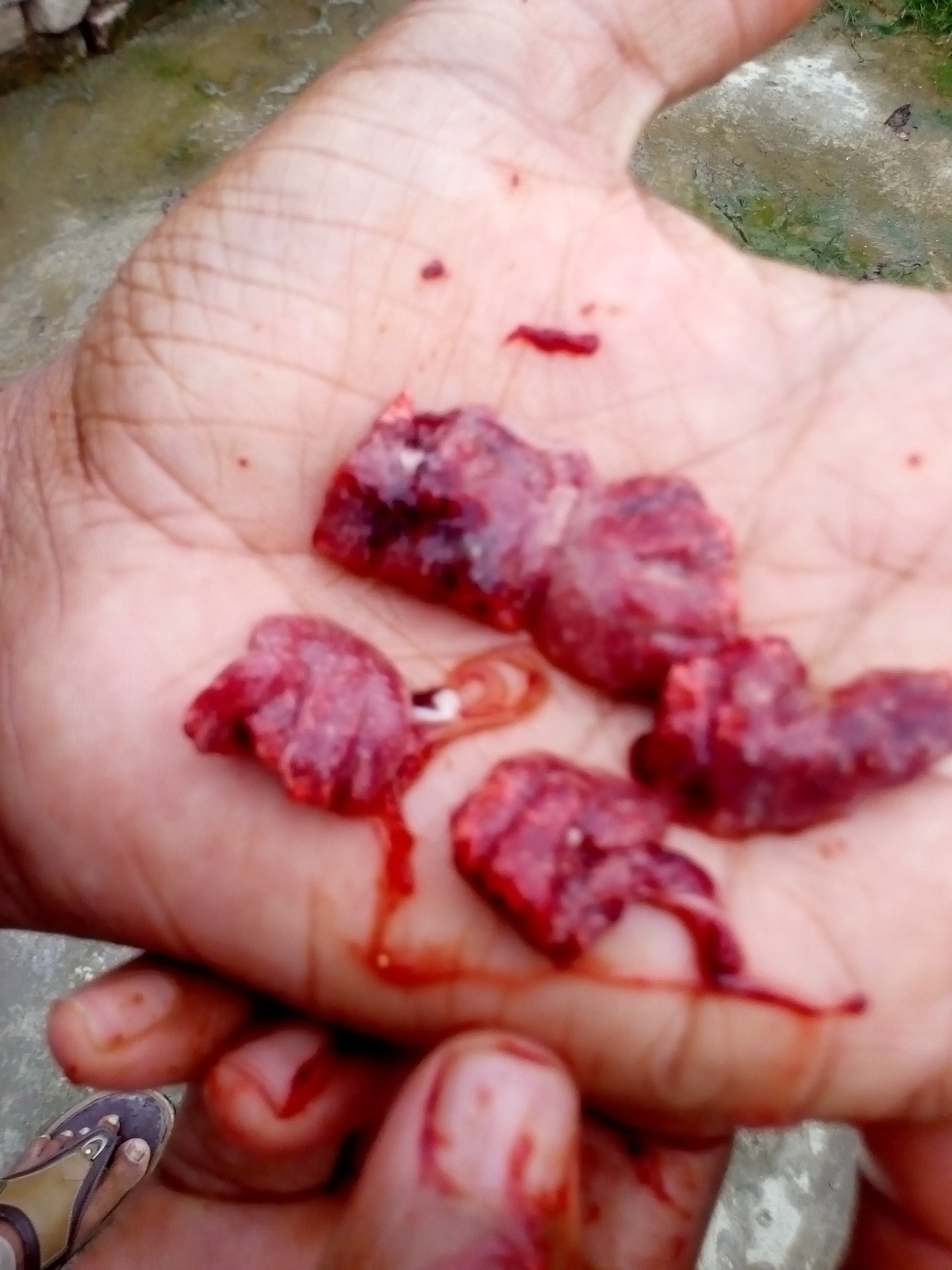
1.Congested,dark lungs( light pink is normal in chick)
#Chilling( brooding period if temperature is not right)
2.Pneumona,greyish or red consolidated lungs
# chronic F C
#Coryza( swollen face& infraorbital sinus,nasal catarrha
3.Mild cloudy pneunonic
#Mycoplasma gallisepticum( Air sac,trachea)
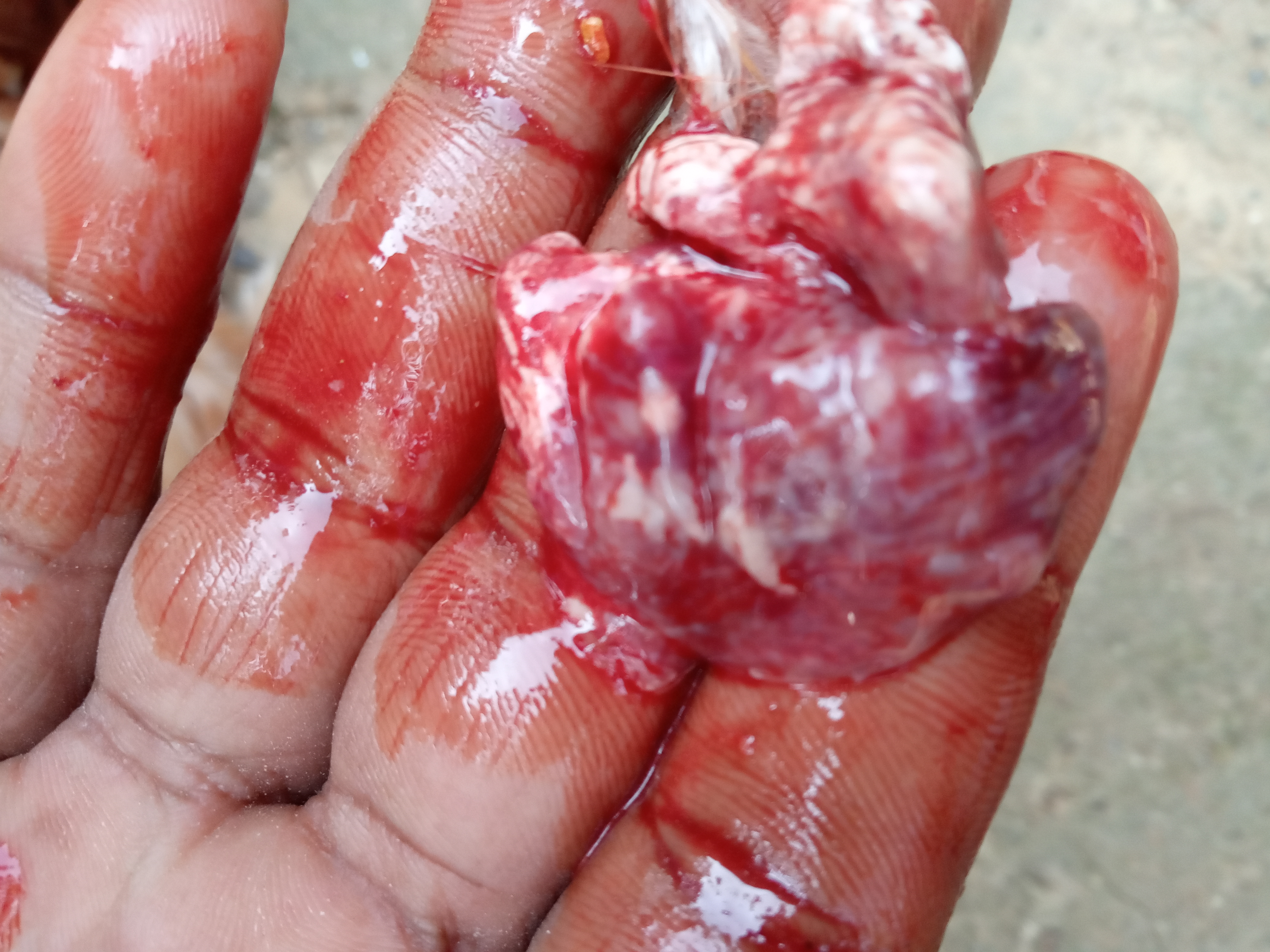
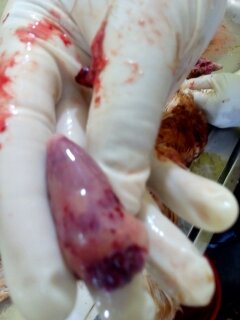
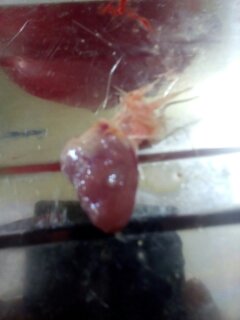
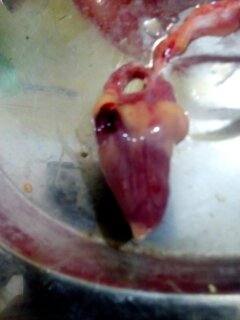
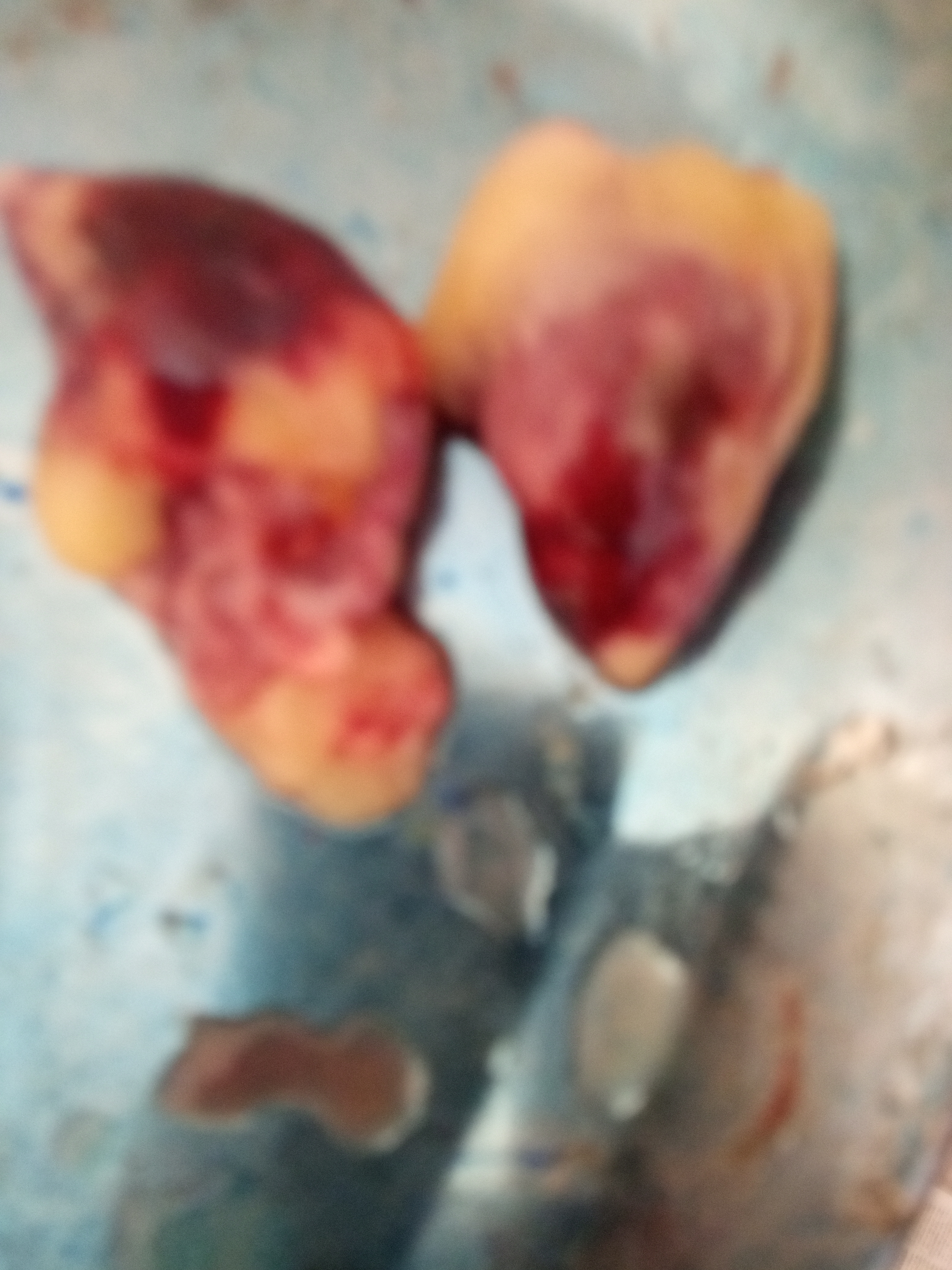
২৭।হার্ট দেখে রোগ নির্ণয়
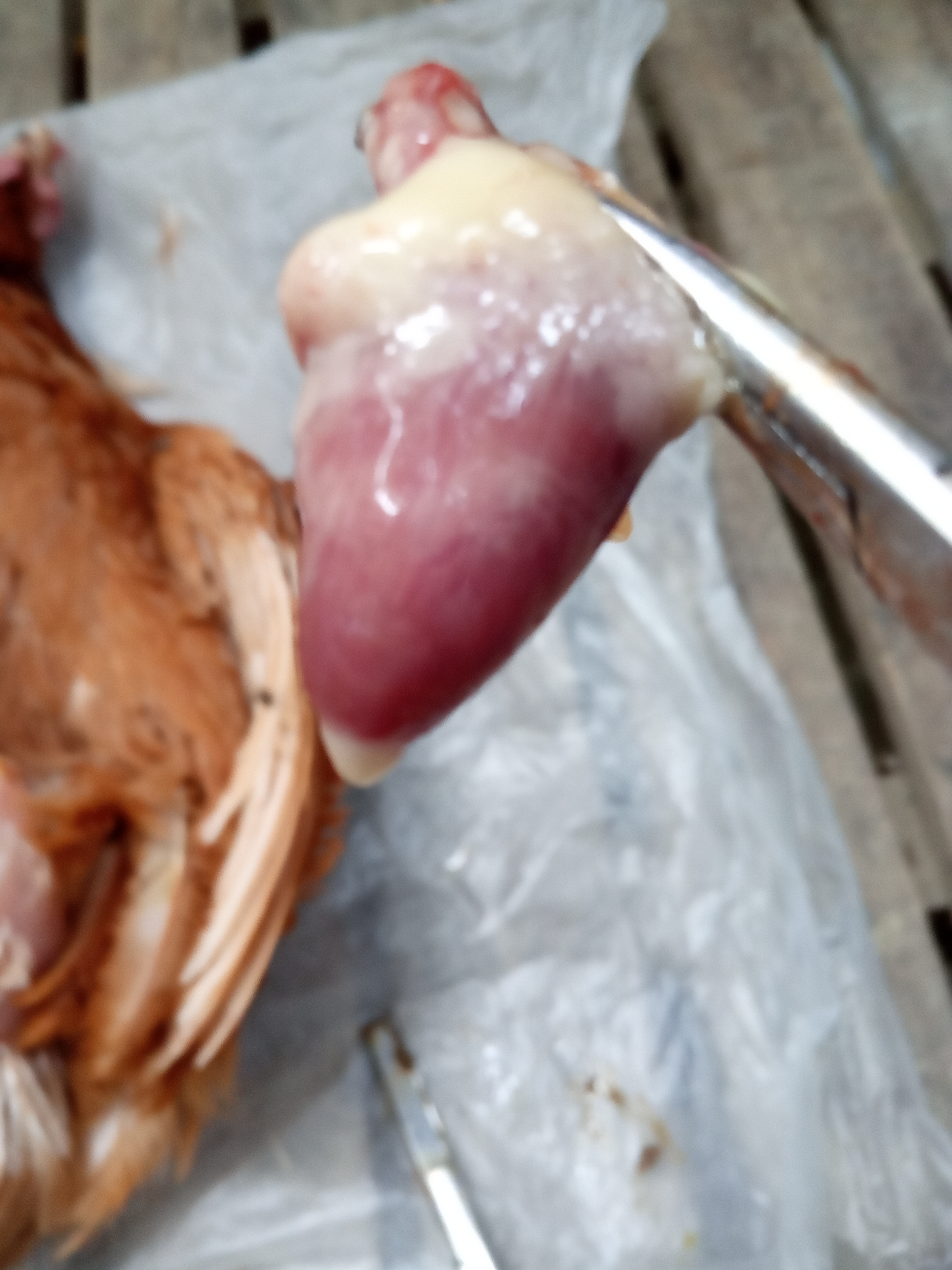 1.pericarditis with milky or fibrinous exudate;
1.pericarditis with milky or fibrinous exudate;
paratyphoid9 mortality and age 203 wks)
colisepticemia,fibrinour perihepatitis,peritonitis,salpingitis
C R D( Airsacculitis,cheesy exudate very common)
pollurum (3 wks)
typhoid
Streptococcusis (sporadic ) infarct in liver
2.hydropericardium (watery fluid around heart)
camylobactor hepatiticus
toxic fat syndrome
fluid in abdomen,s/c tissue.(2-7 wks but 3 wk peak)
botulism9paralysis and rotten feed)
C AB/IBH (pale biood ,liver and bonemarrow yellow brown jaundice,hemorrage in muscle
Leechi diseases(3-6 wks but 4wk peak ni broiler )
3.chalky urate deposit on heart and pericardium
gout
4.petechiae /pinpoint hemorrage on heart of surface
F C
IBH( anemia 4-8 wks
Staphylococcal septicemia (3wks)
salt nacl poisoing(diarrhoea,edema of s/c,leg weakness)
Gangrenous cellulitis(clostridium and staphylococcusis)
pseudomonous( Enteritis)
Erysipelas
5.mycocarditis(grey nodules in heart muscle)
pollurum and typhoid
6.tumer in herat (diffuse or nodular)
MD (gasping)
leucosis
7.vegetative endocarditis(greyish deposit inside heart)
streptococcus(liver and pericarditis)
staphylococcusis(arthritis,myosis,gangren dermatitis)
8.necrotic spot in heart muscle
spirochaetosis(spleen big and hemorrhagic,proventriculus hemorrhagic)
listeriosis
9.round heart
round heart diseases(un known or vit E /selinium deficiencies)
10.pericarditis with yellowish brown ,slimy exudate
campylobacter hepatiticus,typical mottled liver due to hemorrage ,slighty raised,necrotic lesion in liver)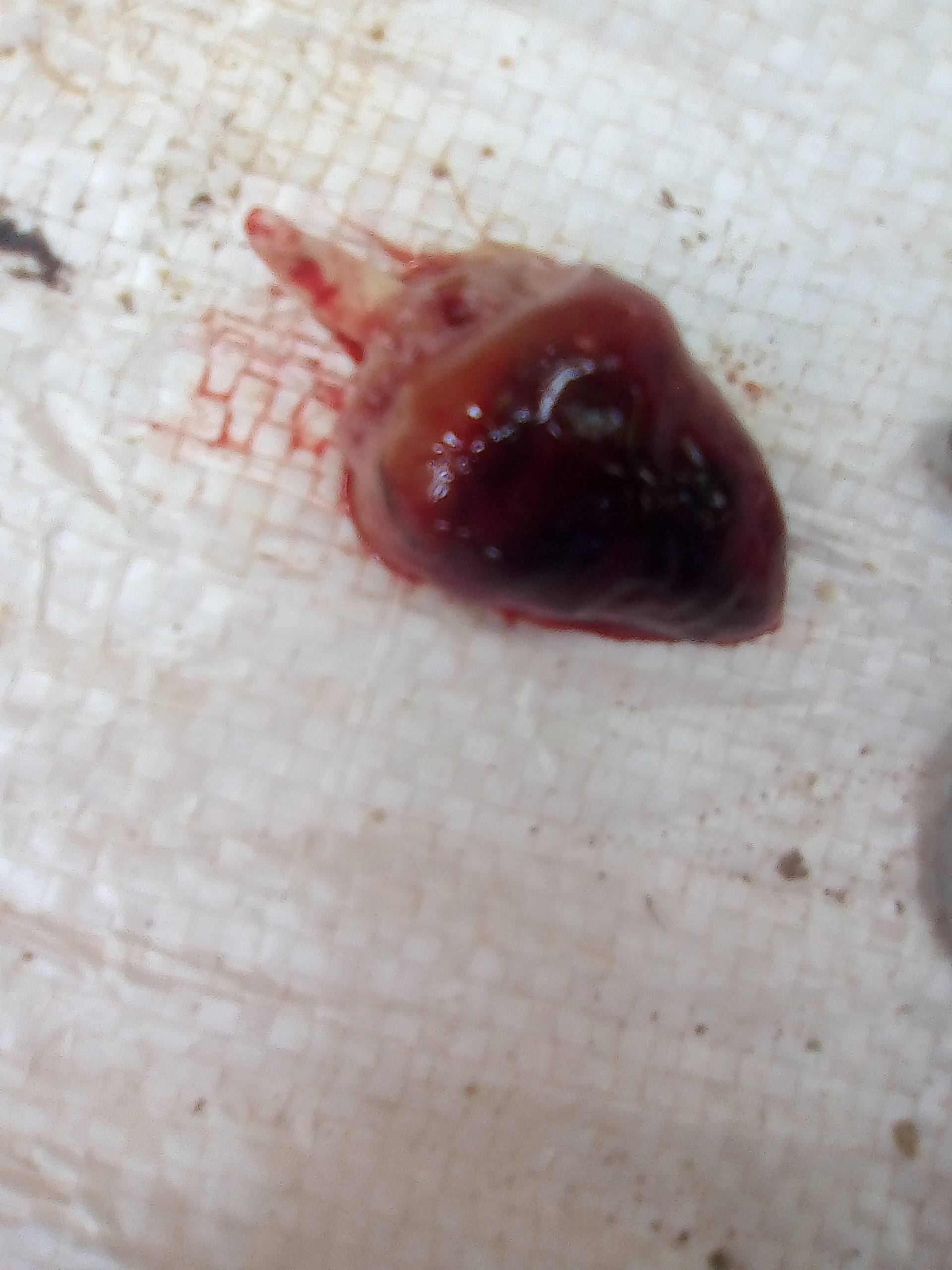
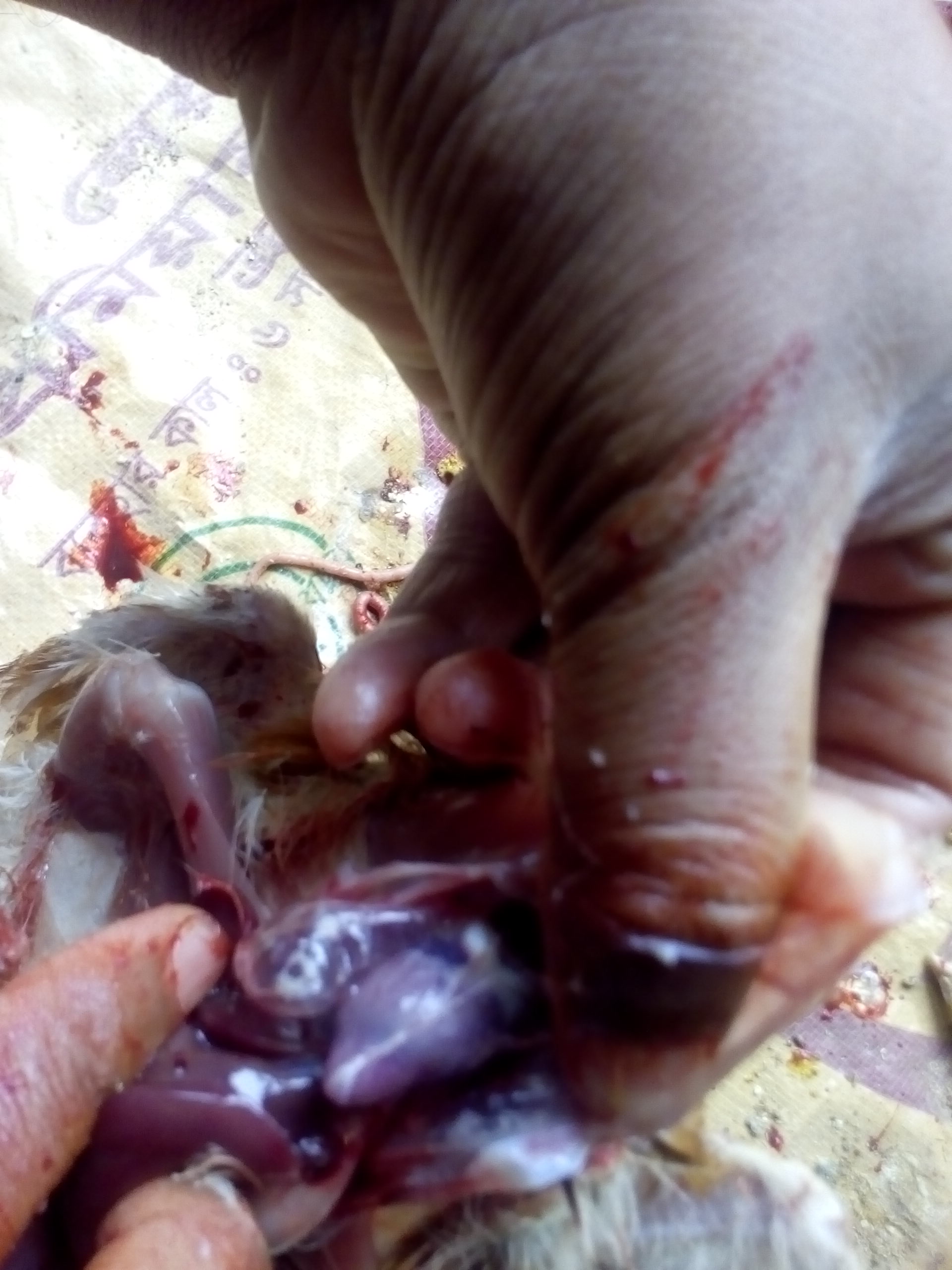
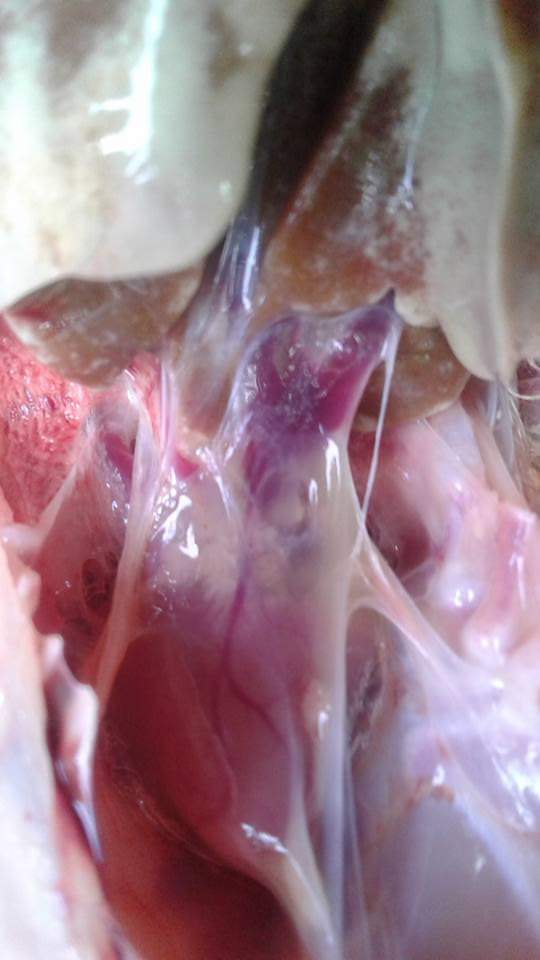
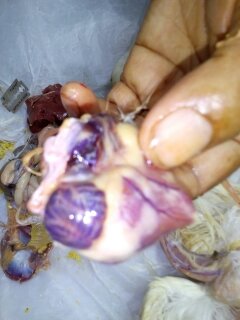
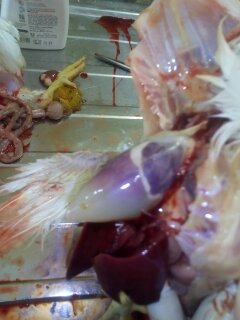
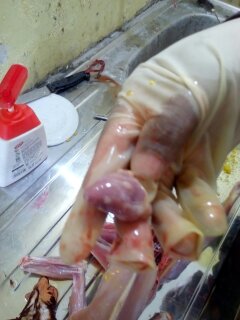
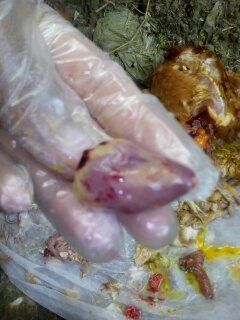
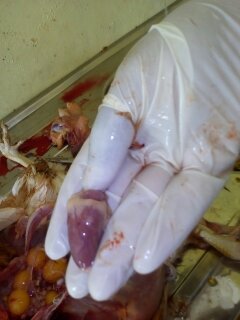

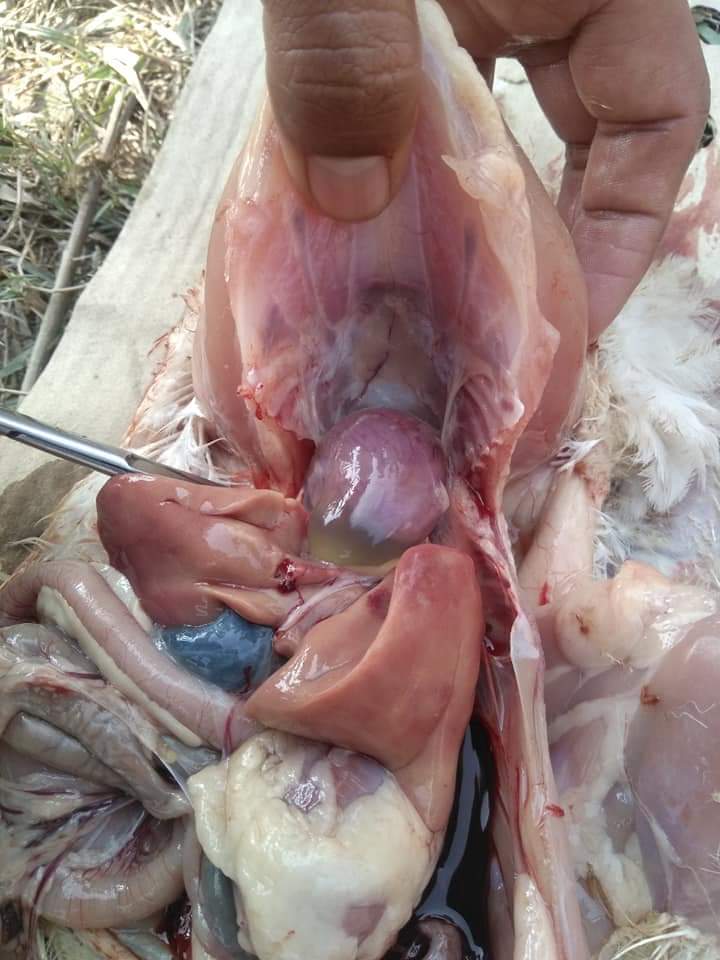
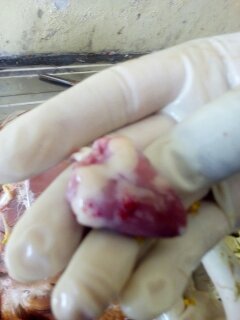
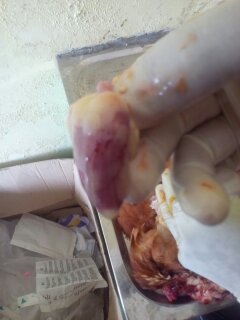
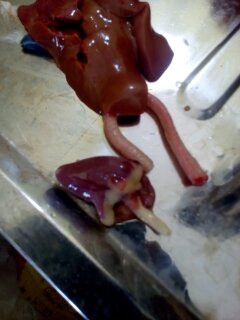

২৮.PD:Diseases Diagnosis by feces color.
1.White in center but surrended by grey color & hard brown color both are normal.
2 pink stain with froth & feather around vent are sticky(brown to black color) both are Necrotic enteritis.
3.Purely white :IBD.
4.White & mortality :Viral.
5.Green& hardbrown :Salmonella.
6.Excess calcium in feces & white :IB.
7.Unbound feed in feces: N E or Nonspecific diarrhora.
8.Green without mortality:Starvation or E coli or mycotoxin.
9.Green & more mortality :ND or viral.
10.Banana tree color :Fowl cholera or A I.
11.Yellow with high mortality : Viral
12.Green yellow :E coli+Protozoa.
13.Loose droping without mortality :High Temperature or high production.
14.Corner of droping carrot color:Subacute coccidiosis.
15.Mortality with droping are green or yellowbrown frothy Enteritis.
16.white and pasty feces;pullorum diseases
শর্টকাট
কালো ফিসিস ঃটক্সিসিটি ও প্রোটিয়েজ এন জাইমের ঘাটতি
পায়খানা ছড়িয়ে থাকলে ঃ প্যারাসাইট(কৃমি)
পায়খানা চকচকেঃখাবারে এনার্জি বেশি
পায়খানা নরমাল কিন্তু সবুজঃসালমোনেলা
ফায়খানার সাথে ফিসিস আসলে ঃএঞ্জাইমের ঘাটতি
ভাতের মাড়যুক্ত পায়খানাঃ আই বি ডি
পায়খানায় ফ্রেশ রক্তঃ কক্সিডিওসিস
ফেনা থাকলে ঃ ডায়রিয়া
কমলা কালার+ফেনা/বুদবুদঃনেক্রোটিক এন্টারাইটিস
পায়খানার ভিতরে সাদা কিন্তু বাহিরে সবুজঃ এ আই
ভিতরে সবুজ আর বাহিরে সাদাঃ রানিক্ষেত।
তাহলে চুন বা সাদা পায়খানা
রানিক্ষেত
আই বি ডি
গাউট
কলেরা
পোলোরাম ডিজিজ
কিডনিতে সমস্যা হলে
এর মধ্যে পেস্ট লাইক সাদা
আই বি এইচ
ই কলাই
পলোরাম ডিজিজ
হলুদ পায়খানা
পোলোরাম ডিজিজ
টাইফয়েড
কলেরা
সবুজ পায়খানা
এ আই
এন ডি
সালমোনেলোসিস
কলেরা
খাবার কম খেলে
ই কলাই
মাইকোটক্সিন
সবুজাভ হলুদ
ই কলাই +প্রোটোজোয়া
টাইফয়েড
এন ডি
ক্লেমাইডিওসিস
স্পাইরুকেটোসিসস
কমলা পায়খানা
নেক্রোটিক এন্টারাইটিস
রক্ত পায়খানা
আমাশয়
খাবারের দানা যুক্ত পায়খানা
ইনডাইজেশন
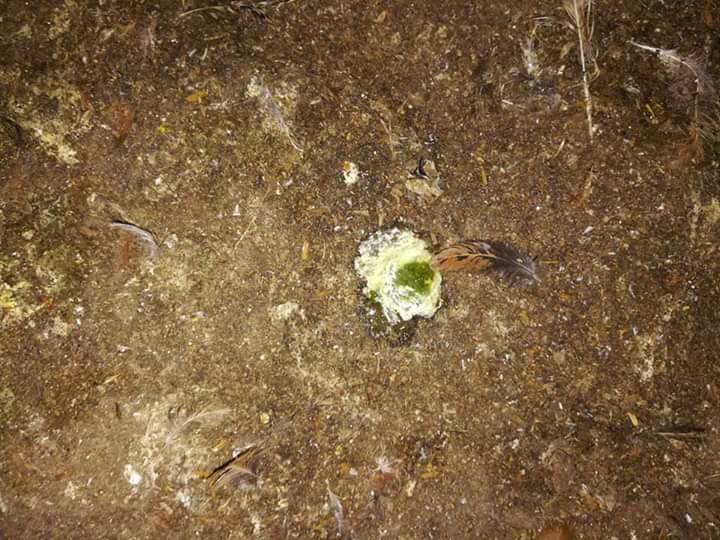
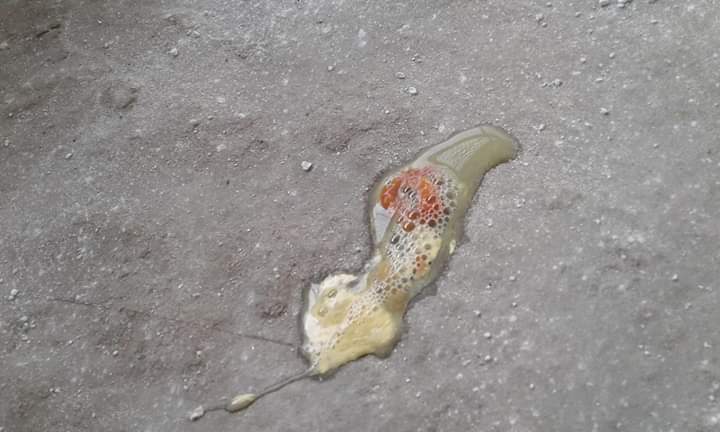
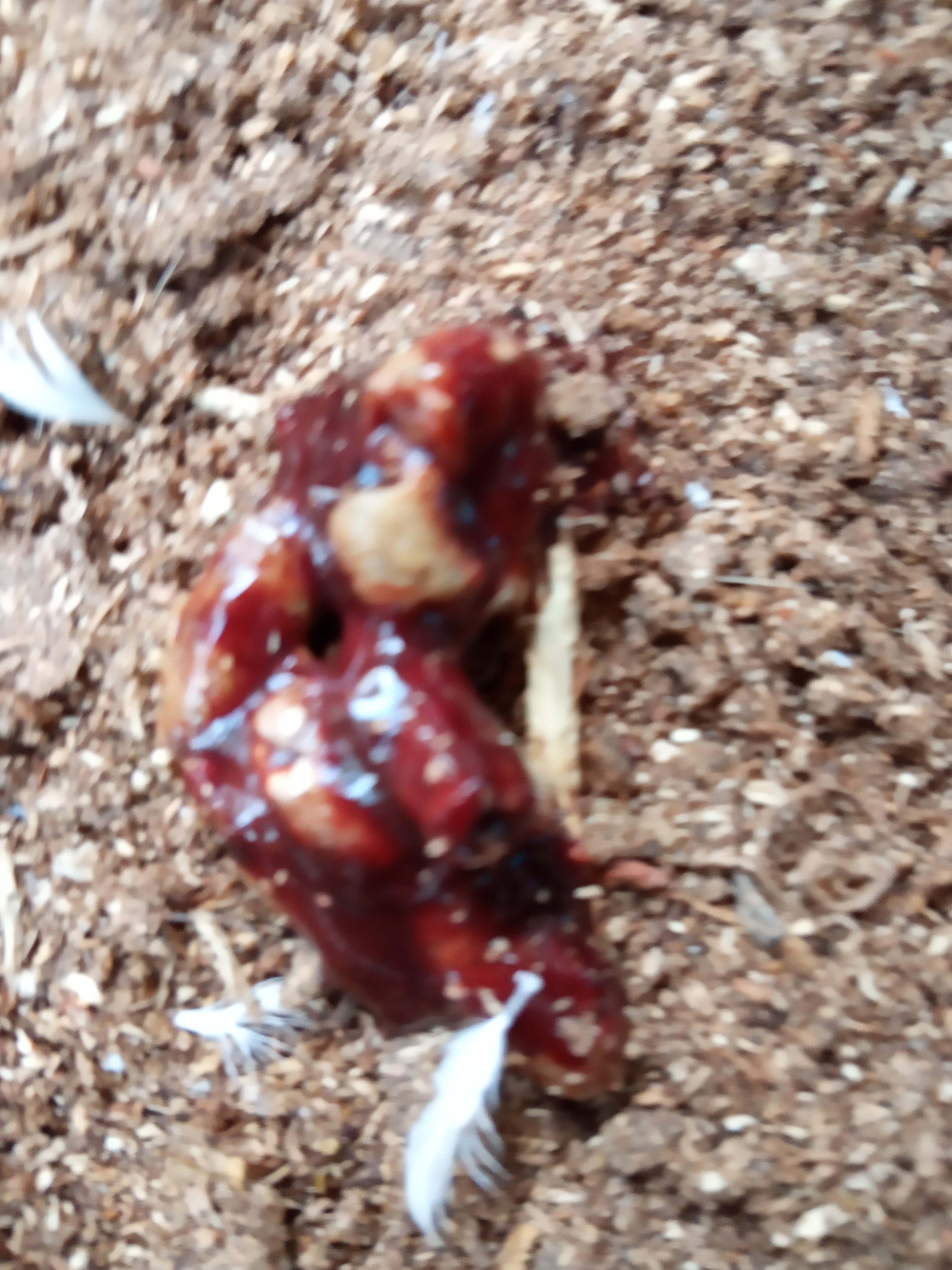
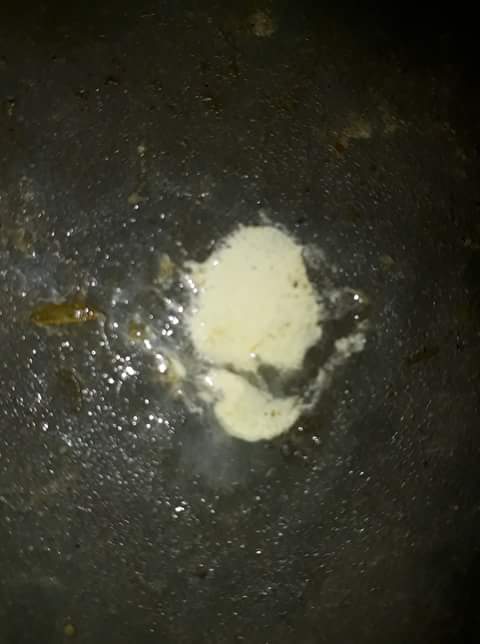


































২৯. ডিমের রং,খোসা এবং আকার:
অনেক খামারির অভি্যোগ ডিমের কালার নষ্ট হয়ে গেছে,খোসা পাতলা,ছোট ডিম এবং আকাবাকা ডিম, তাই দাম কম দিচ্ছে. এভাবে প্রায় ৫%-১০% দাম কম দেয় এবং ডিম বিক্রি করতে কষ্ট হয়.
বংশগত কারনে কিছু জাত ও বন্নের মুরগি মোটা খোলস এবং কোন কোন জাতের মুরগি পাতলা খোলস যুক্ত ডিম পাড়ে.
ডিম উৎপাদনের দিকে খোলস মোটা থাকে এবং শেষের দিকে ডিম বড় হয় কিন্তু খোলস পাতলা হয়.
খোলস শক্ত হলে ডিম ২.৫ কেজি চাপ সহ্য করে কিন্তু নিম্ন মানের হলে ২.৩ কেজি চাপে ভেংগে যায়.
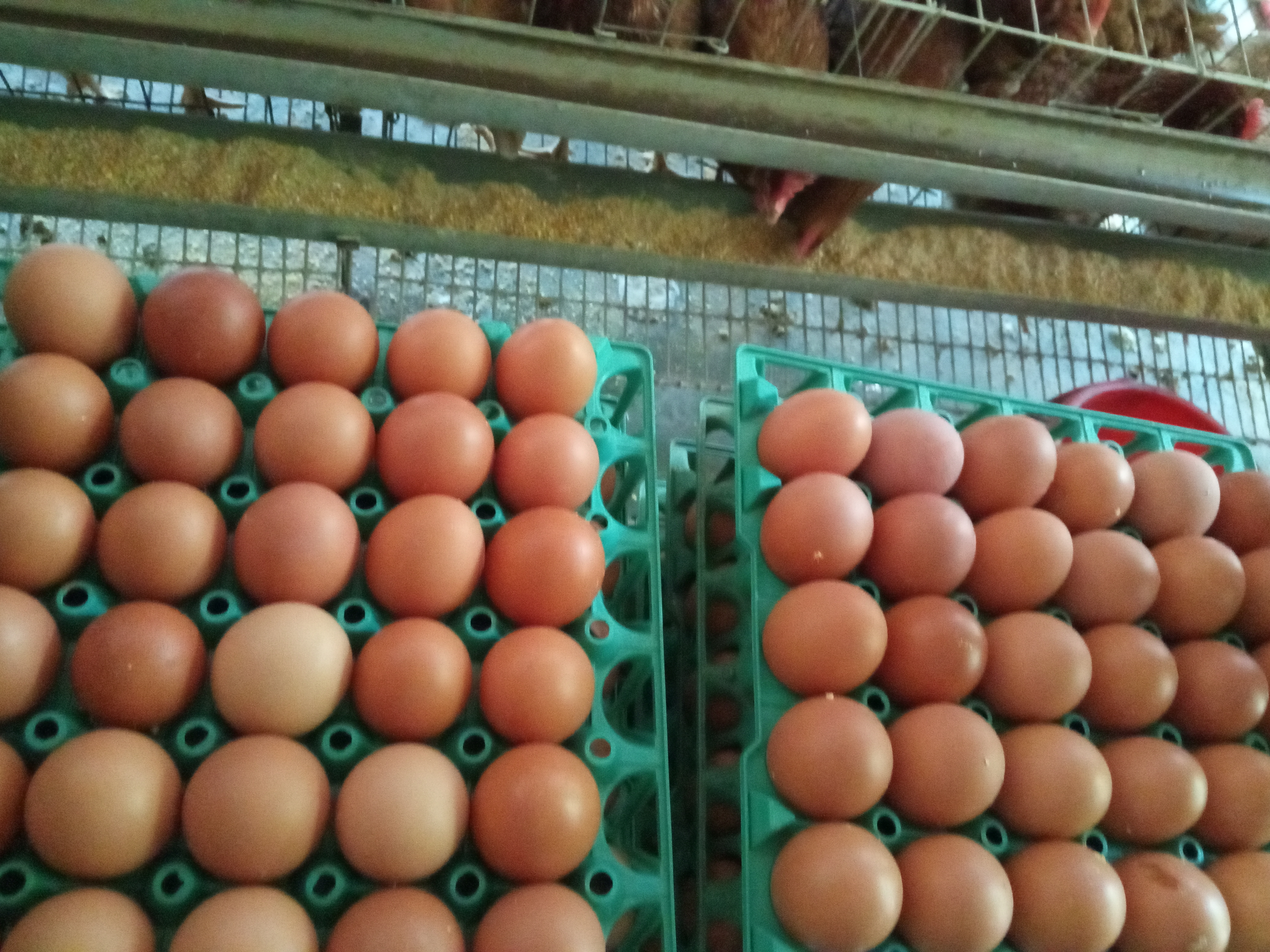
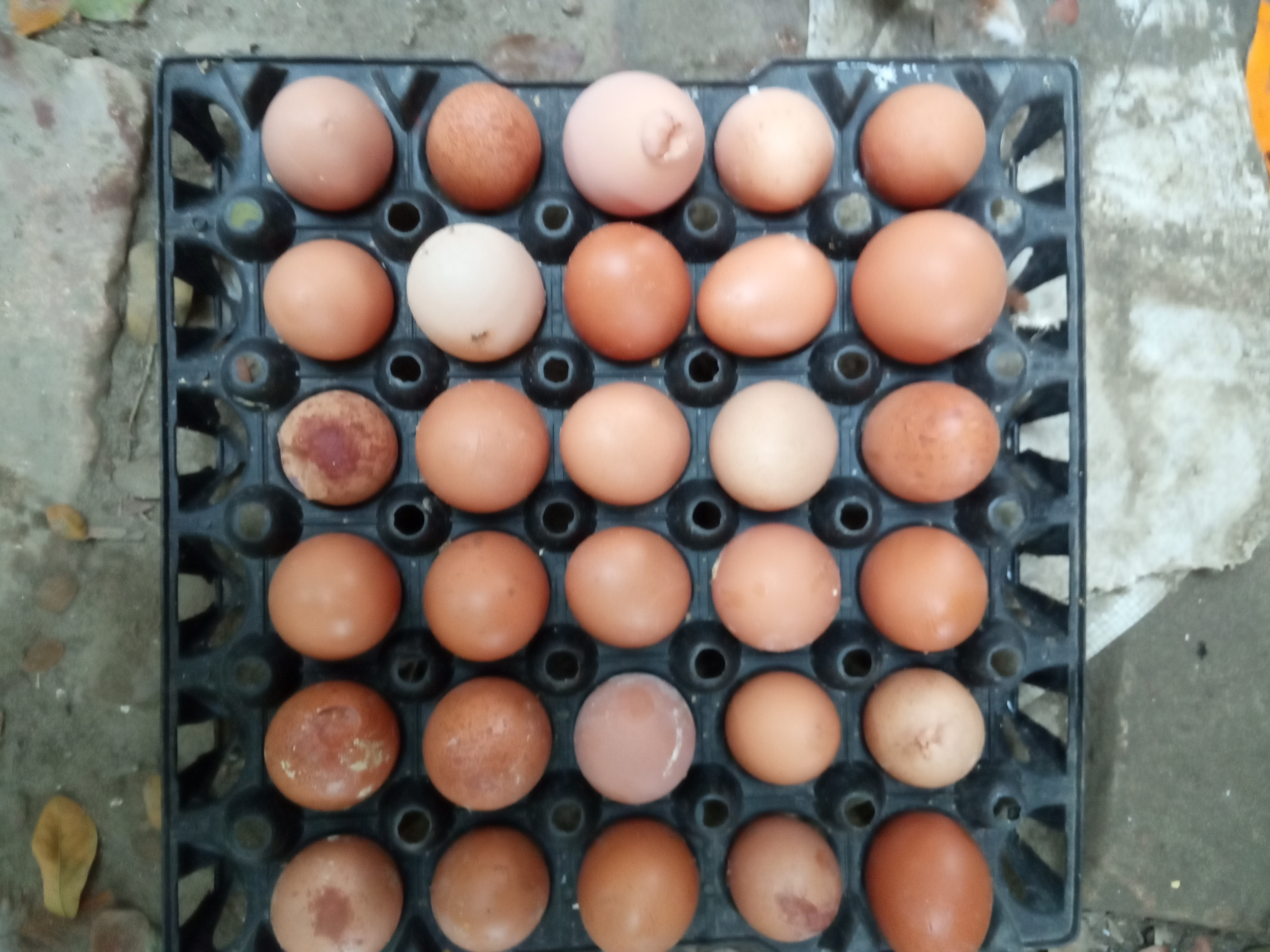
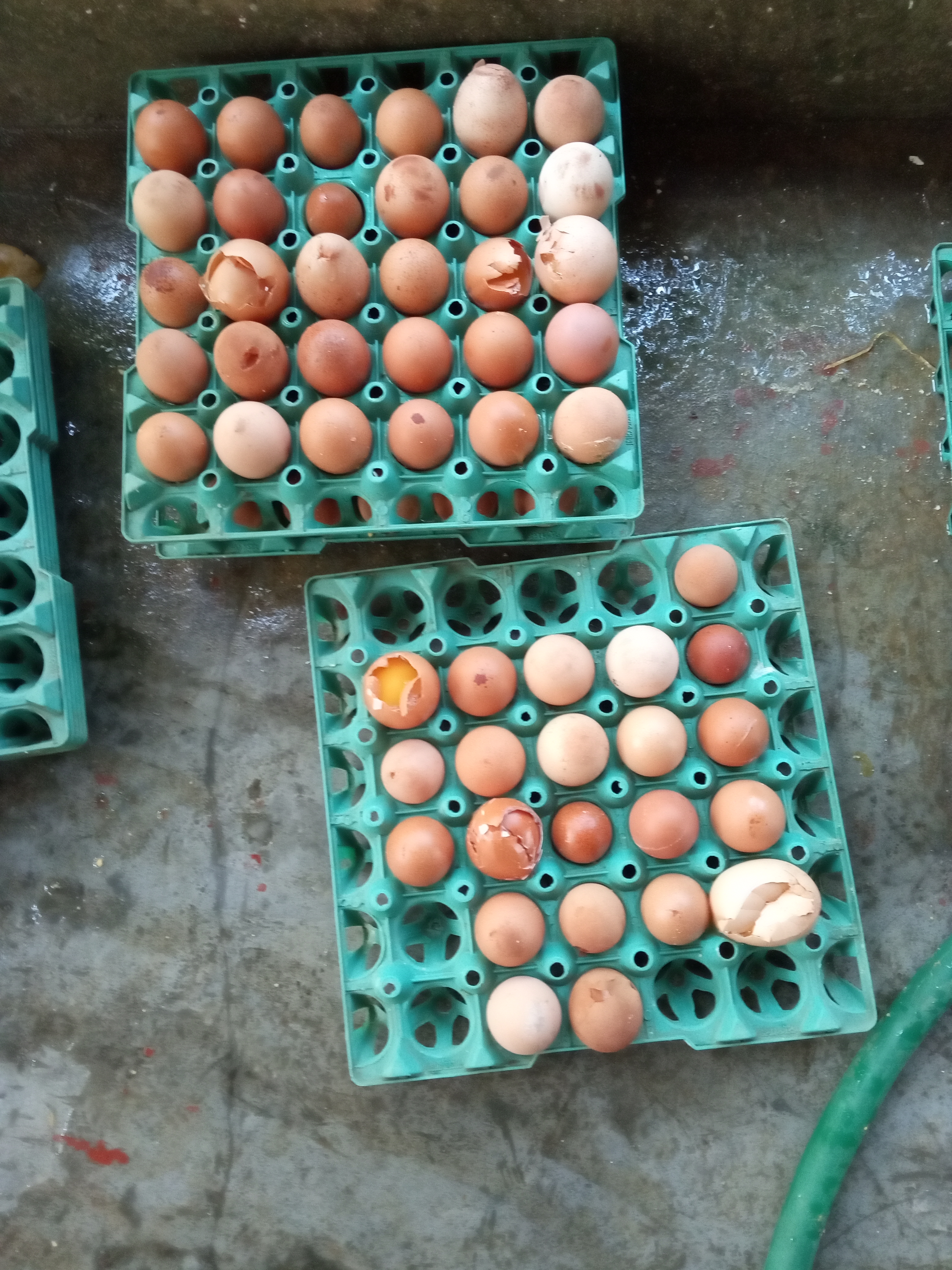














১.ডিমের রং নষ্ট হওয়ার কারণ:
বংশগত কারণ,
রোগ,রানিক্ষেত,ব্রংকাইটিস,ই ডি এস.
পাইপেরাজিন খেলে,
বেশি তাপমাত্রা হ লে,
বেশি ডিম পাড়লে,
রানিক্ষেতের টাইটার কমে গেলে.
টেট্রাসাইক্লিন বেশি খেলে.
২.খোসা পাতলা ও নরম হওয়ার কারণ
এটি উৎপাদক ও ভোক্তার মূল্যায়নে গুরুত্ব পুন্ন ভুমিকা রাখে. হ্যাচিং ডিম নিরবাচনে এটি মূল নিয়ামক.
খোসায় পাচ ধরনের ত্রুটি হয় যেমন
বিকৃত খোসা: এলবুমেনের মান খারাপ হলে ডিমের খোসা ভাল ভিত্তি পায় না.
ভাইরাসের কারনে এমন হয় তাছাড়া খোসা গ্রন্থগ্রন্থিতে খোসা ভেংগে গেলেও এমন হতে পারে.
কোটেড খোসা: অতিরিক্ত ক্যালসিয়াম ডিমের উপর জমা হলে এমন হয় যা স্পালাসিং ( splasing) নামে পরিচিত.
খোসা গ্রন্থিতে অতিরিক্ত সময় ধরে অবস্তান করলে এ ত্রুটি দেখা যায়.
ডিম উৎপাদনের শুরুতে এ সমস্যা বেশি দেখা যায়.
অমসৃন খোসাযুক্ত ডিম:
নরম ও দূরবল খোসাযুক্ত ডিম:
ফাটল ডিম
# চলের রেখার মত ফাটল
# তারার মত ফাটল
# ময়লা ও গ্লেজযুক্ত খোসা
# শরীরে ফাটল (body checks)
বংশগত ( স্টেইন) : কিছু জাতের মুরগিতে ক্যালসিয়ামের জমা হওয়ার হার বেশি ফলে খোসা পুরু হয়। গাড় বাদামি মুরগির ডিমের খোসা ভাল হয়.
বয়স:
বয়স বেশি হওয়ার সাথে সাথে খোসার পুরুত্ত কমে যায়. বয়স্ক মুরগির ডিম বড় হয় এবং সহজে ভেংগে যায়. এ সময় মুরগি হাড় থেকে ক্যালসিয়াম অবমুক্ত করার সামর্থ্য হ্রাস পায় এবং ক্যালসিয়াম কারবূনেট উৎপাদন কমে যায়. ৪০ সপ্তাহে ক্যালসিয়াম শোষন ও স্তানান্তর ক্ষমতা সাভাবিকের চেয়ে ৫০% কমে যায়.
পুস্টি:
পুষ্টির অসমতা,
জিংক,মেংগানিজ ও ডি৩ এর ঘাটতি,
কেলসিয়াম ও ফস ফরাস এর ঘাটতি এবং সমনয়ের অভাব. কাংখিত ক্যালসিয়াম ৩.৫-৪% এবং ফসফরাস ০.৩৫-.৪%)
ক্যালসিয়াম:
একটি ডিমে ২ গ্রাম ক্যালসিয়াম থাকে তাই
ডিম পাড়া মুরগিকে দিনে ৪ গ্রাম ক্যালসিয়াম গ্রহন করা প্রয়োজন কারন খোসা তৈরির জন্য ৫০-৬০% গ্রহন উপযোগী থাকে. খোসা তৈরির প্রক্রিয়ায় শেষ ১৪ ঘন্টায় খোসা গ্রন্থিতে ক্যালসিয়াম ১০০-১৫০ মিগ্রাম পার ঘন্টা এ হারে জমা হয়. মূলত হাড় এবং খাদ্যই ক্যালসিয়ামের মুল উৎস. রক্তে ক্যালসিয়ামের মাত্রা ২০-৩০ মিগ্রাম পার ডেসি লিটার যখন খাদ্যে ক্যালসিয়াম ৩.৫৬% বা বেশি. কিন্তু ২% হলে ৩০-৪০% আসে হাড় থেকে. তাই ডিম পাড়ার আগে ১৭-২১ সপ্তাহে খাদ্যে বেশি ক্যালসিয়াম দিতে হয় মানে প্রিলেয়ার খাবার দিতে হয় যাতে মুরগির দেহে ক্যালসিয়াম জমা থাকে. খাবার হতে প্রায় ৪০% ক্যালসিয়াম শোষিত হয় যখন খোসা গ্রন্থি নিষ্কিয় থাকে কিন্তু সক্রিয় অবস্তায় ৭২% এ উন্নিত হয়. বিকেল বা অন্ধকারে অন্ত্রে উচ্চ মাত্রায় ক্যালসিয়াম থাকে বিধায় হাড় ব্যতীত শুধু খাবার হতে মুরগি পেয়ে থাকে.
গ্রোয়ার খাবারে ক্যালসিয়াম বেশি দিলে অন্ত্রে পি এইচ বেড়ে যায় এবং প্যারাথাইরয়েড গ্রন্থির সাভাবিক গঠনে ব্যাঘাত ঘটে যার ফলে শোষন ক্ষমতা হ্রাস পায়.
ফসফরাস:
খোসায় এর পরিমান ২০ মিগ্রাম এবং সমগ্র ডিমে ১২০ মিগ্রাম.
ফসফেট আয়ন ক্যালসিয়াম কারবোনেট রুপান্তরে বাধা দেয় এবং খোসা গঠন প্রক্রিয়ায় সমাপ্তি টানে. রক্তে উচ্চ মাত্রায় ফসফরাস থাকলে হাড় থেকে ক্যালসিয়াম স্তানান্তর প্রক্রিয়া বাধাপ্রাপ্ত হয়.
# ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাসের উৎস ও গঠন:
অন্ত্রে ক্যালসিয়াম এর মাত্রা ধরে রাখার জন্য ক্যালসিয়াম এর উৎস ও পারটিকেল সাইজ গুরুত্বপুন্ন ভূমিকা পালন করে. ফসফরাস ও যাতে সহজলভ্য এবং ডিম পাড়া মুরগির খাদ্যের সাথে ব্যবহার করা যায় সেটি লক্ষ্য রাখতে হবে.
# আন্ত্রিক পি এইচ :
যখন পি এইচ এর মাত্রা ৫.৫ থেকে ৬ এর মধ্যে থাকে তখন ফসফরাস শোষণ সরবোচ্চ থাকে. আবার পি এইচ ৬.৫ এর বেশি হলে ফসফরাসের শোষণ নাটকীয়ভাবে কমে আসে. খাদ্যে অতিরিক্ত মুক্ত ফ্যাটি এসিড থাকলে পি এইচ হ্রাস পায় এবং এ কারনে ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাসের শোষণ ব্যাহত হয়.
# ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাসের অনুপাত:
অন্ত্রে উচ্চ মাত্রার ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাস থাকলে এদের উভয়ের শোষণ বাধাপ্রাপ্ত হয়. উচ্চ মাত্রায় ক্যালসিয়াম অন্ত্রের পি এইচ বাড়ায় ফলে জিংক ও ম্যাংগানিজ এর সাথে ফসফরাসের শোষণ হ্রাস পায়. রক্তরসে উচ্চ মাত্রায় ফসফরাস থাকলে অন্ত্রে ক্যালসিয়াম শোষণ এবং হাড় থেকে ক্যালসিয়াম স্তানান্তর উভয়ই হ্রাস পায়. শরীরের অম্লের ভারসাম্য রক্ষার জন্য ফসফরাস গুরুত্বপুন্ন. গ্রোয়ার খাদ্যে ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাসের অনুপাত ১.৫-২:১।
ভিটামিন ডি:
ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফসফরাসের শোষণের জন্য ভিটামিন ডি দরকার.
ক্যালসিয়াম বাইন্ডিং প্রোটিন সংশ্লেষন এ প্রক্রিয়াকে সাহায্য করে, ভিটামিন ডি৩ এর কার্যক্রমে এর মেটাবোলাইট ১,২৫ ডাইহাইড্রক্সি সম্পরক যুক্ত যা মুরগির যকৃত ও কিডনে তৈরি হয়.
খাদ্য :
খোসার ভাংগন সহনশীলতা গম বা বারলি অপেক্ষা জোয়ার জাতীয় খাদ্যে বেশি হয়.
খাদ্যে বেশি ক্যালসিয়াম ও ফাইটেট বেশি থাকলে জিংক ও মেংগানিজ এর ঘাটতি হয়.
ফাইটেজ যুক্ত এনজাইম খাদ্যে যোগ করলে খোসার মান ভাল হয়.
খাদ্যে অতিরিক্ত ক্লোরিন থাকলে রক্তে বাইকারবোনেট এর ঘনত্ব কমে আসে কন্তু ডিমের খোসার ক্যালসিয়াম সংশ্লেষনে গুরুত্বপুন্ন ভুমিকা পালন করে.
খাদ্যে নিম্ন মাত্রার ক্যাটায়নিক – আনায়নিক সাম্যতা,নন স্টাস পলিস্যাকারাইড এর উপস্তিতি,মাইকোটক্সিন এবং ভেজাম দ্রব্যের কারনে খোসার মান খারাপ হয়.
ভিটামিন সি এর ঘাটতি
পানি:
পানিতে অতিরিক্ত ক্লোরিন বা ফ্লোরিন
খাবার কম খেলে,
রোগ: রানিক্ষেত, ই ডি এস( ডিম্বনালিকে আক্রমন করে,সাথে রানিক্ষেত ও আই বি থাকতে পারে) ,ব্রংকাইটিস( নরম,অমসৃন ও বিবন্ন ডিম)এভিয়ান ইনফ্লুয়েঞ্জা এবং নেক্রোটিক এন্টারাইটিস
বেশি তাপমাত্রা,
ধকল: ডিম তৈরির সময় ফেলোপিয়ান নালি ও জরায়ুর কোষগুলির যুগপৎ ক্রিয়ার ফলে খোলস গঠিত হয়. ধকল জনিত অবস্তায় এ কোষগুলি অম্লীয় অবস্তা ধারন করে এবং কোষ নষ্ট হয়. ধকলজনিত কারনে খোলসের উপর পাউডারের মত জমা হয় যা বিকৃত ডিম তৈরি করে.
পরিস্তাপন জনিত ধকলের কারনে ক্যালসিয়াম কোটিং হয়ে চেকযুক্ত ডিম পাড়ে.
রাত্রে মুরগিকে বিরক্ত ক রলে,
ক্ষতিকর সালফোনেমাইড খাওয়ালে খোসার মান খারাপ হয় কিন্তু টেট্রাসাইক্লিন খাওয়ালে মান ভাল হয়
মাইকোটকসিকোসিস বিশেষ করে টি ২ টক্সিন বা ফুসারিয়াম টক্সিন.
৩. ডিমের আকার ছোট হোয়ার কারণ
ডিম পাড়া আগে শুরু হলে,
পুষ্টি গ্রহন কম হলে,
খাদ্যে মেথিওনিন কম হলে,
এনারজি কম হলে,
খাদ্যে লিনোলেয়িক এসিড কম হলে,
তাপমাত্রা বেশি হলে,
পানি কম খেলে,
রোগ হলে.
ক. ডিমের খোসার গঠন সংযুক্তি ও উপাদান:
ডিমের ওজনের প্রায় ১০-১১% খোসা এবং খোসার ওজন প্রায় ৫-৬ গ্রাম.
ডিমের ভাংগন সহনশীলতা ৩০ নিউটন এবং ৩০০-৩৫০ মিলিমিটার পুরুত্ত সম্পন্ন.
এ বিশেষ গঠনের কারনে ডিম জীবানু ঘটিত এবং পারিপার্শ্বিক পরিবেশ থেকে রক্ষা পায় ও পানি এবং গ্যাস বিনিময় নিয়ন্ত্রন করে. খোসায় প্রায় ১.৭-২.৫ গ্রাম ক্যালসিয়াম থাকে.
খ. খোসার গাঠনিক সংযুক্তি:
ক্যালসিয়াম কারবনেট ৯৪-৯৭%
ফসফরাস ০.৩%. ম্যাগনেসিয়াম ০.২%.
সোডিয়াম,পটাসিয়াম,মেংগানিজ,আয়রন ও কপার: সামান্য এবং জৈব উপাদান ২% এর নিচে.
জৈব উপাদান : ম্যাট্রিক্স প্রোটিন ( পলিস্যাকারাইড ও প্রোটিন) ও রঞ্জক পদার্থ
ডিমের খোসার গঠন নির্ধারনে ও ক্যালসিয়াম কারবুনেট এর আত্তীকরনে এটি মূল ভিত্তি হিসেবে কাজ করে.
ডিমের খোসায় প্রায় ৮০০০ ক্ষুদ্র ছিদ্র আছে.
##খোসার মান উন্নয়নে করনীয়##
খাদ্যে ক্যালসিয়াম:
গরমকালে বেশি ক্যালসিয়াম দিতে হবে মানে মুরগি প্রতি ১ গ্রাম বেশি দিতে হবে. ক্যলাসিয়ামের সাইজ এবং কমপক্ষে ১ মিমি হতে হবে যাতে গিজারডে বেশিক্ষন থাকতে পারে.ক্যালসিয়ামের সাথে ম্যাগ্নেসিয়াম যাতে কম হয় সে দিকে খেয়াল রাখতে হবে.
ভিটামিন সি:
ডিমের খোসার জৈব উপাদান ( অরফানিক মেট্রিক্স যা টকোকোলাজেন) সংশ্লেষনে সি অপরিহার্য.. এটি প্লাজমা করটিসনের মাত্রা কমেয়ে গরমের ধকল থেকে রক্ষা করে. এটি ভিটামিন ডি৩ কে সক্রিয় হরমোনাল মেয়াবোলাইট ক্যালসিট্রলে রুপান্তরে কো ফ্যাক্টর হিসেবে কাজ করে অন্ত্রে ক্যালসিয়াম শোষনে উদ্দীপনা যোগায় এবং প্লাজমায় ক্যালসিয়ামের মাত্রা এমন পরযারে উন্নীত করে যাতে হাড়ের মিনারেল
উৎপাদেন সাহায্য করে. প্রতি কেজি খাদ্যে ২৫০ মিগ্রাম সি দিলে ডিম উৎপাদন বাড়ে এবং খোসার মান বাড়ে.
খাদ্যে সোডিয়াম বাইকারবোনেট:
এটি দিনে ১% হারে ৩০ সপ্তাহ বয়সে ৩২ ” সেন্তগ্রেট আপমাত্রায় দিলে খোসা ভাংগা কমে যায়.এটি এসিড ক্ষার সমতা,ইলেক্টোলাইট ঠিক রাখে ফলে খোসার মান ভাল হয়.
খাদ্যে এলমিনিসিলিকেট: এটি ০.৭৫ ভাগ করলে ডিমের আপেক্ষিক গুরুত্ব ৪০ ভাগ বেড়ে যায় এবং খাদ্য রুপান্তর হার ২.২ ভাগ উন্নত হয়.
ব্যবস্তাপনা
তিন বার ডিম তুলতে হবে
গরমের ধকল থেকে মুক্ত রাখতে হবে
অতিরিক্ত হৈ চৈ করা যাবে না
লিটারে ডিম পাড়ার ক্ষেত্রে বক্স সঠিক ভাবে দিতে হবে
ডিম পাড়ার খাচায় নরম প্যাড দেয়া যায়.
৩০.মুুরগির শরীরের পরিবরতন এবং কারণ
1. Growth poor(chick)
aflatoxicosis
infectious synovitis
candidiasis
vit A & B deficiencies
2 Emaciation( wasting of body muscle)
chronic enteritis
poor or off feeding
nutritional deficiency
3. muscular tremors or twiching
IBD
avian encephalitis( head & neck muscle)
listeriosis
mouldy corn disease
4. paralysis
Mareks diseases
Botulism
late A E
Acute ND
Heat stroke
Cage layer fatigue diseases
poisoning
5. Hysteria/ nervousness
Avian hysteria
ND
Sudden Death syndrome
6. opisthotonous( head pulled backward)
chick :star gazing, B1 deficiency
7.Crazy chick disease(,head drawn downward under chest)
ND
vit E & A deficiency
8.Enlarged hock joint
vit E, niacin & nickel deficiency
9. Torticolis( head turned upside down)
chronic Fowl cholera
Rarely ND
10. shank of legs scaly ( thick rough,scaly limb)
zinc deficiency
leg mite infestetion
11. swelling due to air under skin
Rupture airsac
 Poultry Doctors BD PoultryDoctorsBD can provide specialist Poultry Farming Guide & Chicken Care Tips
Poultry Doctors BD PoultryDoctorsBD can provide specialist Poultry Farming Guide & Chicken Care Tips